83 KiB
+++ title = "Bj Homework" date = 2022-10-12 draft = false author = "Logic" +++
第一部分
- str大小为指针的大小即8字节,p的大小也为指针的大小即8字节。因为C++传数组给一个函数,数组类型自动转换为指针类型,因而传的实际是地址。创建一个数组,数组名实际为一指针变量,指向该数组的起始地址。
- 运行测试的结果为段错误。这是因为p是形参,p相当于str指针的复制,在函数内部new申请新内存后将内存地址赋给p并不会改变str指针的值。故str指针仍为NULL,则在将数据复制到str指针指向的地址时会段错误。
- 运行结果为一串未知字符,这是因为函数内部申请的变量为局部变量,其作用域仅限于函数执行过程中,在函数执行结束后局部变量即这里的p指向的栈空间中的内存区域就会被释放,返回值只是p指针的拷贝,指向原来p指向的地址。此时返回的指针指向的地址中的数据是不确定的,故可能会打印出一串未知字符或出现错误。 4. 会正常打印出“你好世界”。
- 会打印出“世界”,因为使用new在堆上分配了内存后,str指向分配的这片内存,即str保存了这片内存的起始地址,而使用delete清理这片内存只是回收了这片内存空间,并没有将str指针重置。str仍然指向这片内存空间,则str并非空指针,strcpy可以正常的复制字符串,printf也可以正常打印输出。
第三次作业
-
使用I/O流以文本方式建立一个文件test1.txt,写入字符"已成功写入文件!",用其他字处理程序(例如Windows记事本程序Notepad)打开,看看是否正确写入。 本题比较简单,只需掌握C++中基本的I/O输入输出方式即可,这里重要的是掌握C++中流的概念。这一部分可以参考 C++ Prime Plus(第6版)中文版 第17章相关内容。简单理解流相当于管道,在文件(硬件也可视为文件)和程序之间传递字节数据。因此文件流相关的类fstream对应的重载如<<和标准输入输出流iostream中的用法类似。则代码如下
#include <fstream> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { fstream iofile("test1.txt", ios::out); iofile << "已成功写入文件!"; cout << "写入成功"; iofile.close(); }
编译运行如下
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1004jRF7OH.png" >}}
查看文件内容如下
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1004TxWH43.png" >}}
- 声明一个dog类,包含体重合年龄两个成员变量及相应的成员两数.声明一个实例dog1.体重为5,年龄为10,使用I/O流把dog1的状态写入磁盘文件,再声明另一个实例dog2,通过读文件把dog1的状态赋给dog2。分别使用文本方式和二进制方式操作文件,看看有何不同:再看看磁盘文件的ASCI码有何不同。
这个题只是在第一个题的基础上结合面向对象编程,简单的声明一个类并构造两个成员函数,一个用于修改对象的信息,一个用于打印对象的信息。在打开文件流的时候用两种不同的方式打开文件流即可。
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class dog {
public:
int weight;
int age;
void change_attr(int x1, int x2) {
weight = x1;
age = x2;
}
// 打印dog信息
void print() { cout << "weight: " << weight << " age: " << age << endl; }
dog() {}
};
int main() {
string line;
dog dog1;
dog1.change_attr(5, 10);
// 文本模式
fstream doginfo("./test2.txt", ios::out);
// cout << doginfo.is_open();
// 写入文件
doginfo << dog1.weight << " " << dog1.age;
dog dog2;
doginfo.close();
doginfo.open("./test2.txt", ios::in);
getline(doginfo, line);
stringstream ss;
// 读取文件内容转换成字符串流并读入
string wei;
string ag;
ss << line;
ss >> wei >> ag;
int x1 = stoi(wei), x2 = stoi(ag);
dog2.change_attr(x1, x2);
dog2.print();
doginfo.close();
// 二进制模式
doginfo.open("test3.txt", ios::out | ios::binary);
// 写入文件
doginfo << dog1.weight << " " << dog1.age;
doginfo.close();
doginfo.open("test3.txt", ios::in | ios::binary);
getline(doginfo, line);
ss << line;
ss >> wei >> ag;
x1 = stoi(wei);
x2 = stoi(ag);
dog2.change_attr(stoi(wei), stoi(ag));
dog2.print();
doginfo.close();
}
运行结果为
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1007fXhkIJ.png" >}}
用文本编辑器打开test2.txt和test3.txt得
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1007LKkmym.png" >}}
这里并没有显示出什么差异主要是因为对于可见字符来说,使用二进制方式和文本方式差异不大,但是对于一些不可见字符如文件的文件头等,二进制读取方式会将数据原封不动的读取出来,而文本则会处理为文本后读取,因为txt文件除了编码类型外无文件头,所以二者没什么区别,但对于其他有格式文件来说可能就会存在区别,另外,以文本方式打开时,遇到结束符CTRLZ(0x1A)就认为文件已经结束。所以,若使用文本方式打开二进制文件,就很容易出现文件读不完整,或內容不对的错误。即使是用文本方式打开文本文件,也要谨慎使用,比如复制文件,就不应该使用文本方式。
- 编写程序提示用户输入一个十进制整数.分别用十进制、八进制、和十六进制形式输出。
对进制进行转换可以使用短除反取余的方式,除对应进制数然后反向取余数即可。但是如果用int 或者long int类型存储输入的十进制数并进行转换,能转换的数字大小是有限的,在考虑可能有大整数的情况下,使用字符串存储并进行大整数的模数运算,从而实现了大整数的进制转换。该程序可以输入任意大的整数,都可以完成进制转换。
#include <algorithm>
#include <atomic>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 字符转数字
int ctoi(char num) { return num - '0'; }
// 8进制大整数转换
pair<string, int> big_mod_eight(string now) {
string quo;
int remain;
int before = ctoi(now[0]);
if (now.length() == 1) {
remain = before % 8;
int result = before / 8;
quo = to_string(result);
return make_pair(quo, remain);
}
before = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < now.length(); i++) {
int number = before * 10 + ctoi(now[i]);
before = number % 8;
remain = number / 8;
quo = quo + to_string(remain);
}
if (quo[0] == '0')
quo.erase(quo.begin());
return make_pair(quo, before);
}
// 16进制大整数转换
pair<string, int> big_mod_hex(string now) {
string quo;
int remain;
// 只有一位直接返回
if (now.length() == 1) {
remain = ctoi(now[0]);
quo = "0";
return make_pair(quo, remain);
}
// 两位及以上进行处理
int before = ctoi(now[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < now.length(); i++) {
int number = before * 10 + ctoi(now[i]);
if (number < 16) {
quo += "0";
i++;
if (i < now.length())
number = number * 10 + ctoi(now[i]);
}
before = number % 16;
remain = number / 16;
quo = quo + to_string(remain);
}
if (quo[0] == '0')
quo.erase(quo.begin());
return make_pair(quo, before);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
string interger;
vector<int> convert;
while (true) {
cout << "Please enter a decimal, and q for quit: ";
cin >> interger;
// interger = "23";
string result;
int remain;
pair<string, int> temp;
result = interger;
if (interger == "q") {
break;
} else {
cout << "Dec = " << interger;
while (result != "0") {
temp = big_mod_eight(result);
result = temp.first;
remain = temp.second;
convert.push_back(remain);
}
cout << " Oct = ";
// 将结果逆序
reverse(begin(convert), end(convert));
for (auto n : convert) {
cout << n;
}
convert.clear();
result = interger;
while (result != "0") {
temp = big_mod_hex(result);
result = temp.first;
remain = temp.second;
convert.push_back(remain);
}
cout << " Hex = ";
// 将结果逆序
reverse(begin(convert), end(convert));
for (auto n : convert) {
cout << hex << n;
}
cout << endl;
convert.clear();
}
}
return 0;
}
运行结果图如下
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1011Jy1fbS.png" >}}
- 编写程序实现如下功能:打开指定的一个文木文件,在每一个行前加行号。
本题考察C++基本的文件IO和文件指针,比较方便的做法是用一个中间文件,首先读取原文件的内容,每读取一行加一个行号并写入到中间文件中,最后将加了行号的中间文件内容再写入原文件并删除中间文件。
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Please input the filename you want to open: ";
string filename;
cin >> filename;
ifstream fin(filename);
string backup = filename + ".back_up";
ofstream fout(backup);
int number = 1;
string sline;
while (true) {
getline(fin, sline);
if (fin.eof())
break;
fout << number << " " << sline << endl;
number++;
}
fin.close();
fout.close();
fout.open(filename);
fin.open(backup);
while (true) {
getline(fin, sline);
if (fin.eof())
break;
fout << sline << endl;
}
fin.close();
fout.close();
// 删除临时文件
const char *filerename = backup.c_str();
if (remove(filerename) == 0) {
cout << "Add line number success!";
} else {
cout << "Remove backup file error!";
}
return 0;
}
效果如下,原文件内容为
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1011AbNMl5.png" >}}
运行程序后,文件内容为
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1011d5ZAut.png" >}}
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1011FgrC32.png" >}}
- 定义一个保存学生信息的结构体STUDENT,包含的学生信息有:学号、姓名、专业和平均分。其中学号和平均分使用整型,姓名和专业使用宁符数组。使用动态数组存储学生信息,并编写菜单,实现学生信息的录入、删除和显示功能。由手录入学生的数量未知,因此要使用new运算符实现动态内存的分配、使用delete运算符实现动态内存的回收。另外,使用标准流对象cin和cout完𢦓数据的输入输出;使用函数重载(例如添加学生到数组时可以采用不同的参数列表、显示学生信息时可以指定成绩区间等)、默认形参、引用变量;以上功能实现在自定义的名字空间中(建议使用学号做名字空间)。
定义命名空间为zqy19281235,定义STUDENT结构体,定义添加学生函数,使用默认形参和引用变量。考虑到学号的唯一性,使用map模板来存储学生信息。并将map通过引用传入函数,通过学号删除学生信息并释放申请的内存,重载显示学生信息的函数,当不输入指定的成绩区间时默认全部显示,当输入指定成绩区间时可以仅指定最大值或者最小值,另一个使用默认形参进行处理。代码如下
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
namespace zqy19281235 {
struct STUDENT {
int sno;
string name;
string specialty;
int average;
};
// 有默认形参,使用引用变量
void add_stu(map<int, struct STUDENT *> &students, int sno, string name,
string specialty, int average = 60) {
struct STUDENT *new_stu = new (struct STUDENT);
new_stu->sno = sno;
new_stu->name = name;
new_stu->specialty = specialty;
new_stu->average = average;
students.insert(make_pair(sno, new_stu));
}
void del_stu(map<int, struct STUDENT *> &students, int sno) {
// 释放内存
delete (students.find(sno)->second);
students.erase(sno);
cout << "Delete success!";
}
// 默认全部显示
void look_up_stu(map<int, struct STUDENT *> &students) {
for (auto stu : students) {
cout << "Sno = " << stu.second->sno << " Name = " << stu.second->name
<< " Specialty = " << stu.second->specialty
<< " Average = " << stu.second->average << endl;
}
}
// 重载的显示函数
void look_up_stu(map<int, struct STUDENT *> &students, int flag, int min = 0,
int max = 100) {
for (auto stu : students) {
if (stu.second->average >= min && stu.second->average <= max) {
cout << "Sno = " << stu.second->sno << " Name = " << stu.second->name
<< " Specialty = " << stu.second->specialty
<< " Average = " << stu.second->average << endl;
}
}
}
} // namespace zqy19281235
int main() {
char select;
cout << "Welcome to my student manage system!!!!!" << endl;
map<int, zqy19281235::STUDENT *> students;
while (true) {
cout << "Please select the operation you want:" << endl
<< "\t1.add a student.\n"
<< "\t2.delete a student\n"
<< "\t3.display students infomation\n"
<< "\tq for quit\n"
<< "your select:";
cin >> select;
switch (select) {
case '1': {
int number, average;
string aver;
string name, specialty;
cout << "The student number:";
cin >> number;
cout << "The student name:";
cin >> name;
cout << "The student specialty:";
cin >> specialty;
cin.get();
cout << "The student average(can be nothing):";
getline(cin, aver);
if (aver.length() == 0) {
zqy19281235::add_stu(students, number, name, specialty);
} else {
average = stoi(aver);
zqy19281235::add_stu(students, number, name, specialty, average);
}
break;
}
case '2': {
int number;
cout << "The student number:";
cin >> number;
zqy19281235::del_stu(students, number);
break;
}
case '3': {
string min, max;
cout << "Enter the min average of the students:";
cin.get();
getline(cin, min);
cout << "Enter the max average of the students:";
getline(cin, max);
if (min.length() == 0 && max.length() == 0) {
zqy19281235::look_up_stu(students);
break;
} else if (max.length() == 0) {
zqy19281235::look_up_stu(students, 1, stoi(min));
} else if (min.length() == 0) {
zqy19281235::look_up_stu(students, 1, 0, stoi(max));
} else {
zqy19281235::look_up_stu(students, 1, stoi(min), stoi(max));
}
break;
}
case 'q': {
return 0;
}
default:
break;
}
}
}
功能展示如下:
- 添加学生
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1012YB8d7l.png" >}}
- 显示学生信息(无限制)
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1012NSCVin.png" >}}
- 显示学生信息(有限制)
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1012JkQKxs.png" >}}
- 删除学生信息
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1012uB9SkP.png" >}}
第四次作业
1
设计并测试一个名为Rectangle的矩形类,其属性为矩形的左下角与右上角两个点的坐标,提供能计算矩形的面积的成员函数。
设计一个结构体表示点坐标,设计矩形类的属性为两个坐标,成员函数为计算面积。并在main函数中简单测试,代码如下
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
typedef struct point {
int x;
int y;
} Point;
// 方形类
class Rectangle {
public:
Point left_bottom;
Point right_top;
Rectangle(Point left, Point right) {
left_bottom.x = left.x;
left_bottom.y = left.y;
right_top.x = right.x;
right_top.y = right.y;
};
int area() {
return abs(right_top.x - left_bottom.x) * abs(right_top.y - left_bottom.y);
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
Point point1 = {1, 1};
Point point2 = {2, 3};
Rectangle *rec1 = new Rectangle(point1, point2);
printf("%d", rec1->area());
return 0;
}
测试结果如下
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1026iUdZ0b.png" >}}
2
设计一个用于人事管理的“人员”类。由于考虑到通用性,这里只抽象出所有类型人员都具有的属性:编号、性别、出生日期、身份证号等。其中“出生日期”声明为一个“日期”类内嵌对象。用成员函数实现对人员信息的录入和显示。要求包括:构造函数和析构函数、拷贝构造函数、内联成员函数、带默认形参值的成员函数、类的组合。
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class date {
public:
string birthday;
};
class Person {
public:
string pno;
string sex;
string idno;
Person();
Person(const Person &obj);
void add(string x, string y, string z, string xx);
inline void display();
~Person();
private:
date date_;
};
Person::Person() {}
Person::~Person() {}
Person::Person(const Person &obj) {
cout << "call copy function";
pno = obj.pno;
sex = obj.sex;
idno = obj.idno;
date_.birthday = obj.date_.birthday;
}
void Person::add(string x, string y, string z, string xx = "00000000") {
pno = x;
sex = y;
idno = xx;
date_.birthday = z;
}
inline void Person::display() {
cout << "Info of this Person is: " << endl
<< "No: " << pno << "\tSex: " << sex << "\tBirthday:" << date_.birthday
<< "\tIdno" << idno << endl;
}
3
定义一个Cat类,拥有静态数据成员HowManyCats,记录Cat的对象个体数目;静态成员函数GetHowMany(),存取HowManyCats。非静态数据成员CatID记录当前对象的编号,成员函数GetCatID()存取CatID。设计程序测试这个类,生成若干个Cat对象,输出每个对象的数据成员值,体会静态成员和非静态成员的用法。
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Cat {
public:
static int HowManyCats;
static void GetHowMany() { cout << HowManyCats << endl; }
string CatID;
void GetCatID() { cout << CatID << endl; }
Cat(string);
~Cat();
private:
};
int Cat::HowManyCats = 0;
Cat::Cat(string id) {
HowManyCats++;
CatID = id;
}
Cat::~Cat() { HowManyCats--; }
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
string IDs[5] = {"aaaaaaaa", "bbbbbbbbb", "cccccc", "dddddddd", "eeeeeeeee"};
vector<Cat *> cats;
// 实例化Cat
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Cat *newcat = new Cat(IDs[i]);
cats.push_back(newcat);
}
// 打印所有对象
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cats[i]->GetCatID();
cats[i]->GetHowMany();
delete cats[i];
}
return 0;
}
定义Cat类后,在main中实例化五个Cat并输出。输出时输出CatID和HowManyCats。随后删除该实例。在构造函数中每实例化一个Cat就将HowManyCats加一。删除时则减一。测试结果如下
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1027RWGklD.png" >}}
4
设计一个字符串类MyString,要求如下:
(1) 正确封装数据,要求使用动态内存分配的方式管理封装的数据;
(2) 正确实现构造函数和析构函数,正确初始化数据,防止内存泄露;构造函数要有多个重载版本;
(3) 实现存取字符串的功能,其中取字符串的函数为get_string,存字符串的函数为set_string;
(4) 实现追加字符串的功能、取得字符串长度的功能;
(5) 要求类的声明写在MyString.h文件中,类的实现写在MyString.cpp文件中。
编写函数测试你所设计的类。
使用char指针指示字符串,在构造函数和set_string中为指针动态分配内存并将字符串拷贝过去,连接字符串则重新申请空间并释放之前申请的空间,然后进行字符串的拷贝。代码如下
// MyString.h
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class MyString {
private:
char *str;
int length;
public:
MyString();
MyString(const char *s);
char *get_string();
void set_string(char *s);
int get_length();
void append(char *s);
~MyString();
};
// MyString.cpp
#include "MyString.h"
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
MyString::MyString(const char *s) {
length = strlen(s);
str = new char[length + 1];
str[length] = '\0';
//安全拷贝
strncpy(str, s, length + 1);
}
MyString::~MyString(){};
char *MyString::get_string() { return str; }
void MyString::set_string(char *s) {
length = strlen(s);
str = new char[length + 1];
str[length] = '\0';
//安全拷贝
strncpy(str, s, length + 1);
}
int MyString::get_length() { return length; }
void MyString::append(char *s) {
length = length + strlen(s);
char *str_temp = new char[length + 1];
str_temp[length] = '\0';
strncpy(str_temp, str, length + 1);
strncat(str_temp, s, length + 1);
delete str;
str = str_temp;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char *first = "This is first string";
char *second = "This is second";
MyString mystring(first);
cout << "Length: " << mystring.get_length() << endl;
cout << "String is : " << mystring.get_string() << endl;
// 添加第二字符串
mystring.append(second);
cout << "Length: " << mystring.get_length() << endl;
cout << "String is : " << mystring.get_string() << endl;
return 0;
}
在main中定义两个字符串并测试得
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1027hTiJxJ.png" >}}
5
尝试封装学生列表类。对于学生信息(包含姓名、学号、成绩等),封装一个学生列表类CStudentList,在这个类中实现增加、按学号删除、修改学生信息、显示学生信息的功能,其中保存学生的信息应该使用动态内存的方法,以实现保存"无限"的学生信息。其他要求如下:
(1) 至少显示学生信息的函数要有重载版本,比如可选择根据学生学号显示学生信息、根据学生成绩显示学生信息、根据给定的成绩区间显示学生的信息(此时要练习默认形参值)。
(2) 练习引用,比如可设计根据姓名取得学生信息并以引用的形式返回该学生信息的函数;对于按引用返回的学生信息,可实现修改其成绩的功能。
(3) 学生信息可以仍然使用结构体来表示。
(4) 重点是懂得封装的思想,理解构造函数和析构函数的设计和使用。
注意:由于还没有介绍复制构造函数和赋值运算符函数,所以该类会有不少问题,但对于简单的增加、按学号删除和显示学生信息的功能,还是要能够正常运行的。
这个学生类中的部分函数在之前作业中已经实现过,这里就直接拿来使用。主要是要将函数和数据进行封装。代码如下
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct STUDENT {
int sno;
string name;
string specialty;
int average;
};
class Stu_info {
public:
Stu_info(){};
~Stu_info(){};
// 有默认形参,使用引用变量
void add_stu(map<int, struct STUDENT *> &students, int sno, string name,
string specialty, int average = 60) {
struct STUDENT *new_stu = new (struct STUDENT);
new_stu->sno = sno;
new_stu->name = name;
new_stu->specialty = specialty;
new_stu->average = average;
students.insert(make_pair(sno, new_stu));
}
void del_stu(map<int, struct STUDENT *> &students, int sno) {
// 释放内存
delete (students.find(sno)->second);
students.erase(sno);
cout << "Delete success!";
}
// 默认全部显示
void look_up_stu(map<int, struct STUDENT *> &students) {
for (auto stu : students) {
cout << "Sno = " << stu.second->sno << " Name = " << stu.second->name
<< " Specialty = " << stu.second->specialty
<< " Score = " << stu.second->average << endl;
}
}
// 重载的显示函数
void look_up_stu(map<int, struct STUDENT *> &students, int flag, int min = 0,
int max = 100) {
for (auto stu : students) {
if (stu.second->average >= min && stu.second->average <= max) {
cout << "Sno = " << stu.second->sno << " Name = " << stu.second->name
<< " Specialty = " << stu.second->specialty
<< " Score = " << stu.second->average << endl;
}
}
}
};
int main() {
char select;
cout << "Welcome to my student manage system!!!!!" << endl;
Stu_info *stu_info = new Stu_info();
map<int, STUDENT *> students;
while (true) {
cout << "\nPlease select the operation you want:" << endl
<< "\t1.add a student.\n"
<< "\t2.delete a student\n"
<< "\t3.display students infomation\n"
<< "\tq for quit\n"
<< "your select:";
cin >> select;
switch (select) {
case '1': {
int number, average;
string aver;
string name, specialty;
cout << "The student number:";
cin >> number;
cout << "The student name:";
cin >> name;
cout << "The student specialty:";
cin >> specialty;
cin.get();
cout << "The student score(can be nothing):";
getline(cin, aver);
if (aver.length() == 0) {
stu_info->add_stu(students, number, name, specialty);
} else {
average = stoi(aver);
stu_info->add_stu(students, number, name, specialty, average);
}
break;
}
case '2': {
int number;
cout << "The student number:";
cin >> number;
stu_info->del_stu(students, number);
break;
}
case '3': {
string min, max;
cout << "Enter the min score of the students:";
cin.get();
getline(cin, min);
cout << "Enter the max score of the students:";
getline(cin, max);
if (min.length() == 0 && max.length() == 0) {
stu_info->look_up_stu(students);
break;
} else if (max.length() == 0) {
stu_info->look_up_stu(students, 1, stoi(min));
} else if (min.length() == 0) {
stu_info->look_up_stu(students, 1, 0, stoi(max));
} else {
stu_info->look_up_stu(students, 1, stoi(min), stoi(max));
}
break;
}
case 'q': {
return 0;
}
default:
break;
}
}
}
测试结果如下:
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1028t4AFaW.png" >}}
编程题1
编写并测试一个单件类:该类能够控制系统中最多只存在一个该类的对象。
该题其实背后涉及的原理很复杂,在查阅资料后可以找到一种最简洁的实现方式,该方式也被称为Meyers' Singleton.其实现代码如下
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Singleton {
private:
Singleton() { test = 0; };
~Singleton(){};
Singleton(const Singleton &);
Singleton &operator=(const Singleton &);
public:
int test;
static Singleton *getInstance() {
static Singleton instance;
return &instance;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
Singleton *object1 = Singleton::getInstance();
object1->test = 1;
Singleton *object2 = Singleton::getInstance();
printf("%d", object2->test);
return 0;
}
这里使用了静态局部变量,该变量在第一次调用getInstance函数时会被初始化,在之后即便再次调用getInstance函数,该变量的地址也不会变化,即在该函数内该变量唯一。这一点可以通过main中的测试来说明,首先调用公有的静态方法获取一个实例。然后修改实例中的test。因为构造函数中test的值为0,若再次获取到的为新实例,则object2的test值应为0,但实际运行结果如下
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1028sPiBf8.png" >}}
这说明object2获取到的仍然为同一实例,打印指针可更直观的了解object1、2为同一实例。
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/1028wdh3Oj.png" >}}
编程题2
魔兽世界之一:备战描述魔兽世界的西面是红魔军的司令部,东面是蓝魔军的司令部。两个司令部之间是依次排列的若干城市。
红司令部,City 1,City 2,........,City n,蓝司令部
两军的司令部都会制造武士。武士一共有 dragon 、ninja、iceman、lion、wolf 五种。每种武士都有编号、生命值、攻击力这三种属性。双方的武士编号都是从1开始计算。红方制造出来的第n个武士,编号就是n。同样,蓝方制造出来的第n个武士,编号也是n。
武士在刚降生的时候有一个生命值。在每个整点,双方的司令部中各有一个武士降生。红方司令部按照iceman、lion、wolf、ninja、dragon的顺序循环制造武士。蓝方司令部按照lion、dragon、ninja、iceman、wolf的顺序循环制造武士。制造武士需要生命元。制造一个初始生命值为m的武士,司令部中的生命元就要减少m个。如果司令部中的生命元不足以制造某个按顺序应该制造的武士,那么司令部就试图制造下一个。如果所有武士都不能制造了,则司令部停止制造武士。给定一个时间,和双方司令部的初始生命元数目,要求你将从0点0分开始到双方司令部停止制造武士为止的所有事件按顺序输出。一共有两种事件,其对应的输出样例如下:
武士降生输出样例: 004 blue lion 5 born with strength 5,2 lion in red headquarter
表示在4点整,编号为5的蓝魔lion武士降生,它降生时生命值为5,降生后蓝魔司令部里共有2个lion武士。(为简单起见,不考虑单词的复数形式)注意,每制造出一个新的武士,都要输出此时司令部里共有多少个该种武士。
司令部停止制造武士输出样例: 010 red headquarter stops making warriors
表示在10点整,红方司令部停止制造武士
输出事件时:首先按时间顺序输出;同一时间发生的事件,先输出红司令部的,再输出蓝司令部的。输入第一行是一个整数,代表测试数据组数。每组测试数据共两行。第一行:一个整数M。其含义为, 每个司令部一开始都有M个生命元( 1 <= M <= 10000)。第二行:五个整数,依次是 dragon 、ninja、iceman、lion、wolf 的初始生命值。它们都大于0小于等于10000。输出对每组测试数据,要求输出从0时0分开始,到双方司令部都停止制造武士为止的所有事件。对每组测试数据,首先输出"Case:n" n是测试数据的编号,从1开始 。接下来按恰当的顺序和格式输出所有事件。每个事件都以事件发生的时间开头,时间以小时为单位,有三位。样例输入
1
20
3 4 5 6 7
样例输出
Case:1
000 red iceman 1 born with strength 5,1 iceman in red headquarter
000 blue lion 1 born with strength 6,1 lion in blue headquarter
001 red lion 2 born with strength 6,1 lion in red headquarter
001 blue dragon 2 born with strength 3,1 dragon in blue headquarter
002 red wolf 3 born with strength 7,1 wolf in red headquarter
002 blue ninja 3 born with strength 4,1 ninja in blue headquarter
003 red headquarter stops making warriors
003 blue iceman 4 born with strength 5,1 iceman in blue headquarter
004 blue headquarter stops making warriors
这道题题面比较复杂。但是仔细分析后可知指挥部只有制造武士这一种行为,实际上比较简单。只需读取输入为每个武士赋予相应的属性即可。这里因为武士本身没有行为,可以使用结构体存储。司令部为一个类,其中包含了生命元数量,制造武士顺序,现在制造的武士的下标,司令部的颜色,武士的标号和所有武士的信息这几个成员变量。使用武士名作为key构造哈希表存储武士信息可以快速获得某种武士的数量。构造函数中初始化成员变量。成员函数为制作武士和判断两个函数。制造武士用于根据指定下标制造对应顺序的武士,判断则用于判断当前应制造的武士能否制造,不能则寻找下一个能制造的武士,如果已经不能制造则终止制造武士并将over置为true; 代码如下
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef struct own_warrior {
int number;
int life_value;
int attacker;
} own_warrior;
struct warrior {
string name;
int life_value;
};
// 构造战士信息哈希表
map<int, struct warrior *> warriors;
vector<string> warrior_name = {"dragon", "ninja", "iceman", "lion", "wolf"};
class headquarter {
public:
int meta_life;
vector<int> order;
int warrior_now;
bool over;
string color;
int warrior_num;
map<string, vector<struct own_warrior *> *> warrior_info;
headquarter(int, vector<int>, string);
headquarter(headquarter &&) = default;
headquarter(const headquarter &) = default;
headquarter &operator=(headquarter &&) = default;
headquarter &operator=(const headquarter &) = default;
~headquarter();
void make_warrior(int);
void judge_make();
private:
};
// 构造函数,初始化生命元和战士信息
headquarter::headquarter(int life, vector<int> my_order, string my_color) {
meta_life = life;
order = my_order;
color = my_color;
warrior_num = 1;
over = false;
warrior_now = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < warrior_name.size(); i++) {
vector<struct own_warrior *> *temp_vector =
new vector<struct own_warrior *>;
warrior_info.insert(make_pair(warrior_name[i], temp_vector));
}
}
headquarter::~headquarter() {}
// 制造战士
void headquarter::make_warrior(int warr_now) {
int life_value = warriors[order[warr_now]]->life_value;
string name = warriors[order[warr_now]]->name;
// 为新战士分配内存空间放入对应的map中
own_warrior *new_warrior = new own_warrior;
new_warrior->number = warrior_num;
new_warrior->life_value = life_value;
new_warrior->attacker = 0;
warrior_info[name]->push_back(new_warrior);
cout << color << " " << warriors[order[warr_now]]->name << " " << warrior_num
<< " born with strength " << warriors[order[warr_now]]->life_value << ","
<< warrior_info[name]->size() << " " << name << " in " << color
<< " headquarter" << endl;
warrior_num++;
warrior_now = (warr_now + 1) % (warriors.size());
// cout << warriors.size() << " " << warrior_now << endl;
meta_life -= life_value;
return;
}
// 判能否制造下一个战士,不能则继续制造下一个,直到都不能则结束.
void headquarter::judge_make() {
if (warriors[order[warrior_now]]->life_value <= meta_life) {
make_warrior(warrior_now);
return;
} else {
for (int i = 1; i < warriors.size(); i++) {
if (warriors[order[(warrior_now + i) % warriors.size()]]->life_value <=
meta_life) {
warrior_now = (warrior_now + i) % warriors.size();
make_warrior(warrior_now);
return;
}
}
over = true;
cout << color << " headquarter stops making warriors" << endl;
return;
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int case_no = 0;
int length = 5;
vector<int> red_order = {2, 3, 4, 1, 0};
vector<int> blue_order = {3, 0, 1, 2, 4};
//处理每组数据
while (cin >> case_no) {
int time = 0;
int case_life = 20;
cin >> case_life;
warriors.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int wa_life = 0;
cin >> wa_life;
struct warrior *new_warrior = new struct warrior;
new_warrior->life_value = wa_life;
new_warrior->name = warrior_name[i];
warriors.insert(make_pair(i, new_warrior));
}
headquarter *red_headquarter = new headquarter(case_life, red_order, "red");
headquarter *blue_headquarter =
new headquarter(case_life, blue_order, "blue");
cout << "Case:" << case_no << endl;
while (!red_headquarter->over || !blue_headquarter->over) {
if (!red_headquarter->over) {
printf("%03d ", time);
red_headquarter->judge_make();
}
if (!blue_headquarter->over) {
printf("%03d ", time);
blue_headquarter->judge_make();
}
time++;
}
}
return 0;
}
运行结果如下
{{< figure src="https://gcore.jsdelivr.net/gh/game-loader/picbase@master/uPic/10290QUmPy.png" >}}
第五次作业
完善字符串类
编写封装完善的MyString类并测试,要求有多个构造函数、完成深拷贝的拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符函数以及一些其他功能函数;练习掌握内联函数的使用。
该题为完善之前的字符串类,需要为之前的字符串类添加深拷贝的拷贝构造函数,即在拷贝字符串的过程中为指针申请新的内存空间。同时还要重载赋值运算符‘=’,在重载运算符的过程中,若想直接修改赋值运算符的左值,则需使用this指针指向调用运算符的对象本身。重载的运算符可以看做对象的成员函数,即object.operator=()。返回对象本身即返回*this,对this指针解引用即可得到对象本身,代码如下
// MyString.h
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class MyString {
private:
char *str;
int length;
public:
MyString();
MyString(char *s);
MyString(const MyString &obj);
MyString &operator=(const MyString &obj);
char *get_string();
void set_string(char *s);
int get_length();
void append(char *s);
void append(const MyString &obj);
~MyString();
};
// MyString.cpp
#include "MyString.h"
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
MyString::MyString() { cout << "MyString类的默认构造函数被调用" << endl; }
MyString::MyString(char *s) {
length = strlen(s);
str = new char[length + 1];
str[length] = '\0';
//安全拷贝
strncpy(str, s, length + 1);
cout << "MyString类的有参构造函数被调用,当前字符串为:" << str << endl;
}
MyString::~MyString() {
cout << "MyString类的析构函数被调用,当前字符串为:" << str << endl;
delete str;
};
MyString::MyString(const MyString &obj) {
set_string(obj.str);
cout << "MyString类的复制构造函数被调用,当前字符串为:";
cout << obj.str << endl;
}
MyString &MyString::operator=(const MyString &obj) {
set_string(obj.str);
cout << "MyString类的赋值运算符被调用,当前字符串为:";
cout << obj.str << endl;
return *this;
}
char *MyString::get_string() { return str; }
void MyString::set_string(char *s) {
length = strlen(s);
str = new char[length + 1];
str[length] = '\0';
//安全拷贝
strncpy(str, s, length + 1);
}
int MyString::get_length() { return length; }
void MyString::append(char *s) {
length = length + strlen(s);
char *str_temp = new char[length + 1];
str_temp[length] = '\0';
strncpy(str_temp, str, length + 1);
strncat(str_temp, s, length + 1);
delete str;
str = str_temp;
}
void MyString::append(const MyString &obj) { this->append(obj.str); }
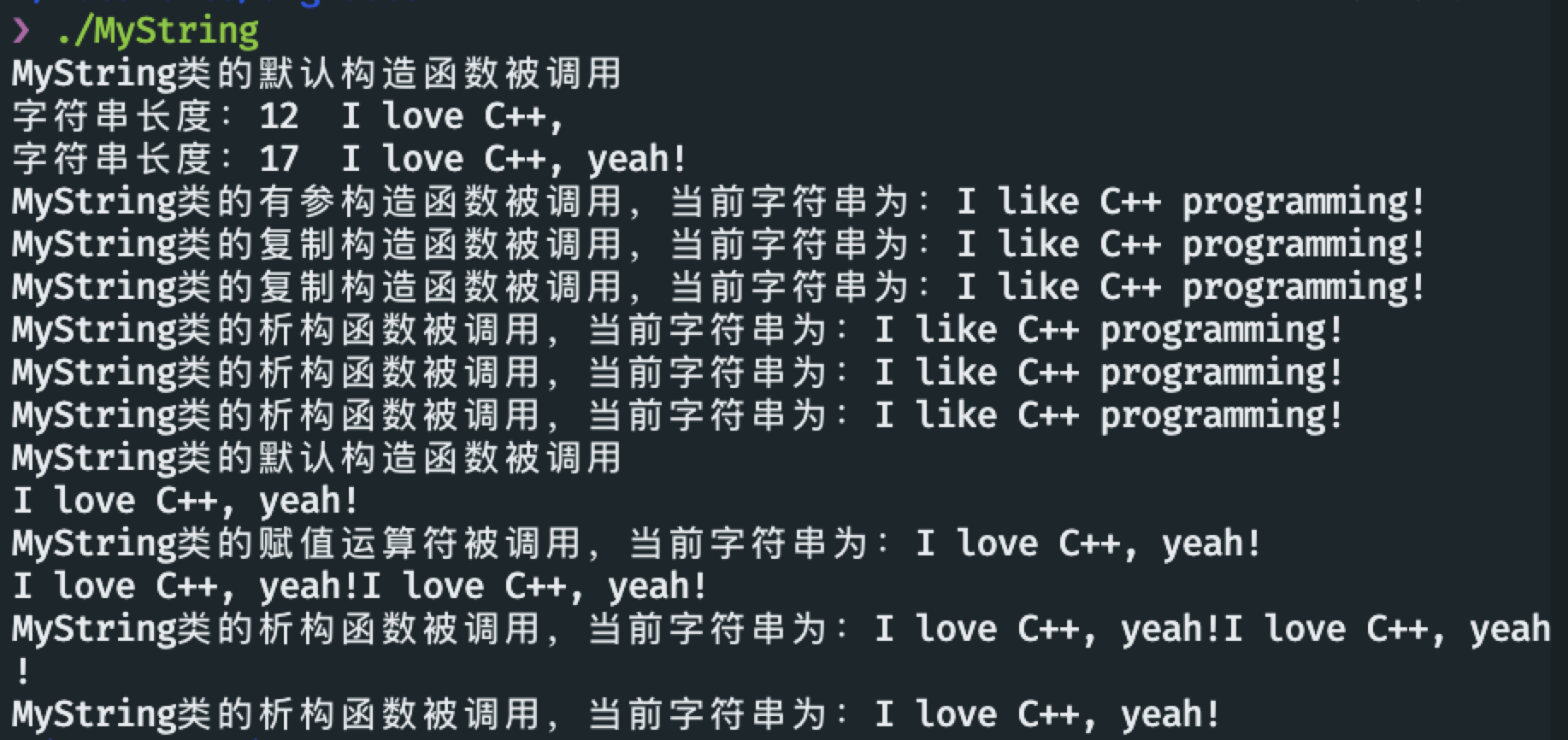
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
MyString str;
str.set_string("I love C++, ");
cout << "字符串长度:" << str.get_length() << "\t" << str.get_string()
<< endl;
str.append("yeah!");
cout << "字符串长度:" << str.get_length() << "\t" << str.get_string()
<< endl;
{
MyString str("I like C++ programming!");
MyString str2(str), str3 = str;
}
MyString str2;
cout << str.get_string() << endl;
str2 = str;
str2.append(str2);
cout << str2.get_string() << endl;
return 0;
}
组合类
设计一个学生类,该类与MyString类构成组合类;重新设计学生列表类。
对于学生(包含姓名、学号、成绩等),请完善封装学生类CStudent(将之前使用的结构体STUDENT封装为该类),其中学生的姓名、专业要使用上题的MyString类的对象存储;完善封装学生列表类CStudentList保存数量不定的学生,并在这个类中实现增加学生、按学号删除、修改学生信息、显示学生信息的功能,显示学生信息的函数要有重载版本;为CStudentList类提供复制构造函数、赋值运算符函数;注意初始化列表的使用。
该题是将字符串类和之前构造的学生类进行组合。这道题的关键在于CStudentList类中的拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符的重载,这两部分的代码如下
// CStudentList的拷贝构造函数
CStudentList(const CStudentList &obj) {
for (auto stu : obj.students) {
CStudent *stu_temp = new CStudent();
stu_temp->sno = stu.second->sno;
// 使用了MyString的拷贝构造函数
stu_temp->name = stu.second->name;
stu_temp->score = stu.second->score;
stu_temp->specialty = stu.second->specialty;
students.insert(make_pair(stu.second->sno, stu_temp));
}
}
// 赋值运算符函数
CStudentList &operator=(const CStudentList &obj) {
for (auto stu : obj.students) {
CStudent *stu_temp = new CStudent();
stu_temp->sno = stu.second->sno;
// 使用了MyString的拷贝构造函数
stu_temp->name = stu.second->name;
stu_temp->score = stu.second->score;
stu_temp->specialty = stu.second->specialty;
students.insert(make_pair(stu.second->sno, stu_temp));
this->students.insert(make_pair(stu.second->sno, stu_temp));
}
return *this;
}
剩余的部分主要在于用MyString类替代之前CStudent的char*,此时我们的MyString类已经可以通过'='进行直接赋值,非常方便,不再需要操作char*时的strcpy等函数。再用CStudentList来操作CStudent即可,这里在修改学生信息时,如果不存在该学生的信息则会报错,不能修改。代码如下
#include "MyString.h"
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
MyString::MyString() { cout << "MyString类的默认构造函数被调用" << endl; }
MyString::MyString(char *s) {
length = strlen(s);
str = new char[length + 1];
str[length] = '\0';
//安全拷贝
strncpy(str, s, length + 1);
cout << "MyString类的有参构造函数被调用,当前字符串为:" << str << endl;
}
MyString::~MyString() {
cout << "MyString类的析构函数被调用,当前字符串为:" << str << endl;
delete str;
};
MyString::MyString(const MyString &obj) {
set_string(obj.str);
cout << "MyString类的复制构造函数被调用,当前字符串为:";
cout << obj.str << endl;
}
MyString &MyString::operator=(const MyString &obj) {
set_string(obj.str);
cout << "MyString类的赋值运算符被调用,当前字符串为:";
cout << obj.str << endl;
return *this;
}
char *MyString::get_string() { return str; }
void MyString::set_string(char *s) {
length = strlen(s);
str = new char[length + 1];
str[length] = '\0';
//安全拷贝
strncpy(str, s, length + 1);
}
int MyString::get_length() { return length; }
void MyString::append(char *s) {
length = length + strlen(s);
char *str_temp = new char[length + 1];
str_temp[length] = '\0';
strncpy(str_temp, str, length + 1);
strncat(str_temp, s, length + 1);
delete str;
str = str_temp;
}
void MyString::append(const MyString &obj) { this->append(obj.str); }
// CStudent类
class CStudent {
public:
int sno;
MyString name;
MyString specialty;
int score;
CStudent();
CStudent(CStudent &&) = default;
CStudent(const CStudent &) = default;
CStudent &operator=(CStudent &&) = default;
CStudent &operator=(const CStudent &) = default;
~CStudent();
private:
};
class CStudentList {
public:
CStudentList(){};
// CStudentList的拷贝构造函数
CStudentList(const CStudentList &obj) {
for (auto stu : obj.students) {
CStudent *stu_temp = new CStudent();
stu_temp->sno = stu.second->sno;
// 使用了MyString的拷贝构造函数
stu_temp->name = stu.second->name;
stu_temp->score = stu.second->score;
stu_temp->specialty = stu.second->specialty;
students.insert(make_pair(stu.second->sno, stu_temp));
}
}
// 赋值运算符函数
CStudentList &operator=(const CStudentList &obj) {
for (auto stu : obj.students) {
CStudent *stu_temp = new CStudent();
stu_temp->sno = stu.second->sno;
// 使用了MyString的拷贝构造函数
stu_temp->name = stu.second->name;
stu_temp->score = stu.second->score;
stu_temp->specialty = stu.second->specialty;
students.insert(make_pair(stu.second->sno, stu_temp));
this->students.insert(make_pair(stu.second->sno, stu_temp));
}
return *this;
}
~CStudentList(){};
map<int, CStudent *> students;
// 有默认形参,使用引用变量
void add_stu(int sno, char *name, char *specialty, int score = 60) {
CStudent *student = new CStudent();
student->sno = sno;
student->score = score;
student->name.set_string(name);
student->specialty.set_string(specialty);
students.insert(make_pair(sno, student));
}
void del_stu(int sno) {
// 释放内存
delete (students.find(sno)->second);
students.erase(sno);
cout << "Delete success!";
}
// 默认全部显示
void look_up_stu() {
for (auto stu : students) {
cout << "Sno = " << stu.second->sno
<< " Name = " << stu.second->name.get_string()
<< " Specialty = " << stu.second->specialty.get_string()
<< " Score = " << stu.second->score << endl;
}
}
// 重载的显示函数
void look_up_stu(int flag, int min = 0, int max = 100) {
for (auto stu : students) {
if ((stu.second->score) >= min && stu.second->score <= max) {
cout << "Sno = " << stu.second->sno
<< " Name = " << stu.second->name.get_string()
<< " Specialty = " << stu.second->specialty.get_string()
<< " Score = " << stu.second->score << endl;
}
}
}
// 根据学号修改学生信息
void change_stu(int sno, char *name, char *specialty, int score = 60) {
int keycount = students.count(sno);
if (keycount != 1) {
cout << "Don't have this student, please add it to system!!" << endl;
return;
} else {
students.find(sno)->second->sno = sno;
students.find(sno)->second->name.set_string(name);
students.find(sno)->second->specialty.set_string(specialty);
students.find(sno)->second->score = score;
cout << "Update success!" << endl;
return;
}
}
};
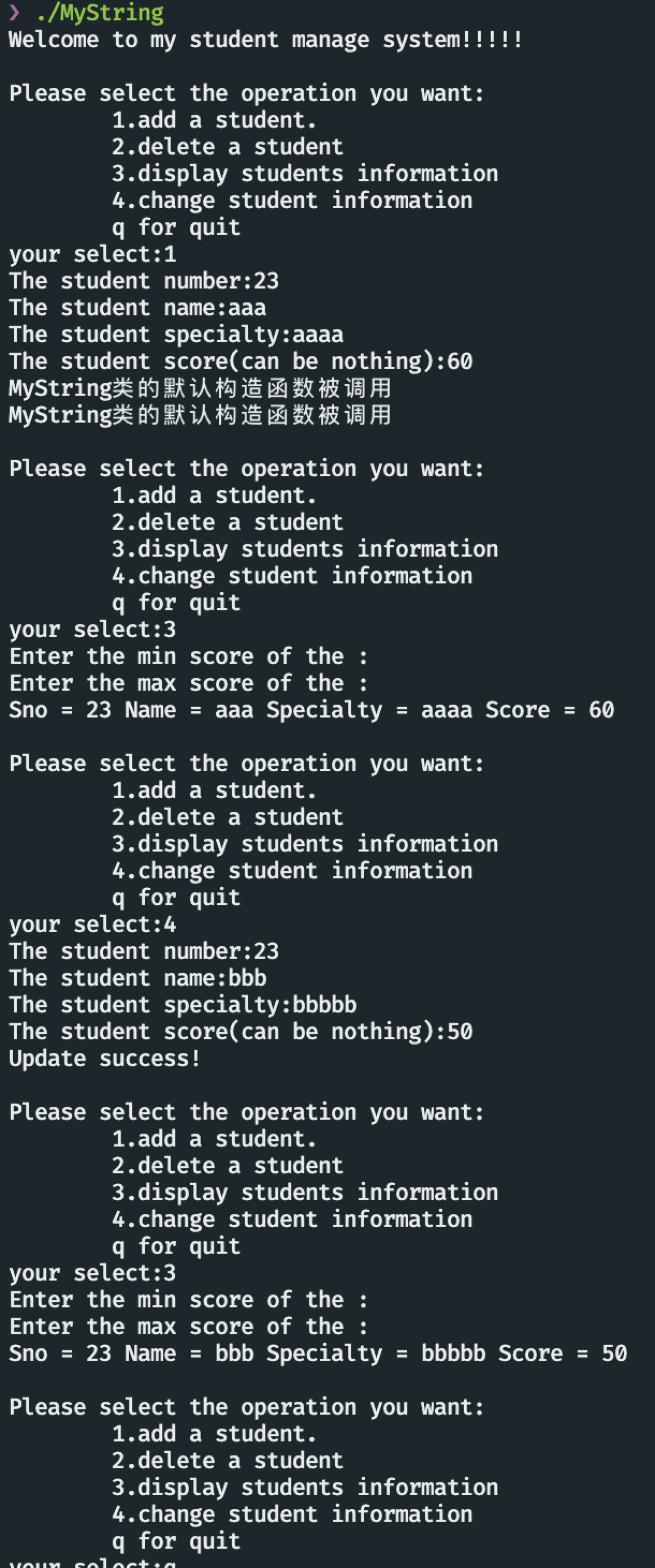
int main() {
char select;
cout << "Welcome to my student manage system!!!!!" << endl;
CStudentList *stu_info = new CStudentList();
while (true) {
cout << "\nPlease select the operation you want:" << endl
<< "\t1.add a student.\n"
<< "\t2.delete a student\n"
<< "\t3.display students information\n"
<< "\t4.change student information\n"
<< "\tq for quit\n"
<< "your select:";
cin >> select;
switch (select) {
case '1': {
int number, average;
string aver;
string name, specialty;
cout << "The student number:";
cin >> number;
cout << "The student name:";
cin >> name;
cout << "The student specialty:";
cin >> specialty;
cin.get();
cout << "The student score(can be nothing):";
getline(cin, aver);
if (aver.length() == 0) {
stu_info->add_stu(number, (char *)name.data(),
(char *)specialty.data());
} else {
average = stoi(aver);
stu_info->add_stu(number, (char *)name.data(), (char *)specialty.data(),
average);
}
break;
}
case '2': {
int number;
cout << "The student number:";
cin >> number;
stu_info->del_stu(number);
break;
}
case '3': {
string min, max;
cout << "Enter the min score of the :";
cin.get();
getline(cin, min);
cout << "Enter the max score of the :";
getline(cin, max);
if (min.length() == 0 && max.length() == 0) {
stu_info->look_up_stu();
break;
} else if (max.length() == 0) {
stu_info->look_up_stu(1, stoi(min));
} else if (min.length() == 0) {
stu_info->look_up_stu(1, 0, stoi(max));
} else {
stu_info->look_up_stu(1, stoi(min), stoi(max));
}
break;
}
case '4': {
int number, average;
string aver;
string name, specialty;
cout << "The student number:";
cin >> number;
cout << "The student name:";
cin >> name;
cout << "The student specialty:";
cin >> specialty;
cin.get();
cout << "The student score(can be nothing):";
getline(cin, aver);
if (aver.length() == 0) {
stu_info->change_stu(number, (char *)name.data(),
(char *)specialty.data());
} else {
average = stoi(aver);
stu_info->change_stu(number, (char *)name.data(),
(char *)specialty.data(), average);
}
break;
}
case 'q': {
return 0;
}
default:
break;
}
}
}
运行的效果为
第六次作业
为MyString类提供重载的运算符
完善之前的MyString类,为其编写赋值运算符函数实现直接使用字符串为其赋值的功能、编写加法(+)运算符函数实现两个对象的相加和一个对象加一个字符串的功能、编写下标运算符函数实现取指定索引的字符的功能、编写函数调用运算符实现使用字符串赋值的功能。编写上述函数后,下面的程序可完成所述功能。
MyString s1("hello "), s2("world!");
const MyString s3 = s1 + s2; //对象s3内容为"hello world!",对象s1和s2不变
s1 = s1 + "world!"; //对象s1的内容为"hello world!"
cout << s1[0] << s3[1] << endl;//输出为"he"
s1("I love C++, yeah!"); //对象s1内容为"I love C++, yeah!"
该实验主要考验对更复杂的运算符的重载,按照各个运算符的重载规则重写对应的重载函数即可,这里一个比较有趣的问题在于,像s3 = s1 + s2这样的语句实际上的执行过程是先调用重载的加法运算符运算得到一个MyString对象,然后再根据MyString重载过的赋值运算符,将得到的MyString对象赋给s3。最后得到s3对象。在这个过程中实际上还使用了重载过的赋值运算符。全部代码如下
// MyString.h
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class MyString {
private:
char *str;
int length;
public:
MyString();
MyString(char *s);
MyString(const MyString &obj);
MyString &operator=(const MyString &obj);
MyString &operator=(const char *s);
MyString operator+(const MyString &obj);
MyString operator+(const char *s);
MyString &operator+(const char c);
char operator[](int i);
MyString &operator()(const char *s);
MyString &operator<=(const MyString &obj);
char *get_string();
void set_string(char *s);
int get_length();
void append(char *s);
void append(const MyString &obj);
~MyString();
};
// MyString.cpp
#include "MyString.h"
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
MyString::MyString() { cout << "MyString类的默认构造函数被调用" << endl; }
MyString::MyString(char *s) {
length = strlen(s);
str = new char[length + 1];
str[length] = '\0';
//安全拷贝
strncpy(str, s, length + 1);
// cout << "MyString类的有参构造函数被调用,当前字符串为:" << str << endl;
}
MyString::~MyString() {
// cout << "MyString类的析构函数被调用,当前字符串为:" << str << endl;
delete str;
};
MyString::MyString(const MyString &obj) {
set_string(obj.str);
// cout << "MyString类的复制构造函数被调用,当前字符串为:";
// cout << obj.str << endl;
}
MyString &MyString::operator=(const MyString &obj) {
set_string(obj.str);
// cout << "MyString类的赋值运算符被调用,当前字符串为:";
// cout << obj.str << endl;
return *this;
}
// 使用字符串赋值
MyString &MyString::operator=(const char *s) {
set_string((char *)s);
return *this;
}
// 实现两个对象相加
MyString MyString::operator+(const MyString &obj) {
MyString temp(str);
temp.append(obj.str);
return temp;
}
// 实现对象和字符串相加
MyString MyString::operator+(const char *s) {
MyString temp(str);
temp.append((char *)s);
return temp;
}
// 实现下标运算符
char MyString::operator[](int i) {
if (i >= length) {
cout << "超过最大索引" << endl;
return *str;
} else {
return *(str + i);
}
}
// 重载函数调用运算符
MyString &MyString::operator()(const char *s) {
set_string((char *)s);
return *this;
}
char *MyString::get_string() { return str; }
void MyString::set_string(char *s) {
length = strlen(s);
str = new char[length + 1];
str[length] = '\0';
//安全拷贝
strncpy(str, s, length + 1);
}
int MyString::get_length() { return length; }
void MyString::append(char *s) {
length = length + strlen(s);
char *str_temp = new char[length + 1];
str_temp[length] = '\0';
strncpy(str_temp, str, length + 1);
strncat(str_temp, s, length + 1);
delete str;
str = str_temp;
}
void MyString::append(const MyString &obj) { this->append(obj.str); }
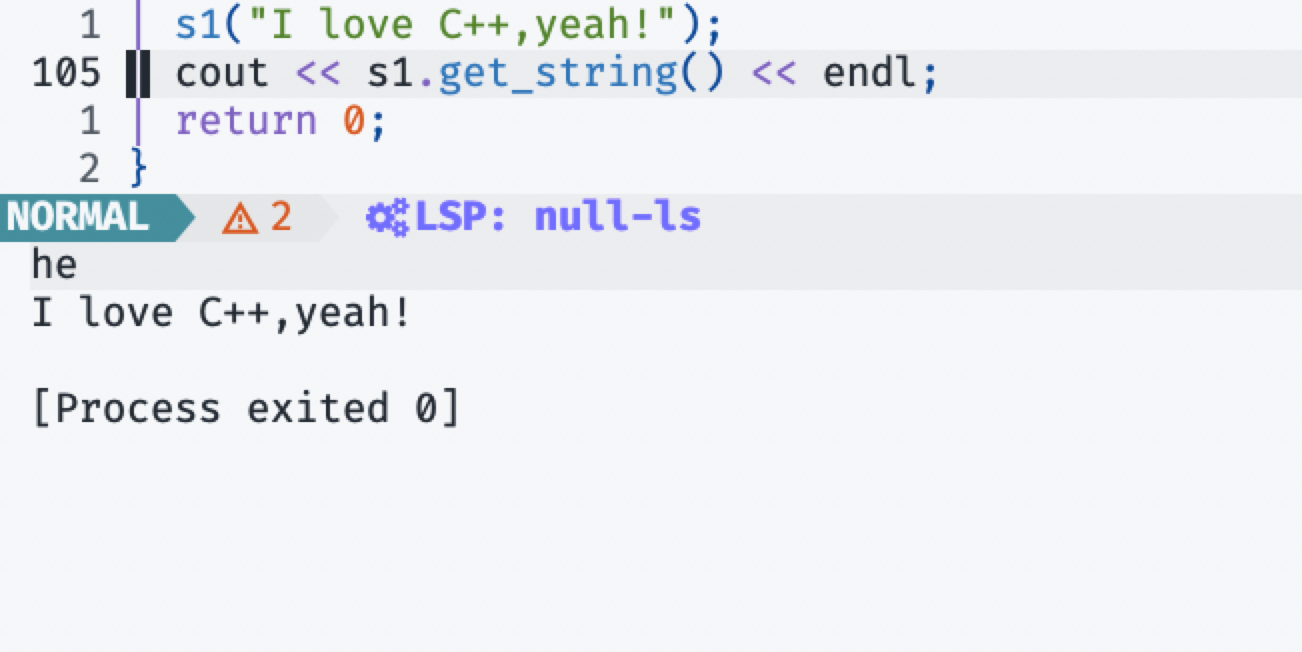
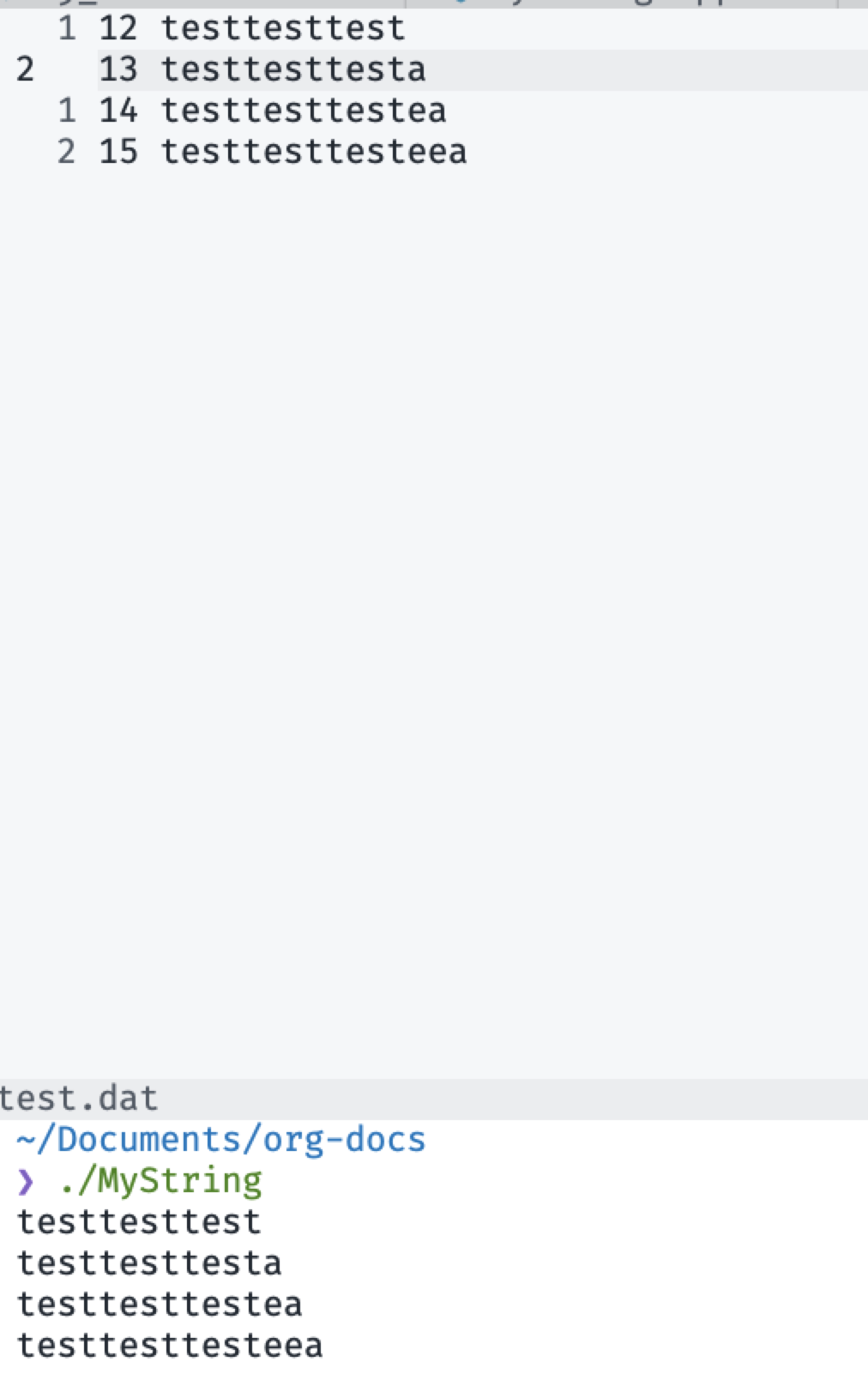
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
MyString s1("hello"), s2("world!");
MyString s3 = s1 + s2;
s1 = s1 + "world";
cout << s1[0] << s3[1] << endl;
s1("I love C++,yeah!");
cout << s1.get_string() << endl;
return 0;
}
为CStudentList类提供重载的运算符
完善之前的CStudentList类,为其编写加法运算符函数实现两个对象的相加(即两个对象中的学生合并构成一个新的CStudentList类的对象)、编写下标运算符函数实现取指定索引的学生的功能。 本实验需要完善之前编写的CStudentList类,重写加法运算符和下标运算符即可,这里注意的是map标准类的复制和访问都可以通过迭代器来完成。完善部分的代码如下
// students数据
map<int, CStudent *> students;
// CStudentList重载加法运算符
CStudentList operator+(const CStudentList &obj) {
CStudentList newstudent;
newstudent.students = students;
newstudent.students.insert(obj.students.begin(), obj.students.end());
return newstudent;
}
// 重载下标运算符
CStudent *operator[](int i) {
if (i >= students.size()) {
cout << "超过最大索引" << endl;
return students.begin()->second;
}
map<int, CStudent *>::iterator iter = students.begin();
for (int j = 0; j != i; j++) {
iter++;
}
return iter->second;
}
通过MyString类练习使用文件I/O
在之前的MyString类的基础上设计输入符和输出符的重载函数,并通过文本文件进行测试:要求将数量不定的MyString类的对象的内容保存在一个文件中,然后从该文件中读取数据恢复这些对象。同时练习使用文本文件和二进制文件完成以上功能。
提示:输出MyString类对象的值时首先应输出其保存的字符串的长度,然后输出字符串。否则,在读取字符串恢复对象时,会因为不知道应该读取多少个字节而无法恢复对象。 本题只需要重载输入输出符的函数即可,每次输入输出只需读取一行数据,可在main中使用循环完成对整个文件的读取,这里注意重载的输入输出符对应的输入输出流为系统流,和输入输出的具体文件无关,从根本上说,对控制台的输入输出也是文件输入输出的一种。所以只需对系统中的istream或者ostream进行读取或写入即可。完善部分的代码如下
// 重载输入输出运算符
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, MyString &obj) {
os << obj.length << " " << obj.str;
return os;
}
istream &operator>>(istream &os, MyString &obj) {
os >> obj.length;
char *data = new char[obj.length + 1];
os >> data;
obj.set_string(data);
delete[] data;
return os;
}
全部代码如下
#include "MyString.h"
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
MyString::MyString() { cout << "MyString类的默认构造函数被调用" << endl; }
MyString::MyString(char *s) {
length = strlen(s);
str = new char[length + 1];
str[length] = '\0';
//安全拷贝
strncpy(str, s, length + 1);
// cout << "MyString类的有参构造函数被调用,当前字符串为:" << str << endl;
}
MyString::~MyString() {
// cout << "MyString类的析构函数被调用,当前字符串为:" << str << endl;
delete str;
};
MyString::MyString(const MyString &obj) {
set_string(obj.str);
// cout << "MyString类的复制构造函数被调用,当前字符串为:";
// cout << obj.str << endl;
}
MyString &MyString::operator=(const MyString &obj) {
set_string(obj.str);
// cout << "MyString类的赋值运算符被调用,当前字符串为:";
// cout << obj.str << endl;
return *this;
}
// 使用字符串赋值
MyString &MyString::operator=(const char *s) {
set_string((char *)s);
return *this;
}
// 实现两个对象相加
MyString MyString::operator+(const MyString &obj) {
MyString temp(str);
temp.append(obj.str);
return temp;
}
// 实现对象和字符串相加
MyString MyString::operator+(const char *s) {
MyString temp(str);
temp.append((char *)s);
return temp;
}
// 实现下标运算符
char MyString::operator[](int i) {
if (i >= length) {
cout << "超过最大索引" << endl;
return *str;
} else {
return *(str + i);
}
}
// 重载函数调用运算符
MyString &MyString::operator()(const char *s) {
set_string((char *)s);
return *this;
}
// 重载输入输出运算符
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, MyString &obj) {
os << obj.length << " " << obj.str;
return os;
}
istream &operator>>(istream &os, MyString &obj) {
os >> obj.length;
char *data = new char[obj.length + 1];
os >> data;
obj.set_string(data);
delete[] data;
return os;
}
char *MyString::get_string() { return str; }
void MyString::set_string(char *s) {
length = strlen(s);
str = new char[length + 1];
str[length] = '\0';
//安全拷贝
strncpy(str, s, length + 1);
}
int MyString::get_length() { return length; }
void MyString::append(char *s) {
length = length + strlen(s);
char *str_temp = new char[length + 1];
str_temp[length] = '\0';
strncpy(str_temp, str, length + 1);
strncat(str_temp, s, length + 1);
delete str;
str = str_temp;
}
void MyString::append(const MyString &obj) { this->append(obj.str); }
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
MyString s2;
ifstream infile;
infile.open("test.dat");
while (!infile.eof()) {
infile >> s2;
cout << s2.get_string() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
// MyString.h
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class MyString {
private:
char *str;
int length;
public:
MyString();
MyString(char *s);
MyString(const MyString &obj);
MyString &operator=(const MyString &obj);
MyString &operator=(const char *s);
MyString operator+(const MyString &obj);
MyString operator+(const char *s);
MyString &operator+(const char c);
char operator[](int i);
MyString &operator()(const char *s);
MyString &operator<=(const MyString &obj);
// 输出运算符函数
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, MyString &obj);
// 输入运算符函数
friend istream &operator>>(istream &os, MyString &obj);
char *get_string();
void set_string(char *s);
int get_length();
void append(char *s);
void append(const MyString &obj);
~MyString();
};
通过学生列表类练习使用文件I/O
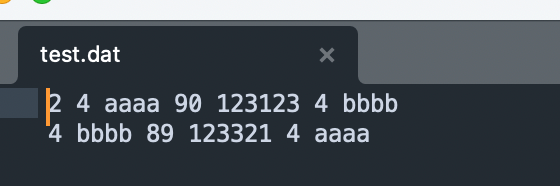
在之前的CStudentList类和CStudent类的基础上,为它们编写文本文件和二进制文件的输入输出功能并测试。请注意,在输入输出CStudent类的MyString类的数据成员时需要通过MyString类的输入输出函数实现;在输入输出CStudentList中的CStudent类的对象时需要通过CStudent类的输入输出函数实现。 这里封装的思想和MyString类类似,在文件头指明学生的数量。要说明的是在对输入输出符进行重载时需要声明其为对应类的友元函数,因为重载的是iostream类下的输入输出运算符,要使其能访问其他类中的成员则需将其声明为该类的友元函数。在使用时用该类的引用作为参数即可直接向文件中输入输出对应的对象的内容。 测试结果如下,测试输出到test.dat文件中如下
关键代码为
// 重载输出输入函数
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, CStudentList &stulist) {
os << stulist.students.size() << " ";
for (auto stu : stulist.students) {
os << *stu.second;
}
return os;
}
friend istream &operator>>(istream &os, CStudentList &stulist) {
int size;
os >> size;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
CStudent *newstudent = new CStudent;
os >> *newstudent;
stulist.students.insert(make_pair(newstudent->sno, newstudent));
}
return os;
}
全部代码如下
#include "MyString.cpp"
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <map>
#include <ostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// CStudent类
class CStudent {
public:
int sno;
MyString name;
MyString specialty;
int score;
CStudent(){};
~CStudent(){};
// Cstudent类输入输出重载
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, CStudent &stu) {
os << stu.name << " " << stu.score << " " << stu.sno << " " << stu.specialty
<< endl;
return os;
}
friend istream &operator>>(istream &os, CStudent &stu) {
os >> stu.name >> stu.score >> stu.sno >> stu.specialty;
return os;
}
private:
};
class CStudentList {
public:
CStudentList(){};
// CStudentList的拷贝构造函数
CStudentList(const CStudentList &obj) {
for (auto stu : obj.students) {
CStudent *stu_temp = new CStudent();
stu_temp->sno = stu.second->sno;
// 使用了MyString的拷贝构造函数
stu_temp->name = stu.second->name;
stu_temp->score = stu.second->score;
stu_temp->specialty = stu.second->specialty;
students.insert(make_pair(stu.second->sno, stu_temp));
}
}
// 赋值运算符函数
CStudentList &operator=(const CStudentList &obj) {
for (auto stu : obj.students) {
CStudent *stu_temp = new CStudent();
stu_temp->sno = stu.second->sno;
// 使用了MyString的拷贝构造函数
stu_temp->name = stu.second->name;
stu_temp->score = stu.second->score;
stu_temp->specialty = stu.second->specialty;
students.insert(make_pair(stu.second->sno, stu_temp));
this->students.insert(make_pair(stu.second->sno, stu_temp));
}
return *this;
}
~CStudentList() {
for (auto stu : students) {
delete &stu.second->name;
delete &stu.second->specialty;
}
};
// students数据
map<int, CStudent *> students;
// CStudentList重载加法运算符
CStudentList operator+(const CStudentList &obj) {
CStudentList newstudent;
newstudent.students = students;
newstudent.students.insert(obj.students.begin(), obj.students.end());
return newstudent;
}
// 重载下标运算符
CStudent *operator[](int i) {
if (i >= students.size()) {
cout << "超过最大索引" << endl;
return students.begin()->second;
}
map<int, CStudent *>::iterator iter = students.begin();
for (int j = 0; j != i; j++) {
iter++;
}
return iter->second;
}
// 重载输出输入函数
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, CStudentList &stulist) {
os << stulist.students.size() << " ";
for (auto stu : stulist.students) {
os << *stu.second;
}
return os;
}
friend istream &operator>>(istream &os, CStudentList &stulist) {
int size;
os >> size;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
CStudent *newstudent = new CStudent;
os >> *newstudent;
stulist.students.insert(make_pair(newstudent->sno, newstudent));
}
return os;
}
// 有默认形参,使用引用变量
void add_stu(int sno, char *name, char *specialty, int score = 60) {
CStudent *student = new CStudent();
student->sno = sno;
student->score = score;
student->name.set_string(name);
student->specialty.set_string(specialty);
students.insert(make_pair(sno, student));
}
void del_stu(int sno) {
// 释放内存
delete (students.find(sno)->second);
students.erase(sno);
cout << "Delete success!";
}
// 默认全部显示
void look_up_stu() {
for (auto stu : students) {
cout << "Sno = " << stu.second->sno
<< " Name = " << stu.second->name.get_string()
<< " Specialty = " << stu.second->specialty.get_string()
<< " Score = " << stu.second->score << endl;
}
}
// 重载的显示函数
void look_up_stu(int flag, int min = 0, int max = 100) {
for (auto stu : students) {
if ((stu.second->score) >= min && stu.second->score <= max) {
cout << "Sno = " << stu.second->sno
<< " Name = " << stu.second->name.get_string()
<< " Specialty = " << stu.second->specialty.get_string()
<< " Score = " << stu.second->score << endl;
}
}
}
// 根据学号修改学生信息
void change_stu(int sno, char *name, char *specialty, int score = 60) {
int keycount = students.count(sno);
if (keycount != 1) {
cout << "Don't have this student, please add it to system!!" << endl;
return;
} else {
students.find(sno)->second->sno = sno;
students.find(sno)->second->name.set_string(name);
students.find(sno)->second->specialty.set_string(specialty);
students.find(sno)->second->score = score;
cout << "Update success!" << endl;
return;
}
}
};
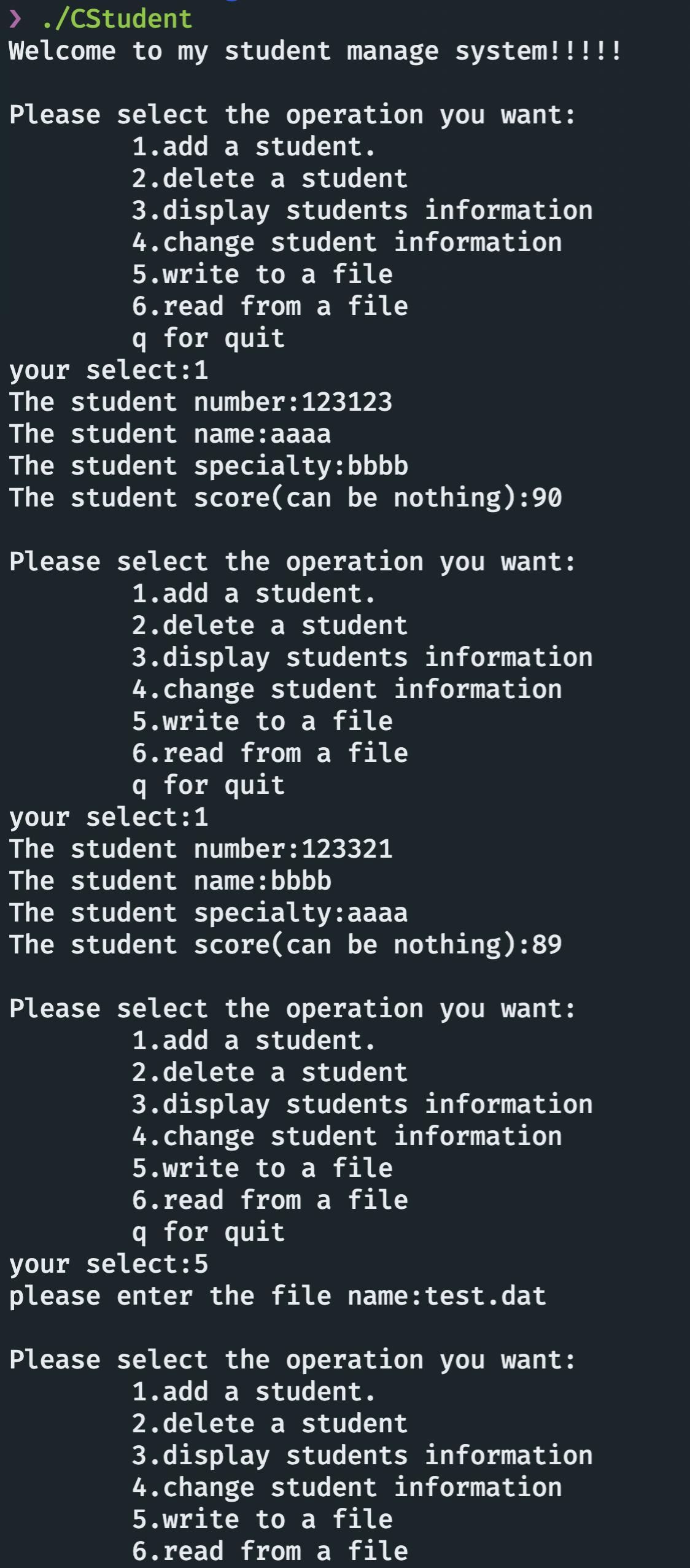
int main() {
char select;
cout << "Welcome to my student manage system!!!!!" << endl;
CStudentList *stu_info = new CStudentList();
while (true) {
cout << "\nPlease select the operation you want:" << endl
<< "\t1.add a student.\n"
<< "\t2.delete a student\n"
<< "\t3.display students information\n"
<< "\t4.change student information\n"
<< "\t5.write to a file\n"
<< "\t6.read from a file\n"
<< "\tq for quit\n"
<< "your select:";
cin >> select;
switch (select) {
case '1': {
int number, average;
string aver;
string name, specialty;
cout << "The student number:";
cin >> number;
cout << "The student name:";
cin >> name;
cout << "The student specialty:";
cin >> specialty;
cin.get();
cout << "The student score(can be nothing):";
getline(cin, aver);
if (aver.length() == 0) {
stu_info->add_stu(number, (char *)name.data(),
(char *)specialty.data());
} else {
average = stoi(aver);
stu_info->add_stu(number, (char *)name.data(), (char *)specialty.data(),
average);
}
break;
}
case '2': {
int number;
cout << "The student number:";
cin >> number;
stu_info->del_stu(number);
break;
}
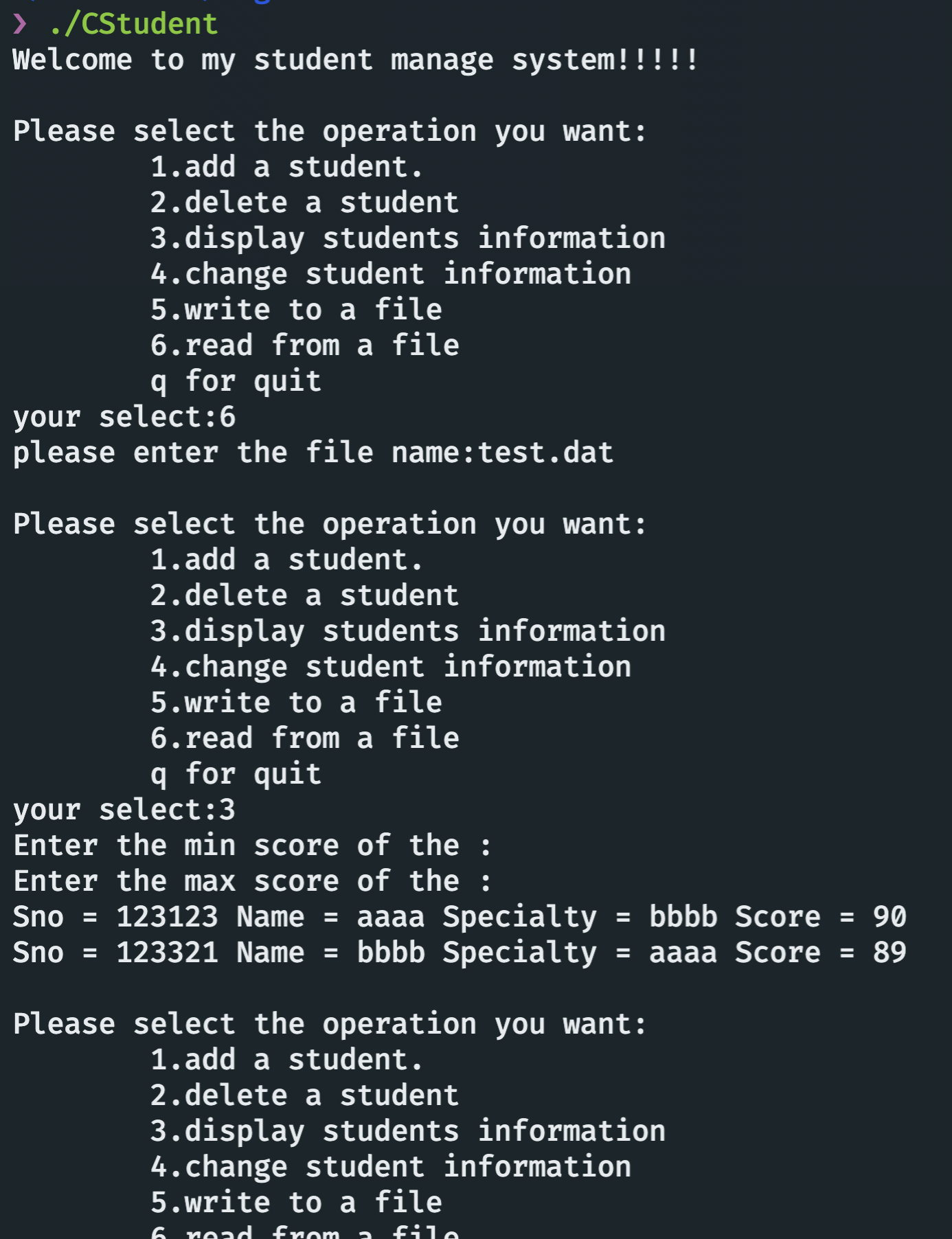
case '3': {
string min, max;
cout << "Enter the min score of the :";
cin.get();
getline(cin, min);
cout << "Enter the max score of the :";
getline(cin, max);
if (min.length() == 0 && max.length() == 0) {
stu_info->look_up_stu();
break;
} else if (max.length() == 0) {
stu_info->look_up_stu(1, stoi(min));
} else if (min.length() == 0) {
stu_info->look_up_stu(1, 0, stoi(max));
} else {
stu_info->look_up_stu(1, stoi(min), stoi(max));
}
break;
}
case '4': {
int number, average;
string aver;
string name, specialty;
cout << "The student number:";
cin >> number;
cout << "The student name:";
cin >> name;
cout << "The student specialty:";
cin >> specialty;
cin.get();
cout << "The student score(can be nothing):";
getline(cin, aver);
if (aver.length() == 0) {
stu_info->change_stu(number, (char *)name.data(),
(char *)specialty.data());
} else {
average = stoi(aver);
stu_info->change_stu(number, (char *)name.data(),
(char *)specialty.data(), average);
}
break;
}
case '5': {
cout << "please enter the file name:";
string filename;
cin >> filename;
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open(filename);
outfile << *stu_info;
outfile.close();
break;
}
case '6': {
ifstream infile;
cout << "please enter the file name:";
string filename;
cin >> filename;
infile.open(filename);
infile >> *stu_info;
infile.close();
break;
}
case 'q': {
return 0;
}
default:
break;
}
}
}
大整数运算
封装一个大整数类HugeInt,以支持任意大整数的四则运算,重载你认为需要的所有运算符,比如=,==,>等等运算符。
测试类是否正确:如计算 n=100! + 50!
通过字符串运算及位运算可重载各种运算符,代码如下
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/*
######################################################################
####################### THE BIG INT ##########################
*/
const int base = 1000000000;
const int base_digits = 9;
struct bigint {
vector<int> a;
int sign;
/*<arpa>*/
int size() {
if (a.empty())
return 0;
int ans = (a.size() - 1) * base_digits;
int ca = a.back();
while (ca)
ans++, ca /= 10;
return ans;
}
bigint operator^(const bigint &v) {
bigint ans = 1, a = *this, b = v;
while (!b.isZero()) {
if (b % 2)
ans *= a;
a *= a, b /= 2;
}
return ans;
}
string to_string() {
stringstream ss;
ss << *this;
string s;
ss >> s;
return s;
}
int sumof() {
string s = to_string();
int ans = 0;
for (auto c : s)
ans += c - '0';
return ans;
}
/*</arpa>*/
bigint() : sign(1) {}
bigint(long long v) { *this = v; }
bigint(const string &s) { read(s); }
void operator=(const bigint &v) {
sign = v.sign;
a = v.a;
}
void operator=(long long v) {
sign = 1;
a.clear();
if (v < 0)
sign = -1, v = -v;
for (; v > 0; v = v / base)
a.push_back(v % base);
}
bigint operator+(const bigint &v) const {
if (sign == v.sign) {
bigint res = v;
for (int i = 0, carry = 0; i < (int)max(a.size(), v.a.size()) || carry;
++i) {
if (i == (int)res.a.size())
res.a.push_back(0);
res.a[i] += carry + (i < (int)a.size() ? a[i] : 0);
carry = res.a[i] >= base;
if (carry)
res.a[i] -= base;
}
return res;
}
return *this - (-v);
}
bigint operator-(const bigint &v) const {
if (sign == v.sign) {
if (abs() >= v.abs()) {
bigint res = *this;
for (int i = 0, carry = 0; i < (int)v.a.size() || carry; ++i) {
res.a[i] -= carry + (i < (int)v.a.size() ? v.a[i] : 0);
carry = res.a[i] < 0;
if (carry)
res.a[i] += base;
}
res.trim();
return res;
}
return -(v - *this);
}
return *this + (-v);
}
void operator*=(int v) {
if (v < 0)
sign = -sign, v = -v;
for (int i = 0, carry = 0; i < (int)a.size() || carry; ++i) {
if (i == (int)a.size())
a.push_back(0);
long long cur = a[i] * (long long)v + carry;
carry = (int)(cur / base);
a[i] = (int)(cur % base);
// asm("divl %%ecx" : "=a"(carry), "=d"(a[i]) : "A"(cur), "c"(base));
}
trim();
}
bigint operator*(int v) const {
bigint res = *this;
res *= v;
return res;
}
void operator*=(long long v) {
if (v < 0)
sign = -sign, v = -v;
for (int i = 0, carry = 0; i < (int)a.size() || carry; ++i) {
if (i == (int)a.size())
a.push_back(0);
long long cur = a[i] * (long long)v + carry;
carry = (int)(cur / base);
a[i] = (int)(cur % base);
// asm("divl %%ecx" : "=a"(carry), "=d"(a[i]) : "A"(cur), "c"(base));
}
trim();
}
bigint operator*(long long v) const {
bigint res = *this;
res *= v;
return res;
}
friend pair<bigint, bigint> divmod(const bigint &a1, const bigint &b1) {
int norm = base / (b1.a.back() + 1);
bigint a = a1.abs() * norm;
bigint b = b1.abs() * norm;
bigint q, r;
q.a.resize(a.a.size());
for (int i = a.a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
r *= base;
r += a.a[i];
int s1 = r.a.size() <= b.a.size() ? 0 : r.a[b.a.size()];
int s2 = r.a.size() <= b.a.size() - 1 ? 0 : r.a[b.a.size() - 1];
int d = ((long long)base * s1 + s2) / b.a.back();
r -= b * d;
while (r < 0)
r += b, --d;
q.a[i] = d;
}
q.sign = a1.sign * b1.sign;
r.sign = a1.sign;
q.trim();
r.trim();
return make_pair(q, r / norm);
}
bigint operator/(const bigint &v) const { return divmod(*this, v).first; }
bigint operator%(const bigint &v) const { return divmod(*this, v).second; }
void operator/=(int v) {
if (v < 0)
sign = -sign, v = -v;
for (int i = (int)a.size() - 1, rem = 0; i >= 0; --i) {
long long cur = a[i] + rem * (long long)base;
a[i] = (int)(cur / v);
rem = (int)(cur % v);
}
trim();
}
bigint operator/(int v) const {
bigint res = *this;
res /= v;
return res;
}
int operator%(int v) const {
if (v < 0)
v = -v;
int m = 0;
for (int i = a.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i)
m = (a[i] + m * (long long)base) % v;
return m * sign;
}
void operator+=(const bigint &v) { *this = *this + v; }
void operator-=(const bigint &v) { *this = *this - v; }
void operator*=(const bigint &v) { *this = *this * v; }
void operator/=(const bigint &v) { *this = *this / v; }
bool operator<(const bigint &v) const {
if (sign != v.sign)
return sign < v.sign;
if (a.size() != v.a.size())
return a.size() * sign < v.a.size() * v.sign;
for (int i = a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
if (a[i] != v.a[i])
return a[i] * sign < v.a[i] * sign;
return false;
}
bool operator>(const bigint &v) const { return v < *this; }
bool operator<=(const bigint &v) const { return !(v < *this); }
bool operator>=(const bigint &v) const { return !(*this < v); }
bool operator==(const bigint &v) const {
return !(*this < v) && !(v < *this);
}
bool operator!=(const bigint &v) const { return *this < v || v < *this; }
void trim() {
while (!a.empty() && !a.back())
a.pop_back();
if (a.empty())
sign = 1;
}
bool isZero() const { return a.empty() || (a.size() == 1 && !a[0]); }
bigint operator-() const {
bigint res = *this;
res.sign = -sign;
return res;
}
bigint abs() const {
bigint res = *this;
res.sign *= res.sign;
return res;
}
long long longValue() const {
long long res = 0;
for (int i = a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
res = res * base + a[i];
return res * sign;
}
friend bigint gcd(const bigint &a, const bigint &b) {
return b.isZero() ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
friend bigint lcm(const bigint &a, const bigint &b) {
return a / gcd(a, b) * b;
}
void read(const string &s) {
sign = 1;
a.clear();
int pos = 0;
while (pos < (int)s.size() && (s[pos] == '-' || s[pos] == '+')) {
if (s[pos] == '-')
sign = -sign;
++pos;
}
for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= pos; i -= base_digits) {
int x = 0;
for (int j = max(pos, i - base_digits + 1); j <= i; j++)
x = x * 10 + s[j] - '0';
a.push_back(x);
}
trim();
}
friend istream &operator>>(istream &stream, bigint &v) {
string s;
stream >> s;
v.read(s);
return stream;
}
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &stream, const bigint &v) {
if (v.sign == -1)
stream << '-';
stream << (v.a.empty() ? 0 : v.a.back());
for (int i = (int)v.a.size() - 2; i >= 0; --i)
stream << setw(base_digits) << setfill('0') << v.a[i];
return stream;
}
static vector<int> convert_base(const vector<int> &a, int old_digits,
int new_digits) {
vector<long long> p(max(old_digits, new_digits) + 1);
p[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < (int)p.size(); i++)
p[i] = p[i - 1] * 10;
vector<int> res;
long long cur = 0;
int cur_digits = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)a.size(); i++) {
cur += a[i] * p[cur_digits];
cur_digits += old_digits;
while (cur_digits >= new_digits) {
res.push_back(int(cur % p[new_digits]));
cur /= p[new_digits];
cur_digits -= new_digits;
}
}
res.push_back((int)cur);
while (!res.empty() && !res.back())
res.pop_back();
return res;
}
typedef vector<long long> vll;
static vll karatsubaMultiply(const vll &a, const vll &b) {
int n = a.size();
vll res(n + n);
if (n <= 32) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
res[i + j] += a[i] * b[j];
return res;
}
int k = n >> 1;
vll a1(a.begin(), a.begin() + k);
vll a2(a.begin() + k, a.end());
vll b1(b.begin(), b.begin() + k);
vll b2(b.begin() + k, b.end());
vll a1b1 = karatsubaMultiply(a1, b1);
vll a2b2 = karatsubaMultiply(a2, b2);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
a2[i] += a1[i];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
b2[i] += b1[i];
vll r = karatsubaMultiply(a2, b2);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)a1b1.size(); i++)
r[i] -= a1b1[i];
for (int i = 0; i < (int)a2b2.size(); i++)
r[i] -= a2b2[i];
for (int i = 0; i < (int)r.size(); i++)
res[i + k] += r[i];
for (int i = 0; i < (int)a1b1.size(); i++)
res[i] += a1b1[i];
for (int i = 0; i < (int)a2b2.size(); i++)
res[i + n] += a2b2[i];
return res;
}
bigint operator*(const bigint &v) const {
vector<int> a6 = convert_base(this->a, base_digits, 6);
vector<int> b6 = convert_base(v.a, base_digits, 6);
vll a(a6.begin(), a6.end());
vll b(b6.begin(), b6.end());
while (a.size() < b.size())
a.push_back(0);
while (b.size() < a.size())
b.push_back(0);
while (a.size() & (a.size() - 1))
a.push_back(0), b.push_back(0);
vll c = karatsubaMultiply(a, b);
bigint res;
res.sign = sign * v.sign;
for (int i = 0, carry = 0; i < (int)c.size(); i++) {
long long cur = c[i] + carry;
res.a.push_back((int)(cur % 1000000));
carry = (int)(cur / 1000000);
}
res.a = convert_base(res.a, 6, base_digits);
res.trim();
return res;
}
};
/*
####################### THE BIG INT ##########################
######################################################################
*/
string a, b;
int main(void) {
bigint first = 1, second = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < 101; i++) {
first *= i;
}
for (int i = 1; i < 51; i++) {
second *= i;
}
bigint result = first + second;
cout << result.to_string();
return 0;
}
Python作业
pyecharts在jupyter notebook的渲染问题
pyecharts的图形在jupyter notebook中可能会不显示,比较好的解决方案是在使用时在顶部声明环境类型,在python代码的顶部添加如下代码并重启jupyter notebook即可,环境类型在pyecharts的文档中可以找到。
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig, NotebookType
CurrentConfig.NOTEBOOK_TYPE = NotebookType.JUPYTER_NOTEBOOK
重启jupyter服务即可发现pyecharts的图表可以正常加载了。
实验需求分析
本次实验给出了动车故障相关的样例数据信息,通过这些信息可以对数据进行多方面的分析,通过pandas处理数据,再将处理后的数据传给pyecharts,通过pyecharts对数据进行可视化的展示,再利用flask作为承载可视化展示的web服务框架,从而通过网页可直接访问处理后的可视化数据。对数据的分析可以有多个角度的选择,如可以展示各个月份发生的故障数目的折线图,各个月份发生故障类型的条形图,某种故障对应的责任公司占比饼图等等。