mirror of
https://gitlab.com/game-loader/hugo.git
synced 2025-07-12 09:43:46 +08:00
Compare commits
3 Commits
c6ad845913
...
master
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00ab971772 | |||
| 6b9539bd2c | |||
| 4aa9d1532c |
@ -103,6 +103,178 @@ stringData:
|
||||
retries: 5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### k8s 主节点安装及启动
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装docker和containerd
|
||||
|
||||
参照[docker官网ubuntu安装文档](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/)
|
||||
|
||||
如果使用apt包管理器方法安装,安装后会同时安装docker和containerd。无需再额外安装containerd运行时。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 配置cgroup驱动
|
||||
|
||||
cgroup 驱动是用来管理和组织 Linux 系统中的 cgroups(控制组)的接口。ubuntu中默认使用systemd作为初始化系统,而当当某个 Linux 系统发行版使用 systemd 作为其初始化系统时,初始化进程会生成并使用一个 root 控制组(cgroup),并充当 cgroup 管理器。则要将systemd配置为容器运行时的cgroup系统。
|
||||
|
||||
- 生成默认配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo containerd config default | sudo tee /etc/containerd/config.toml
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 编辑配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo vim /etc/containerd/config.toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 找到runc部分并修改(通常在中间位置)
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
|
||||
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc]
|
||||
runtime_type = "io.containerd.runc.v2"
|
||||
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc.options]
|
||||
SystemdCgroup = true
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 重启containerd服务并检查
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo systemctl restart containerd
|
||||
|
||||
sudo crictl info | grep -i cgroup
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此时应该能看到`SystemdCgroup: true`这样的输出
|
||||
|
||||
3. 临时关闭swap
|
||||
|
||||
Kubernetes 默认不支持启用 swap 的节点,因此在启用swap的节点上kubelet无法正常启动,可以临时关闭swap后继续集群的初始化操作。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo swapoff -a
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. 配置容器镜像
|
||||
|
||||
如果不配置容器镜像会导致不能拉取成功从而无法正常启动控制节点,离线情况下要将镜像提前下载好,可以使用如下方式
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 查看需要的镜像
|
||||
kubeadm config images list
|
||||
|
||||
# 拉取镜像
|
||||
kubeadm config images pull
|
||||
|
||||
# 将镜像保存为tar文件
|
||||
docker save -o k8s-images.tar $(kubeadm config images list)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在需要的机器上加载镜像
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 在离线环境中加载镜像
|
||||
docker load -i k8s-images.tar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
而在可以连接网络的情况下,可以设置containerd的镜像地址,修改containerd的配置文件config.toml
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
# 其他配置...
|
||||
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry]
|
||||
config_path = ""
|
||||
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors]
|
||||
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors."docker.io"]
|
||||
endpoint = ["https://hub.rat.dev"]
|
||||
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors."k8s.gcr.io"]
|
||||
endpoint = ["https://registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers"]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. 使用kubeadm 初始化集群
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 初始化集群控制台 Control plane,保险起见此处也加上镜像地址
|
||||
# 失败了可以用 kubeadm reset 重置
|
||||
|
||||
# 此命令某些情况下可行
|
||||
kubeadm init --image-repository=registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
|
||||
|
||||
# 在使用flannel的情况下应该添加下面这条命令中的参数
|
||||
kubeadm init --image-repository=registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
失败需要将集群重置,可参考[移除节点](https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/create-cluster-kubeadm/#remove-the-node)。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kubeadm reset
|
||||
|
||||
iptables -F && iptables -t nat -F && iptables -t mangle -F && iptables -X
|
||||
|
||||
ipvsadm -C
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意此处限于刚启动集群中没有其他工作负载的情况,有工作负载则要先清空节点负载,再重置。
|
||||
|
||||
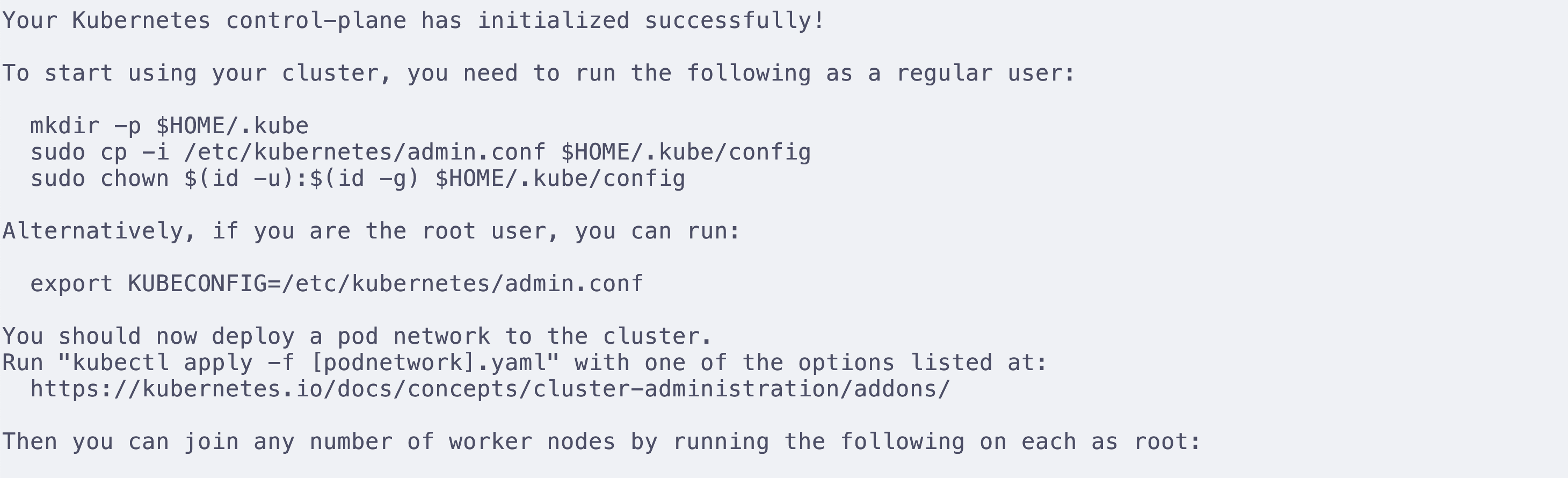
6. 完成初始化工作并安装pod网络附加组件(
|
||||
|
||||
根据控制台给出的提示
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
先设定kubeconfig,kubeconfig可以告诉kubectl在哪里找到集群的配置信息,从而让kubectl能够成功控制集群,其中包含访问k8s集群需要的认证信息。
|
||||
|
||||
非root用户使用
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
|
||||
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
|
||||
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
root用户使用
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装pod网络附加组件,[可用的组件列表](https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/#networking-and-network-policy),这里安装比较常用的flannel。安装网络组件后pod网络之间才能互通,coreDNS才会启动。
|
||||
|
||||
可使用kubectl或者helm安装,这里使用kubectl安装
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/flannel-io/flannel/releases/latest/download/kube-flannel.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意github可能不能访问,可以直接将这个yml下载下来并保存到主机上,随后将apply的文件替换为本地文件即可,注意flannel拉取的仓库是ghcr.io即github的包管理地址,因此也要将这个地址设置镜像地址,可以使用
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors."ghcr.io"]
|
||||
endpoint = ["https://docker.imgdb.de/ghcr.io"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此处使用该方法启动flannel失败,显示不能获取控制平面节点的CIDR,参阅[初始化控制平面节点](https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/create-cluster-kubeadm/#initializing-your-control-plane-node)可知,使用一些第三方网络插件时可能需要设置--pod-network-cidr,因此要重置集群并重新init并加入--pod-network-cidr参数,如下
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kubeadm init --image-repository=registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
再重新启动flannel,至此集群初始化全部完成,已经可以运行负载
|
||||
|
||||
如果想要在该控制平面机器上调度其他pod,则要通过下面的命令将从任何拥有 node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane:NoSchedule 污点的节点(包括控制平面节点)上移除该污点。 这意味着调度程序将能够在任何地方调度 Pod。可参考[控制平面节点隔离](https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/create-cluster-kubeadm/#control-plane-node-isolation)
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kubectl taint nodes --all node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 修复不同节点使用内网ip不互通的问题(异地组网)
|
||||
|
||||
### 修改master节点flannel配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23422,4 +23422,283 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## day348 2025-02-21
|
||||
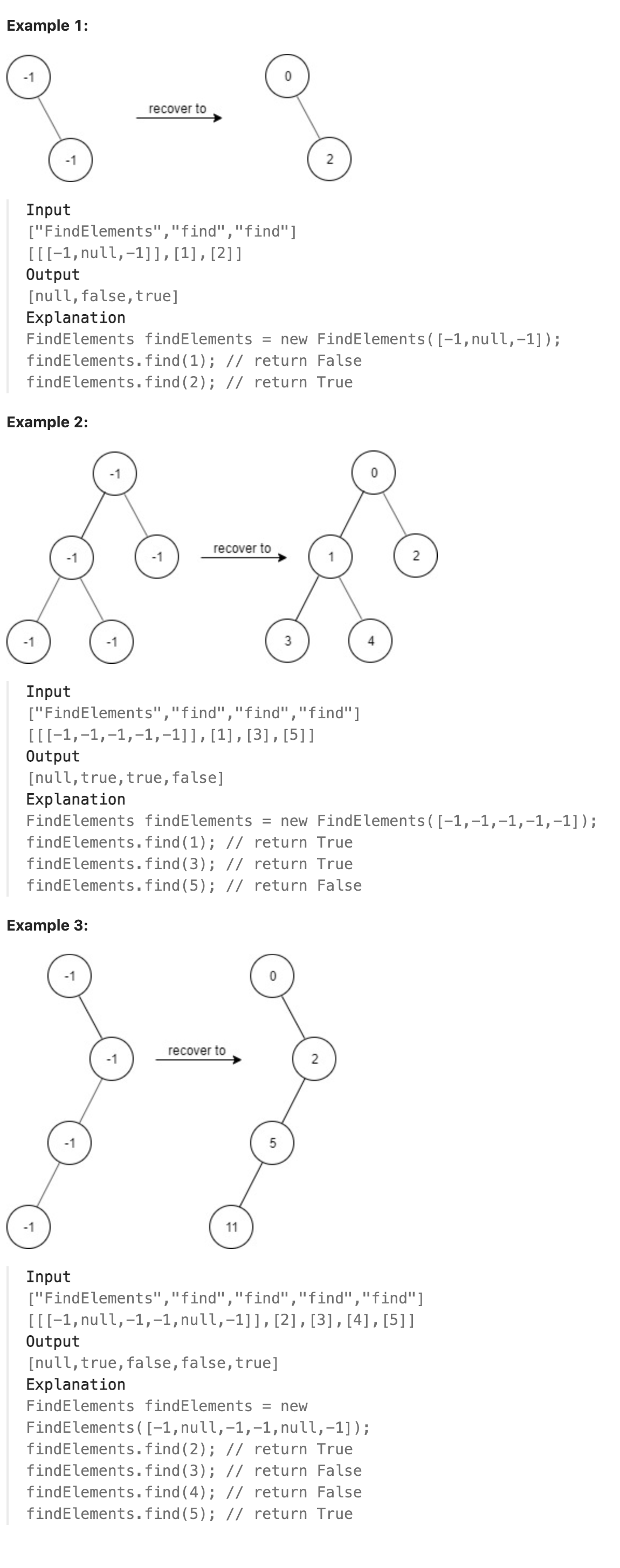
### 1261. Find Elements in a Contaminated Binary Tree
|
||||
Given a binary tree with the following rules:
|
||||
|
||||
root.val == 0
|
||||
For any treeNode:
|
||||
If treeNode.val has a value x and treeNode.left != null, then treeNode.left.val == 2 * x + 1
|
||||
If treeNode.val has a value x and treeNode.right != null, then treeNode.right.val == 2 * x + 2
|
||||
Now the binary tree is contaminated, which means all treeNode.val have been changed to -1.
|
||||
|
||||
Implement the FindElements class:
|
||||
|
||||
FindElements(TreeNode* root) Initializes the object with a contaminated binary tree and recovers it.
|
||||
bool find(int target) Returns true if the target value exists in the recovered binary tree.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
本题思路上并不困难,只需要执行bfs或者dfs(此处使用dfs)遍历树的同时按照对应的计算规则将每个节点的值计算出来并赋给节点,同时将值保存到一个哈希表中(无需排序因此使用unordered_map),对于find函数直接在哈希表中查找。
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
* struct TreeNode {
|
||||
* int val;
|
||||
* TreeNode *left;
|
||||
* TreeNode *right;
|
||||
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
|
||||
* };
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class FindElements {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FindElements(TreeNode* root) {
|
||||
root->val = 0;
|
||||
dfs(root);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void dfs(TreeNode* root){
|
||||
findtable.insert(root->val);
|
||||
if(root->left != nullptr){
|
||||
root->left->val = root->val*2+1;
|
||||
dfs(root->left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(root->right != nullptr){
|
||||
root->right->val = root->val * 2 + 2;
|
||||
|
||||
dfs(root->right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
unordered_set<int> findtable;
|
||||
bool find(int target) {
|
||||
return findtable.find(target) != findtable.end();
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Your FindElements object will be instantiated and called as such:
|
||||
* FindElements* obj = new FindElements(root);
|
||||
* bool param_1 = obj->find(target);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## day349 2025-02-22
|
||||
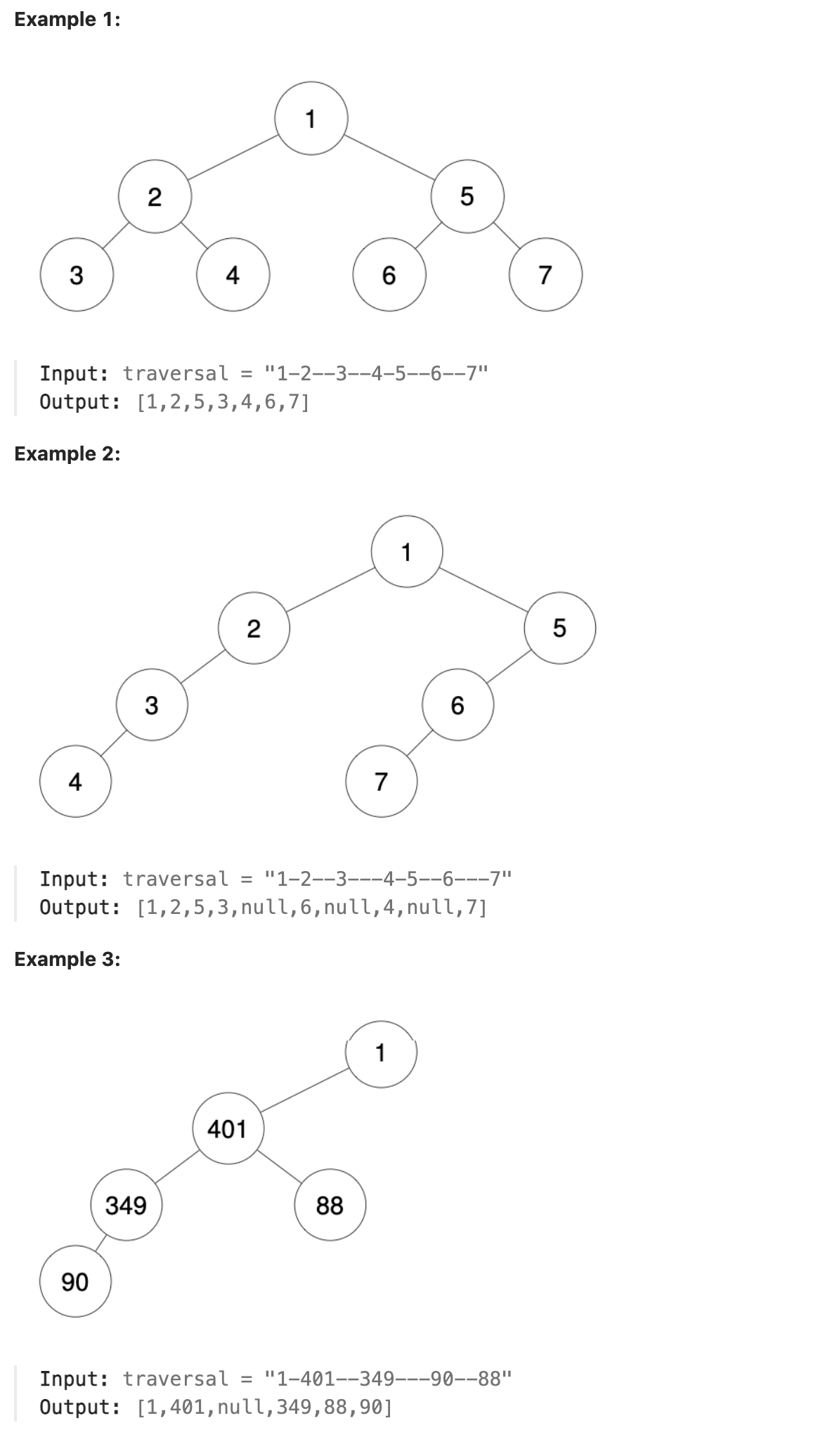
### 1028. Recover a Tree From Preorder traversal
|
||||
We run a preorder depth-first search (DFS) on the root of a binary tree.
|
||||
|
||||
At each node in this traversal, we output D dashes (where D is the depth of this node), then we output the value of this node. If the depth of a node is D, the depth of its immediate child is D + 1. The depth of the root node is 0.
|
||||
|
||||
If a node has only one child, that child is guaranteed to be the left child.
|
||||
|
||||
Given the output traversal of this traversal, recover the tree and return its root.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
本题是一道难题,只要思路清晰还是比较容易解决的,题目中给出的输入为对二叉树进行先序遍历的结果,每个数字前的横线代表该节点所在的深度,则可以直接模拟先序遍历的过程,设置构造函数的参数为字符串和子节点应有的深度,保存一个全局指针指向当前对字符串的扫描位置,扫描字符串获取字符串中下一个节点的深度和节点值,如果节点深度不符合要求,则直接返回,如果节点深度符合要求,则构造新节点并设置节点值,递归尝试给这个新节点构造左右子节点(此处构造时传入的深度为当前的深度加1)。
|
||||
|
||||
除此以外还可以使用栈来保存已经构造好的节点,扫描下一个节点,如果节点深度比栈顶深度小,则弹出栈顶直到栈顶深度为节点深度-1,即弹出栈顶直到栈顶为当前扫描节点的父节点,构造新节点并将其连接到栈顶父节点上,此处要判断是作为左子节点还是右子节点。连接好后将新节点入栈,此处可以发现得到的栈实际上从深度角度来说是一个单调栈。
|
||||
|
||||
这里利用的是先序遍历的特性,即节点的父节点的值一定先于节点的值出现(被遍历到)。
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
* struct TreeNode {
|
||||
* int val;
|
||||
* TreeNode *left;
|
||||
* TreeNode *right;
|
||||
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
|
||||
* };
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
int index = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
TreeNode* recoverFromPreorder(string traversal) {
|
||||
if (traversal.empty()) {
|
||||
return nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return construct(traversal, 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TreeNode* construct(const string& traversal, int depth) {
|
||||
if (index >= traversal.length()) {
|
||||
return nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int nextDepth = 0;
|
||||
int start = index;
|
||||
while (index < traversal.length() && traversal[index] == '-') {
|
||||
nextDepth++;
|
||||
index++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(nextDepth != depth) {
|
||||
index = start;
|
||||
return nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int nextVal = 0;
|
||||
while (index < traversal.length() && isdigit(traversal[index])) {
|
||||
nextVal = nextVal * 10 + (traversal[index] - '0');
|
||||
index++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nextVal);
|
||||
|
||||
root->left = construct(traversal, depth + 1);
|
||||
|
||||
root->right = construct(traversal, depth + 1);
|
||||
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
## day350 2025-02-23
|
||||
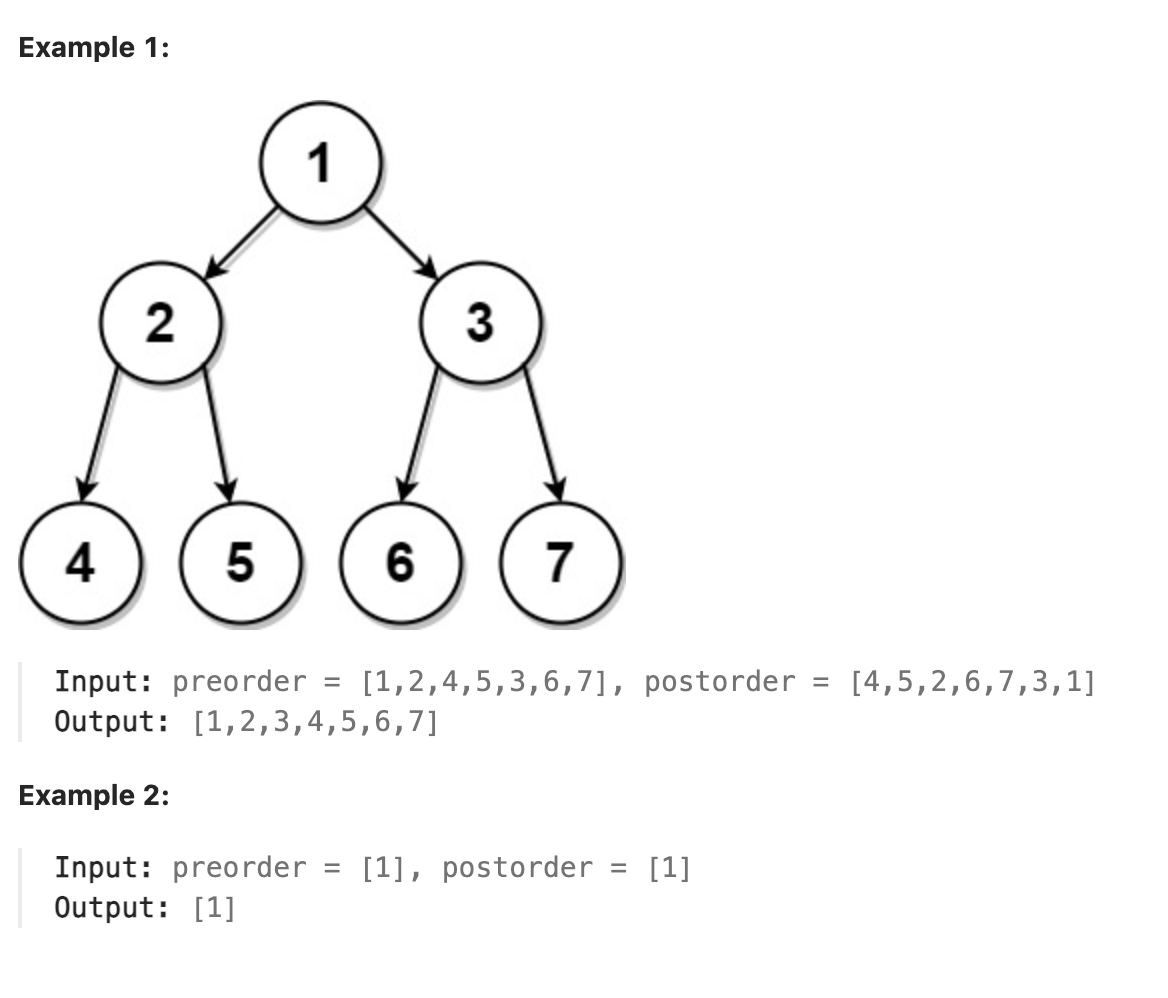
### 889. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Postorder Traversal
|
||||
Given two integer arrays, preorder and postorder where preorder is the preorder traversal of a binary tree of distinct values and postorder is the postorder traversal of the same tree, reconstruct and return the binary tree.
|
||||
|
||||
If there exist multiple answers, you can return any of them.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
本题要思考前序遍历和后序遍历的特点,可以先模拟先序遍历的过程,在模拟的过程中使用一个栈,当栈顶数字和当前 后序遍历指针指向的数字相同时将栈顶出栈并将后序遍历指针后移直到栈顶和后序指针指向数字不同,构造节点并将节点值入栈,构造节点的过程为使用当前遍历的先序数组的数字构造一个新节点,将这个节点作为当前栈顶节点的左子节点或者右子节点(当当前已经有左子节点时)。
|
||||
|
||||
这里考虑的主要是用栈来模拟前序和后序遍历两种,对于前序遍历来说,栈的增长过程是一直向下搜索的过程,当搜索到叶子节点时,就要开始缩小栈直到栈顶节点拥有未被遍历的子节点,再继续向下搜索,前序遍历对当前节点的处理(如打印数值)等是在栈的增长过程中完成的,而后序遍历对节点的处理(如打印数值)是在栈的缩小过程中完成的,即每次弹出栈顶元素时进行相应的处理(打印数值)。则用栈来保存值正好可以通过判断栈顶的弹出时机来确定二叉树的生长形状,栈顶弹出时应该向上走,而栈增长时则是在当前节点继续按照先序遍历向下生长树。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
* struct TreeNode {
|
||||
* int val;
|
||||
* TreeNode *left;
|
||||
* TreeNode *right;
|
||||
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
|
||||
* };
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
TreeNode* constructFromPrePost(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
|
||||
if(preorder.empty()) return nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
|
||||
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
|
||||
stk.push(root);
|
||||
|
||||
int postIndex = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < preorder.size(); i++) {
|
||||
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(preorder[i]);
|
||||
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top()->val == postorder[postIndex]) {
|
||||
stk.pop();
|
||||
postIndex++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (!stk.empty()) {
|
||||
if (stk.top()->left == nullptr)
|
||||
stk.top()->left = node;
|
||||
else
|
||||
stk.top()->right = node;
|
||||
}
|
||||
stk.push(node);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
## day351 2025-02-24
|
||||
### 2467. Most Profitable Path in a Tree
|
||||
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1 where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
|
||||
|
||||
At every node i, there is a gate. You are also given an array of even integers amount, where amount[i] represents:
|
||||
|
||||
the price needed to open the gate at node i, if amount[i] is negative, or,
|
||||
the cash reward obtained on opening the gate at node i, otherwise.
|
||||
The game goes on as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
Initially, Alice is at node 0 and Bob is at node bob.
|
||||
At every second, Alice and Bob each move to an adjacent node. Alice moves towards some leaf node, while Bob moves towards node 0.
|
||||
For every node along their path, Alice and Bob either spend money to open the gate at that node, or accept the reward. Note that:
|
||||
If the gate is already open, no price will be required, nor will there be any cash reward.
|
||||
If Alice and Bob reach the node simultaneously, they share the price/reward for opening the gate there. In other words, if the price to open the gate is c, then both Alice and Bob pay c / 2 each. Similarly, if the reward at the gate is c, both of them receive c / 2 each.
|
||||
If Alice reaches a leaf node, she stops moving. Similarly, if Bob reaches node 0, he stops moving. Note that these events are independent of each other.
|
||||
Return the maximum net income Alice can have if she travels towards the optimal leaf node.
|
||||
|
||||
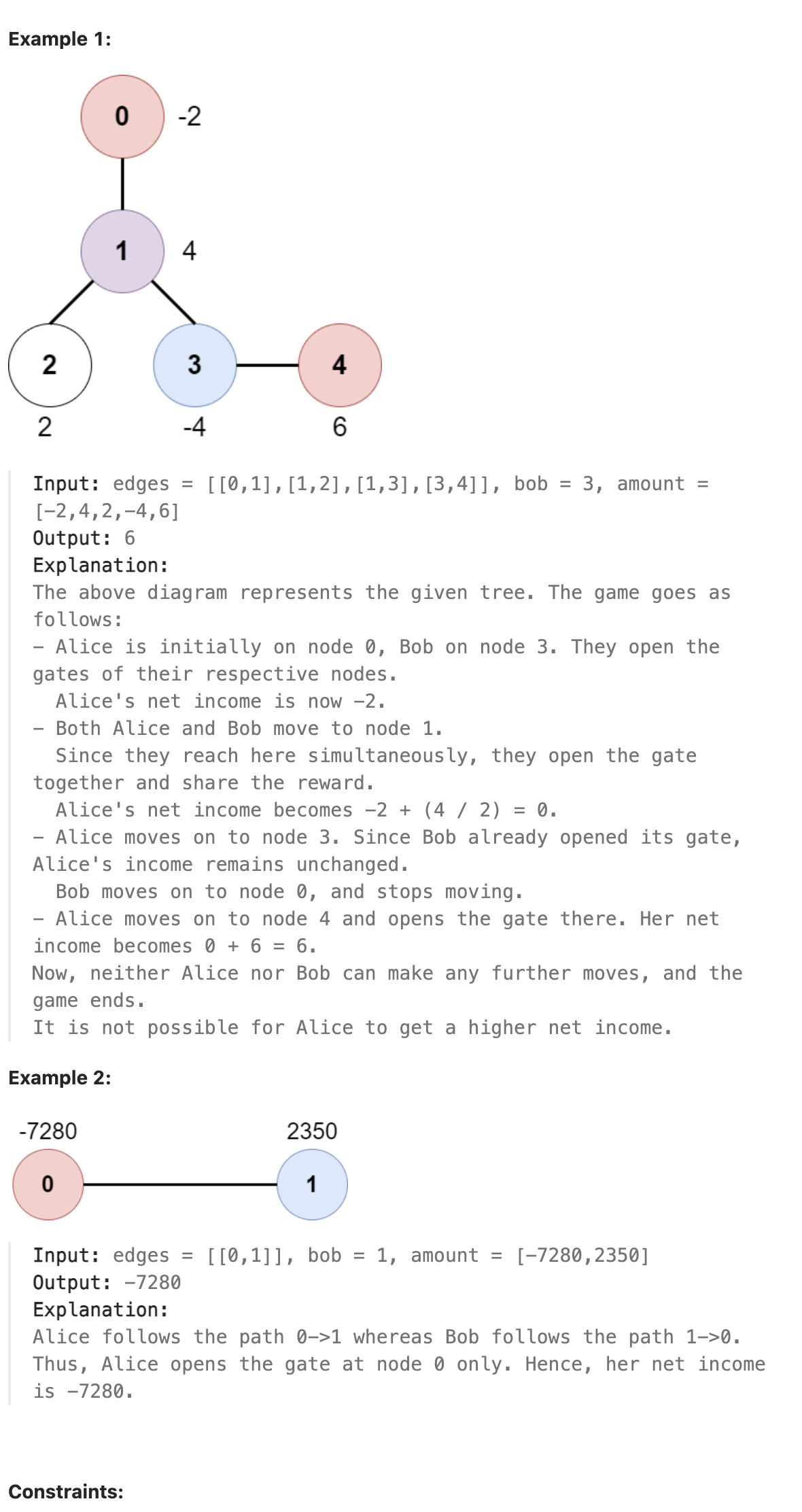
|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
本题首先注意因为是一棵无向树,且节点0确定为树的根,则bob到根节点的路径只能有一条,而对Alice来说,找到能获得最大价值的路径,要通过dfs遍历所有可能的路径并比较,在此过程中,必定会经过Bob经过的路径,考虑Alice是从节点0出发的,因此经过Bob的起始节点时Alice经过的路径必定为Bob经过路径的逆序,根据题目所述可知二人在路径的中间位置必定相遇,因此Alice的路径的后半段Bob已经走过了,根据题目条件可知这段路径上的全部节点的开门奖励均为0(已经被Bob开过了)。则可以先找到Bob到节点0的路径并保存路径上每个节点Bob经过的时间(可以Bob的起始节点作为根节点进行dfs),对Alice来说,如果经过某个节点的时间大于Bob经过的时间,则该节点上Alice能取得的值为0,如果相等则为一半,其余情况均可取到完整的值。
|
||||
|
||||
使用dfs遍历所有可能路径并计算到达各个叶子节点的路径开门成本和,每当到达一个新的叶子节点时即将到该节点的路径成本和与保存的最大值比较,直到遍历完整棵树。
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
int mostProfitablePath(vector<vector<int>>& edges, int bob, vector<int>& amount) {
|
||||
int n = amount.size();
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> graph(n);
|
||||
for (auto &e : edges) {
|
||||
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
|
||||
graph[u].push_back(v);
|
||||
graph[v].push_back(u);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const int INF = 1e9;
|
||||
vector<int> bobTime(n, INF);
|
||||
|
||||
function<int(int, int, int)> dfsBob = [&](int node, int parent, int time) -> int {
|
||||
if (node == 0){
|
||||
bobTime[0] = time;
|
||||
return time;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int nxt : graph[node]) {
|
||||
if (nxt == parent) continue;
|
||||
int d = dfsBob(nxt, node, time+1);
|
||||
if (d != -1) {
|
||||
bobTime[node] = time;
|
||||
cout << node << " "<< time <<endl;
|
||||
return time;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
dfsBob(bob, -1, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int ans = -1e9;
|
||||
function<void(int, int, int, int)> dfsAlice = [&](int node, int parent, int t, int profit) {
|
||||
if (t < bobTime[node])
|
||||
profit += amount[node];
|
||||
else if (t == bobTime[node])
|
||||
profit += amount[node] / 2;
|
||||
|
||||
if(graph[node].size()==1 && node != 0){
|
||||
ans = max(ans, profit);
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int nxt : graph[node]) {
|
||||
if (nxt == parent) continue;
|
||||
dfsAlice(nxt, node, t + 1, profit);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
dfsAlice(0, -1, 0, 0);
|
||||
return ans;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user