18 KiB
title, author, date, categories, tags, draft
| title | author | date | categories | tags | draft | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| leetcode everyday | Logic | 2024-02-27 | false |
day 1 2024-02-27
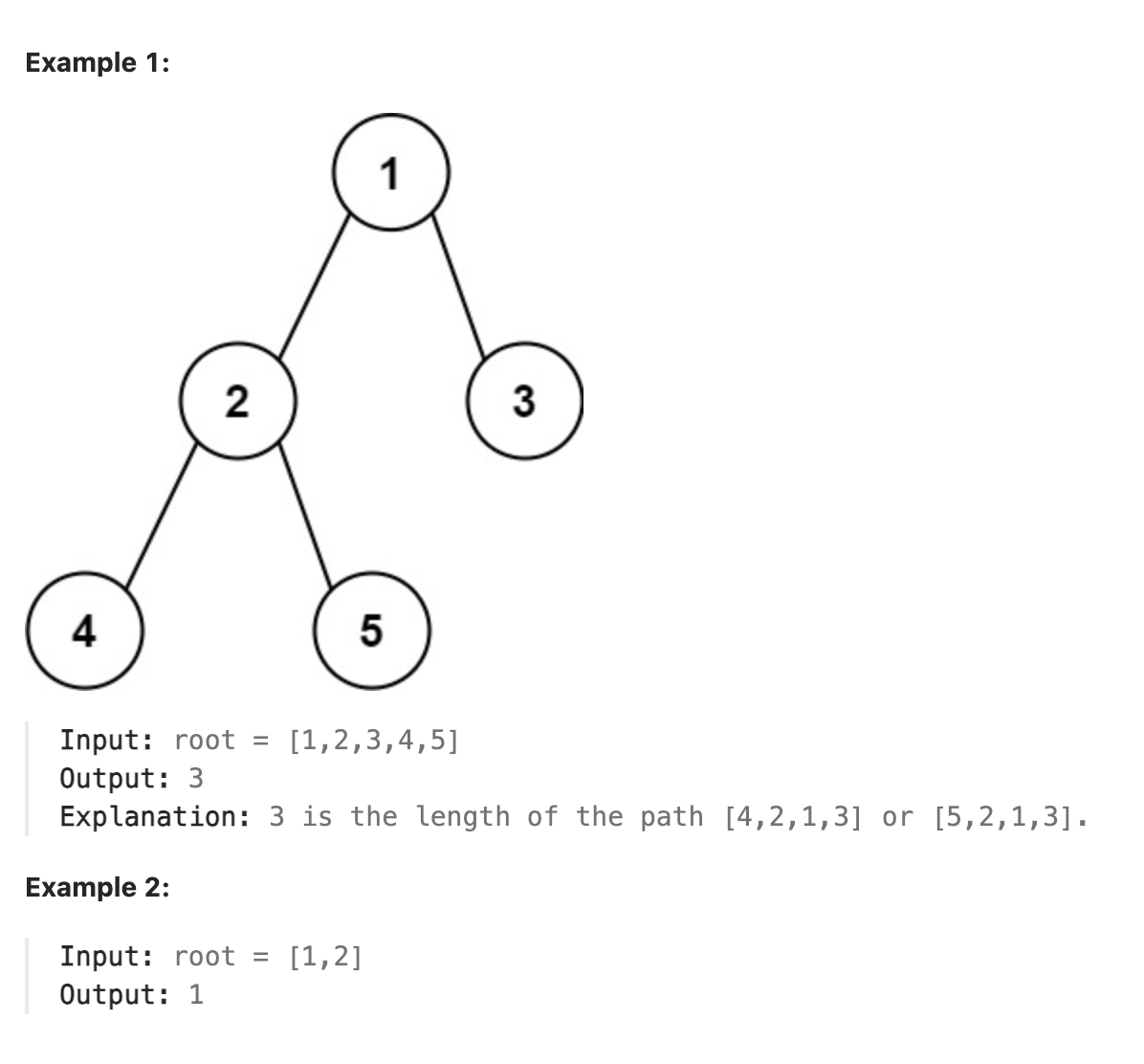
543 Diameter of Binary Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the diameter of the tree.
The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.
The length of a path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
题解
读题, 题目要求寻找二叉树中任意两节点之间的最大距离. 这时这个二叉树更像是一个图的性质而不是树, 即寻找图中任意两节点之间的最大距离. 考虑任意一点到另一点的距离等于其到另一点的父节点的距离减一, 则使用一个二维数组保存每个节点的两个属性:
- 以该节点为根节点且经过该节点的最大直径
- 以该节点为根节点的子树中叶子节点到该节点的最大距离
属性1可以通过将该节点的两个子节点的属性2加和并加1来计算. 属性2取两个子节点属性2的最大值并加1来计算. 最后遍历数组求得数组中属性1的最大值即可. 有一点动态规划的思想.
题目中并没有提供二叉树的节点总数, 则可以使用动态创建的方法, 在遍历过程中每遇到新节点就在二维数组中增加一项. 这里使用递归来对树进行后序遍历, 对空节点, 设置其属性2的值为-1, 这样保证叶子节点的属性2的值为0.
解题时遇到一个小bug, 使用了一个全局切片(数组)来保存变量时, 第一个测试用例的数据会保留到测试第二个测试用例的过程中, 这大概是因为leetcode的测试是对每个用例直接调用给出的解题入口函数, 因此需要在解题函数中将使用的全局变量初始化一下, 将数组设置为空后问题得到解决.
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
var length [][]int
func diameterOfBinaryTree(root *TreeNode) int {
length = nil
_ = postorder(root)
max := -1
for _, value := range length{
if value[0] > max{
max = value[0]
}
}
return max
}
func postorder(father *TreeNode) int {
if father != nil{
len1 := postorder(father.Left)
len2 := postorder(father.Right)
len := make([]int,2)
// find the max diameter pass through current node from the tree rooted current node
len[0] = len1 + len2 + 2
len[1] = max(len1, len2) + 1
length = append(length, len)
return len[1]
} else {
return -1
}
}
day2 2024-02-28
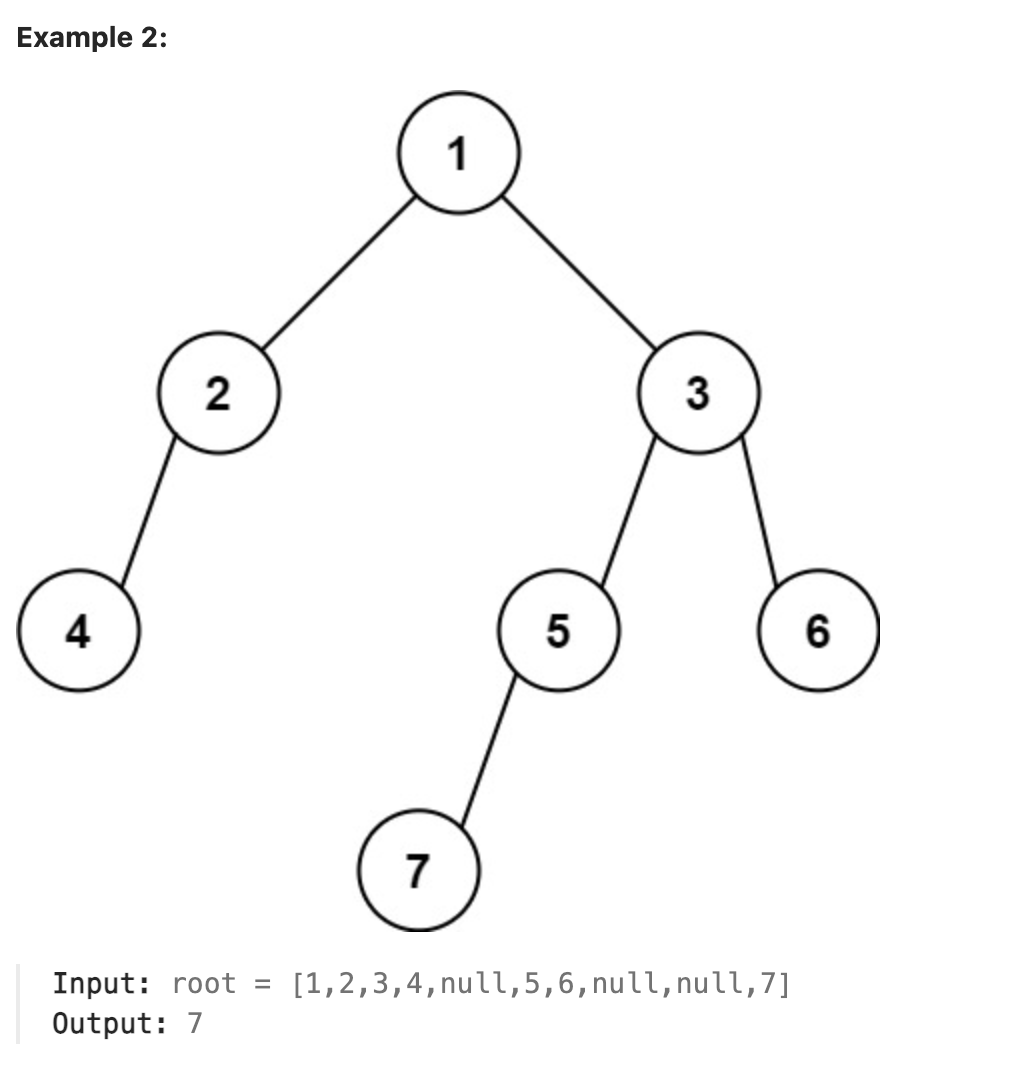
513. Find Bottom Left Tree Value
Given the root of a binary tree, return the leftmost value in the last row of the tree.
题解
找到二叉树最底层最左边的节点值, 用层序遍历遍历到最后一层找到最后一层最左边节点的值即可. 实现层序遍历可以使用一个队列, 将当前层节点的所有子节点入队后将当前层节点出队. 在go中可以使用切片实现一个队列. 使用一个标记变量记录当前层所有节点是否有子节点, 若无子节点则当前层为最低层, 返回当前层最左侧节点的值(此时队列中第一个节点的值).
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func findBottomLeftValue(root *TreeNode) int {
queue := []*TreeNode{root}
lowest := false
key := -1
var father *TreeNode
for !lowest{
queue = queue[key+1:]
lowest = true
for key, father = range queue{
if(father.Left != nil || father.Right != nil){
lowest = false
if(father.Left != nil){
queue = append(queue, father.Left)
}
if(father.Right != nil){
queue = append(queue, father.Right)
}
}
}
}
return queue[0].Val
}
总结
在题解中看到了一个使用深度优先搜索的方法, 记录当前搜索到的层级, 始终保存最大层级的第一个被搜索到的值, 因为使用的是后序遍历, 则每次遇到的当前层大于保存的最大层级时, 该节点就为新的最大层级的第一个节点, 即题目中要求的最左值(leftmost). 算法时间复杂度为O(n)------只遍历一次所有节点.
day3 2024-02-29
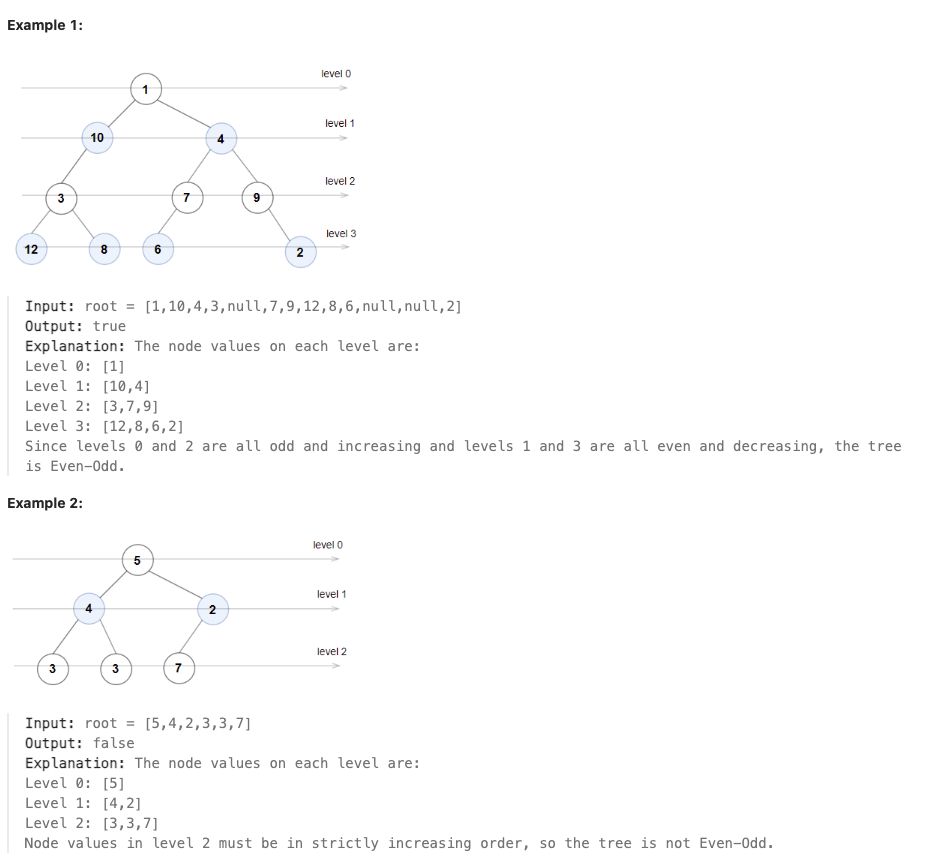
1609. Even Odd Tree
A binary tree is named Even-Odd if it meets the following conditions:
The root of the binary tree is at level index 0, its children are at level index 1, their children are at level index 2, etc. For every even-indexed level, all nodes at the level have odd integer values in strictly increasing order (from left to right). For every odd-indexed level, all nodes at the level have even integer values in strictly decreasing order (from left to right). Given the root of a binary tree, return true if the binary tree is Even-Odd, otherwise return false.
题解
对二叉树的奇数层, 其节点从左到右是严格递减的(意味着有两个节点的值相同是不允许的), 偶数层是严格递增的. 仍然可以使用昨天题目的层序遍历的方法, 增加一个level变量记录当前层数, 对该层内的节点值进行判断是否符合奇数层和偶数层对应的条件即可.
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func isEvenOddTree(root *TreeNode) bool {
level := 0
index := -1
var value *TreeNode
queue := []*TreeNode{root}
saved := 0
for len(queue) != 0{
// remove visited nodes
queue = queue[index+1:]
index = 0
if(level%2 == 0){
for index, value = range queue{
if(index == 0){
saved = value.Val
if(saved %2 != 1){return false}
} else{
if(value.Val <= saved || (value.Val%2) != 1){
return false
} else{
saved = value.Val
}
}
if(value.Left != nil){queue = append(queue, value.Left)}
if(value.Right != nil){queue = append(queue, value.Right)}
}
level++
} else{
for index, value = range queue{
if(index == 0){
saved = value.Val
if(saved %2 != 0){return false}
} else{
if(value.Val >= saved || value.Val %2 != 0){
return false
} else{
saved = value.Val
}
}
if(value.Left != nil){queue = append(queue, value.Left)}
if(value.Right != nil){queue = append(queue, value.Right)}
}
level++
}
}
return true
}
总结
go语言中的for range循环, 如果使用类似for key, value := range list 的形式, 那么key, value这两个变量都会在当前作用域下新建, 意味着即使在前面定义了key, key的值在循环结束后也不会被修改. 若想修改之前定义的key值, 需要将value也提前定义好并使用=而不是:=.
go语言中的for range循环时如果使用:=会新建两个变量, 然后将slice中的值复制给value变量, 将对应的index值赋值给key变量, 这意味着value变量不会指向数组中对应位置的地址, 而是一个不变的单独地址.
day4 2024-03-01
2864. Maximum Odd Binary number
You are given a binary string s that contains at least one '1'.
You have to rearrange the bits in such a way that the resulting binary number is the maximum odd binary number that can be created from this combination.
Return a string representing the maximum odd binary number that can be created from the given combination.
Note that the resulting string can have leading zeros.
Example 1:
Input: s = "010" Output: "001" Explanation: Because there is just one '1', it must be in the last position. So the answer is "001".
Example 2:
Input: s = "0101" Output: "1001" Explanation: One of the '1's must be in the last position. The maximum number that can be made with the remaining digits is "100". So the answer is "1001".
题解
题目中说明了给出的字符串中至少有一个1, 因此可以复制一个字符串, 然后遍历原字符串, 遇到第一个1放在最后一位, 0永远插入到倒数第二位, 不是第一个1放在字符串最前面. 由此除保证字符串是奇数的最后一个1以外, 其余的1都在字符串最前面, 其余的0都插入在最前面的一串1和最后的1之间. 保证了字符串是最大的奇数字符串.
代码
func maximumOddBinaryNumber(s string) string {
s_copy := ""
flag := 0
for _, value := range s{
if value == '1'{
if flag != 0{
s_copy = "1" + s_copy
} else{
s_copy = s_copy + "1"
flag = 1
}
} else{
if(len(s_copy) >=2){
s_copy = string(s_copy[:len(s_copy)-1]) + "0" + string(s_copy[len(s_copy)-1])
} else {
s_copy = "0" + s_copy
}
}
}
return s_copy
}
总结
在处理字符串的时候像中间某个位置插入字符也要使用双引号, 如插入字符0要用+"0"而不是+'0', 此外在截取切片的时候go的切片是左闭右开的. 如[0:3]截取的是0,1,2三个数
day5 2024-03-02
977. Squares of a Sorted Array
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, return an array of the squares of each number sorted in non-decreasing order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-4,-1,0,3,10] Output: [0,1,9,16,100] Explanation: After squaring, the array becomes [16,1,0,9,100]. After sorting, it becomes [0,1,9,16,100].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-7,-3,2,3,11] Output: [4,9,9,49,121]
题解
考虑原数组已经按照非递减排序的情况下, 找到数组中正负交界处元素, 即数组中第一个正数, 以该位置作为起始位置, 使用双指针法, 分别向前和向后遍历数组, 遍历时不断比较两个指针指向的数字的绝对值大小, 将绝对值小的数字平方后追加到结果数组的尾部, 遍历完成即可完成平方值排序. 这样只需要遍历一遍数组即可完成排序.
代码
func sortedSquares(nums []int) []int {
index := 0
value := nums[0]
var result []int
for index, value = range nums{
if(value >= 0){
break
}
}
backward := index - 1
forward := index
if index != 0{
for _,_ = range nums{
if backward<0{
result = append(result, nums[forward]*nums[forward])
forward++
} else if forward>= len(nums){
result = append(result, nums[backward] * nums[backward])
backward--
} else{
if(abs(nums[forward]) < abs(nums[backward])){
result = append(result, nums[forward]*nums[forward])
forward++
} else{
result = append(result, nums[backward] * nums[backward])
backward--
}
}
}
}else{
for _,_ = range nums{
result = append(result, nums[forward]*nums[forward])
forward++
}
}
return result
}
func abs(val int) int {
if(val < 0){
return -val
}else{
return val
}
}
总结
注意一个go的语法问题, 如果在for range循环中两个变量都使用匿名变量, 则应该使用赋值运算符而不是创建并赋值运算符, 即for _,_ = range slice 而不是for _,_ := range slice. 这很可能是因为匿名变量默认为已经创建好的变量, 不需要再创建匿名变量本身了.
day6 2024-03-03
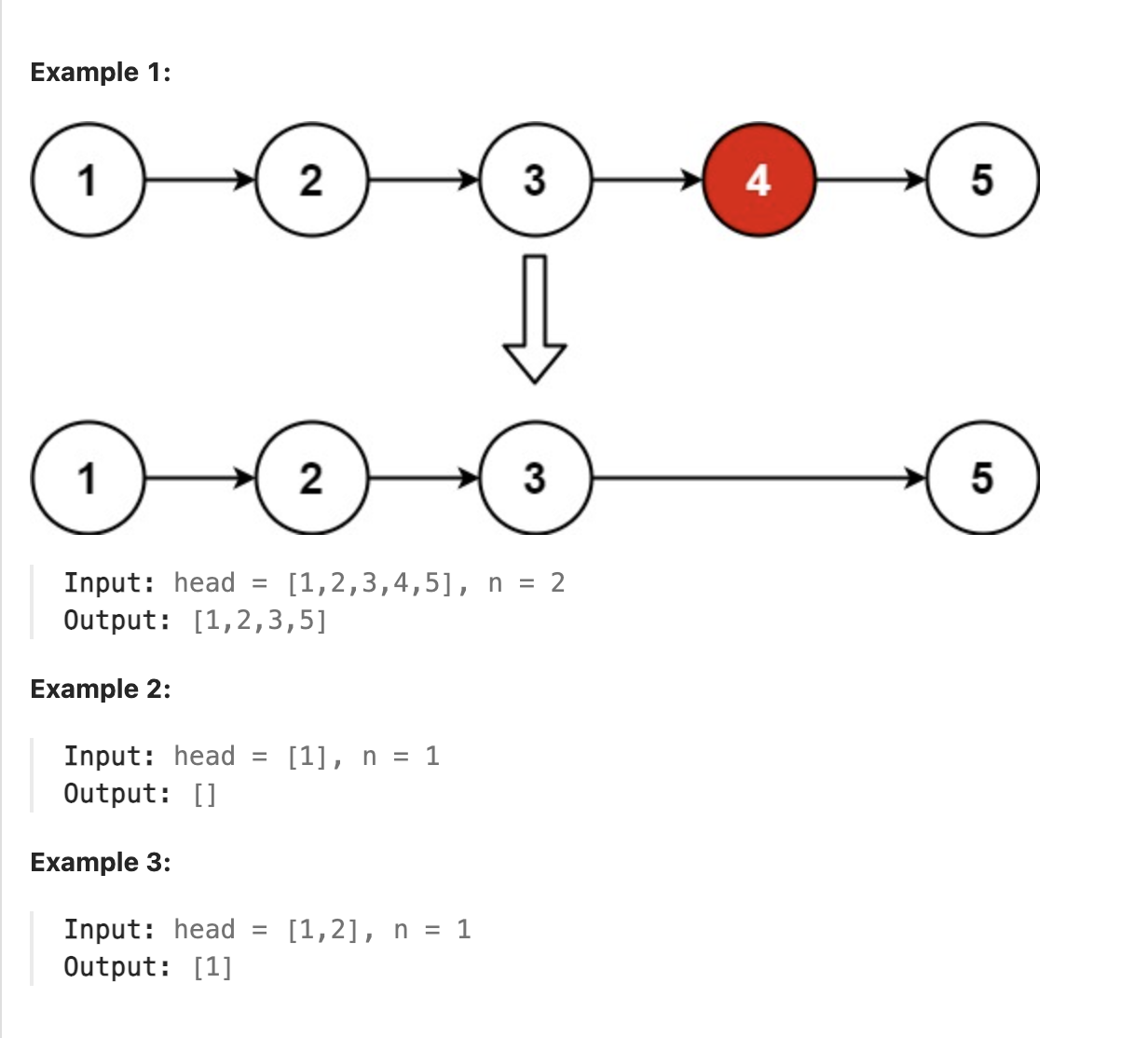
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
题解
给出了链表头, 要求移除从后到前的第n个节点. 如果想一遍遍历就完成这个任务. 就使用空间换时间, 使用一个数组保存所有的Next指针的值. 然后让倒数第n+1个元素的Next指针指向n个元素的Next指针即可, 注意处理链表只有一个元素的特殊情况.
代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
var ptr []*ListNode
current := head
for current.Next != nil{
ptr = append(ptr, current)
current = current.Next
}
ptr = append(ptr, current)
if(len(ptr) == 1){
return nil
}else if len(ptr) == n{
return ptr[1]
}else{
ptr[len(ptr)-n-1].Next = ptr[len(ptr)-n].Next
return head
}
}
总结
在题解中看到大部分使用的是快慢指针的解法, 快慢指针应该是本题想要的解法, 下面贴一个快慢指针的解法示例
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
dummyHead := &ListNode{-1, head}
cur, prevOfRemoval := dummyHead, dummyHead
for cur.Next != nil{
// n step delay for prevOfRemoval
if n <= 0 {
prevOfRemoval = prevOfRemoval.Next
}
cur = cur.Next
n -= 1
}
// Remove the N-th node from end of list
nthNode := prevOfRemoval.Next
prevOfRemoval.Next = nthNode.Next
return dummyHead.Next
}
day7 2024-03-04
948. Bag of Tokens
You start with an initial power of power, an initial score of 0, and a bag of tokens given as an integer array tokens, where each tokens[i] donates the value of tokeni.
Your goal is to maximize the total score by strategically playing these tokens. In one move, you can play an unplayed token in one of the two ways (but not both for the same token):
Face-up: If your current power is at least tokens[i], you may play tokeni, losing tokens[i] power and gaining 1 score. Face-down: If your current score is at least 1, you may play tokeni, gaining tokens[i] power and losing 1 score. Return the maximum possible score you can achieve after playing any number of tokens.
Example 1:
Input: tokens = [100], power = 50
Output: 0
Explanation: Since your score is 0 initially, you cannot play the token face-down. You also cannot play it face-up since your power (50) is less than tokens[0] (100).
Example 2:
Input: tokens = [200,100], power = 150
Output: 1
Explanation: Play token1 (100) face-up, reducing your power to 50 and increasing your score to 1.
There is no need to play token0, since you cannot play it face-up to add to your score. The maximum score achievable is 1.
Example 3:
Input: tokens = [100,200,300,400], power = 200
Output: 2
Explanation: Play the tokens in this order to get a score of 2:
Play token0 (100) face-up, reducing power to 100 and increasing score to 1. Play token3 (400) face-down, increasing power to 500 and reducing score to 0. Play token1 (200) face-up, reducing power to 300 and increasing score to 1. Play token2 (300) face-up, reducing power to 0 and increasing score to 2. The maximum score achievable is 2.
题解
本题的目的是最大化score. 一个基本的策略就是通过小的power换取score, 通过score换取大的power, 利用换到的大power赚取中间水平的token的score. 关键在于, 如何找到最大能换取的score. 首先考虑每次进行一次Face-up和Face-down, score没有变化, 只有power增大了, 那么每次都将score置0, 并判断当前能获得的最大score即可.
通过前面的分析可以得出, 算法分为以下几步
- 将tokens数组排序
- 判断power是否大于tokens[0], 即最小的token, 若大于, 则计算当前能获得的最大score
- 将power的值增加目前tokens数组中最大值和最小值(即排好序后的最后一项和第一项)的差值, 同时将tokens数组中第一项和最后一项移除. 重复2, 3步直到power小于tokens[0]或tokens数组长度为0中止.
- 返回最大的score
代码
func bagOfTokensScore(tokens []int, power int) int {
sort.Ints(tokens)
var powernormal []int
remain := power
score := 0
powernormal = append(powernormal, score)
for len(tokens) != 0 && power > tokens[0]{
remain = power
for _, value := range tokens{
if power >= value{
score++
power -= value
} else{
break
}
}
powernormal = append(powernormal, score)
score = 0
remain += tokens[len(tokens)-1] - tokens[0]
if len(tokens) <= 1{
break
}
tokens = tokens[1:len(tokens)-1]
power = remain
}
sort.Ints(powernormal)
return powernormal[len(powernormal)-1]
}
总结
在实现过程中, 起初使用一个数组来保存每次的score值, 这样空间复杂度略大, 后来查看他人代码, 发现只需要一个max变量来保存当前最大的score值, 并在每次循环计算当前轮次的score值时与当前的最大值比较并根据二者大小更新max变量的值即可, 这样只需要O(1)的空间复杂度.