mirror of
https://gitlab.com/game-loader/hugo.git
synced 2026-02-02 22:02:48 +08:00
leetcode update
This commit is contained in:
@@ -4492,3 +4492,440 @@ func minFallingPathSum(grid [][]int) int {
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
Beats 100%
|
||||
|
||||
## day60 2024-04-27
|
||||
|
||||
### 514. Freedom Trail
|
||||
|
||||
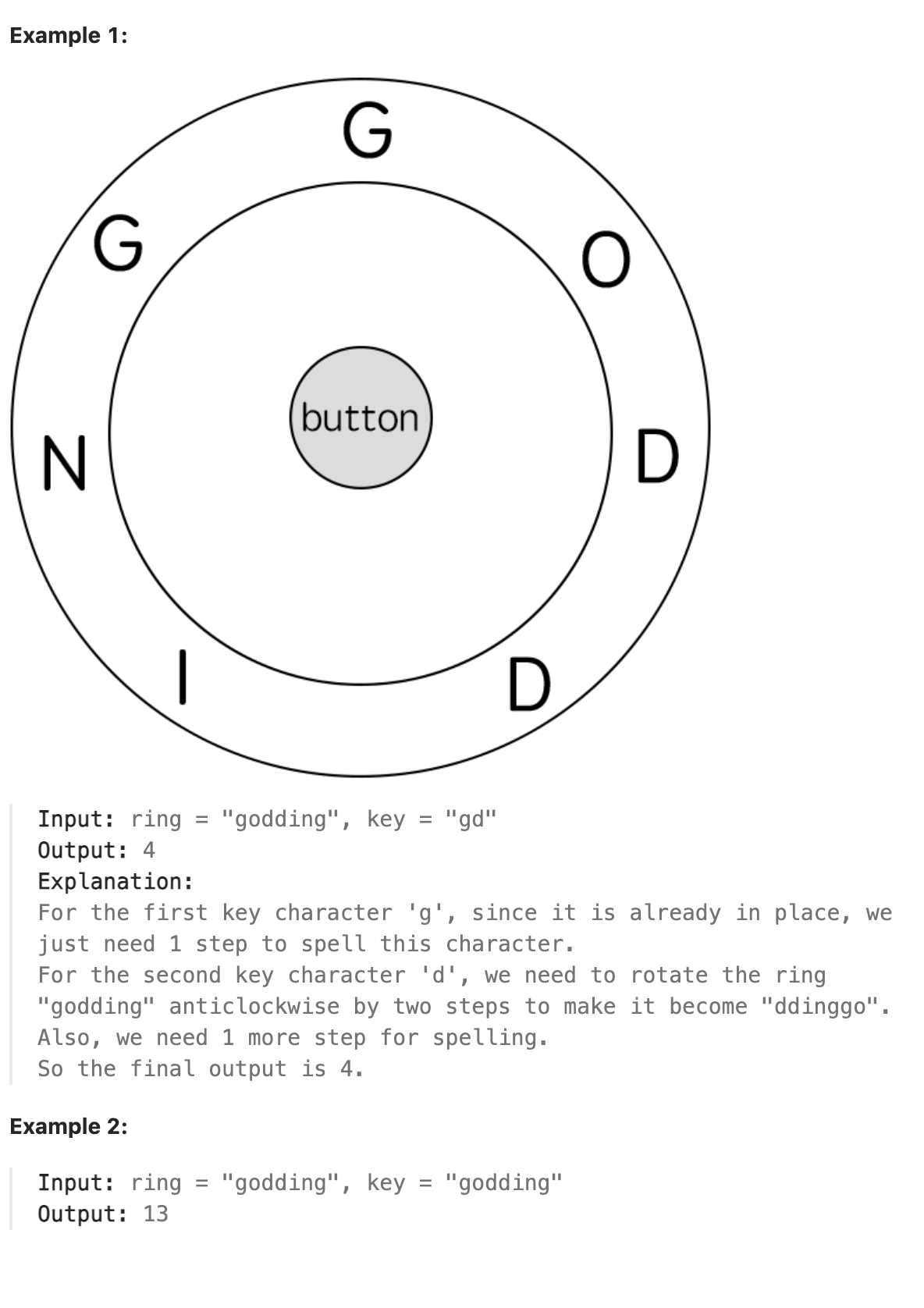
In the video game Fallout 4, the quest "Road to Freedom" requires players to reach a metal dial called the "Freedom Trail Ring" and use the dial to spell a specific keyword to open the door.
|
||||
|
||||
Given a string ring that represents the code engraved on the outer ring and another string key that represents the keyword that needs to be spelled, return the minimum number of steps to spell all the characters in the keyword.
|
||||
|
||||
Initially, the first character of the ring is aligned at the "12:00" direction. You should spell all the characters in key one by one by rotating ring clockwise or anticlockwise to make each character of the string key aligned at the "12:00" direction and then by pressing the center button.
|
||||
|
||||
At the stage of rotating the ring to spell the key character key[i]:
|
||||
|
||||
You can rotate the ring clockwise or anticlockwise by one place, which counts as one step. The final purpose of the rotation is to align one of ring's characters at the "12:00" direction, where this character must equal key[i].
|
||||
|
||||
If the character key[i] has been aligned at the "12:00" direction, press the center button to spell, which also counts as one step. After the pressing, you could begin to spell the next character in the key (next stage). Otherwise, you have finished all the spelling.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
|
||||
本题是一道难题, 花了很长时间, 但理解的还是不够透彻, 关键在于保存什么样的状态是可以避免不必要的运算的. 保存的状态必须是在运算过程中必要的且若之前计算过则避免重复运算. 考虑本题中的关键, key中下一个字符要转动到12点方向只于当前12点方向的字符有关, 也就是只与当前12点方向的ring字符串中对应位置上的字符有关, 因此我们想要知道的是在ring字符串的该位置上的字符转动到key的下一个字符的最短距离是多少, ring中可能有多个key的下一个字符, 转动到这些字符中的哪个能获得全局最短距离在当前场景下是未知的, 因此最好的方法就是延迟决定, 递归的对所有可行位置执行搜索, 这样从上到下一层层深入直到key中最后一个字符, 再将各个路径上得到的距离做比较, 取最小的那个作为下一个转动到12点方向的字符位置, 这里在递归过程中要保存子递归中已经计算过的后面的ring对后面的key的字符的最短距离. 这里要理解保存的状态是在子递归过程中运算出来的一系列子结果, 这些子结果后面可能有用, 也可能没用, 但是算过了就要保存下来, 有没有用在比较高的递归层级是未知因素.
|
||||
|
||||
这里还有一些比较抽象的思考, 该题的解法中使用动态规划思想最小的子问题是什么, 其实是key中从任一个字符到下一个字符移动的最短距离, 可以将寻找路径的过程想象成一棵树, 每一层代表key中以层数为下标对应字符在ring串中的所有可行位置, 这样一棵非常庞大的演化树, 递归的过程就是遍历这棵树的所有到叶子节点的路径并保存该过程中的状态最终找到最短路. 理解这个状态空间是什么以及为什么保存这个状态是很高效的十分重要, 值得细细品味
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func abs(x int) int {
|
||||
if x < 0 {
|
||||
return -x
|
||||
}
|
||||
return x
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func findRotateSteps(ring string, key string) int {
|
||||
var m, n = len(ring), len(key)
|
||||
var pos = make(map[uint8][]int)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(ring); i++ {
|
||||
pos[ring[i]] = append(pos[ring[i]], i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
var mem = make([][]int, m)
|
||||
for i := range mem {
|
||||
mem[i] = make([]int, n)
|
||||
for j := range mem[i] {
|
||||
mem[i][j] = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
var dfs func(i, j int) int // ring[i] is currently at 12 o'clock , j stands for current key[j]
|
||||
dfs = func(i, j int) (res int) {
|
||||
if j == n {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
var p = &mem[i][j]
|
||||
if *p != -1 {
|
||||
return *p
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer func() { *p = res }()
|
||||
res = math.MaxInt
|
||||
for _, po := range pos[key[j]] { // scan all the position key[j] in ring
|
||||
res = min(res, dfs(po, j+1)+min(abs(i-po), m-abs(i-po))) // we need to make po at 12 o'clock by rotating ring clockwise or counterclockwise (choose the smaller one), and then plus dfs(po,j+1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n + dfs(0, 0) // every char in key needs to be pressed too
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## day61 2024-04-28
|
||||
|
||||
### 834. Sum of Distances in Tree
|
||||
|
||||
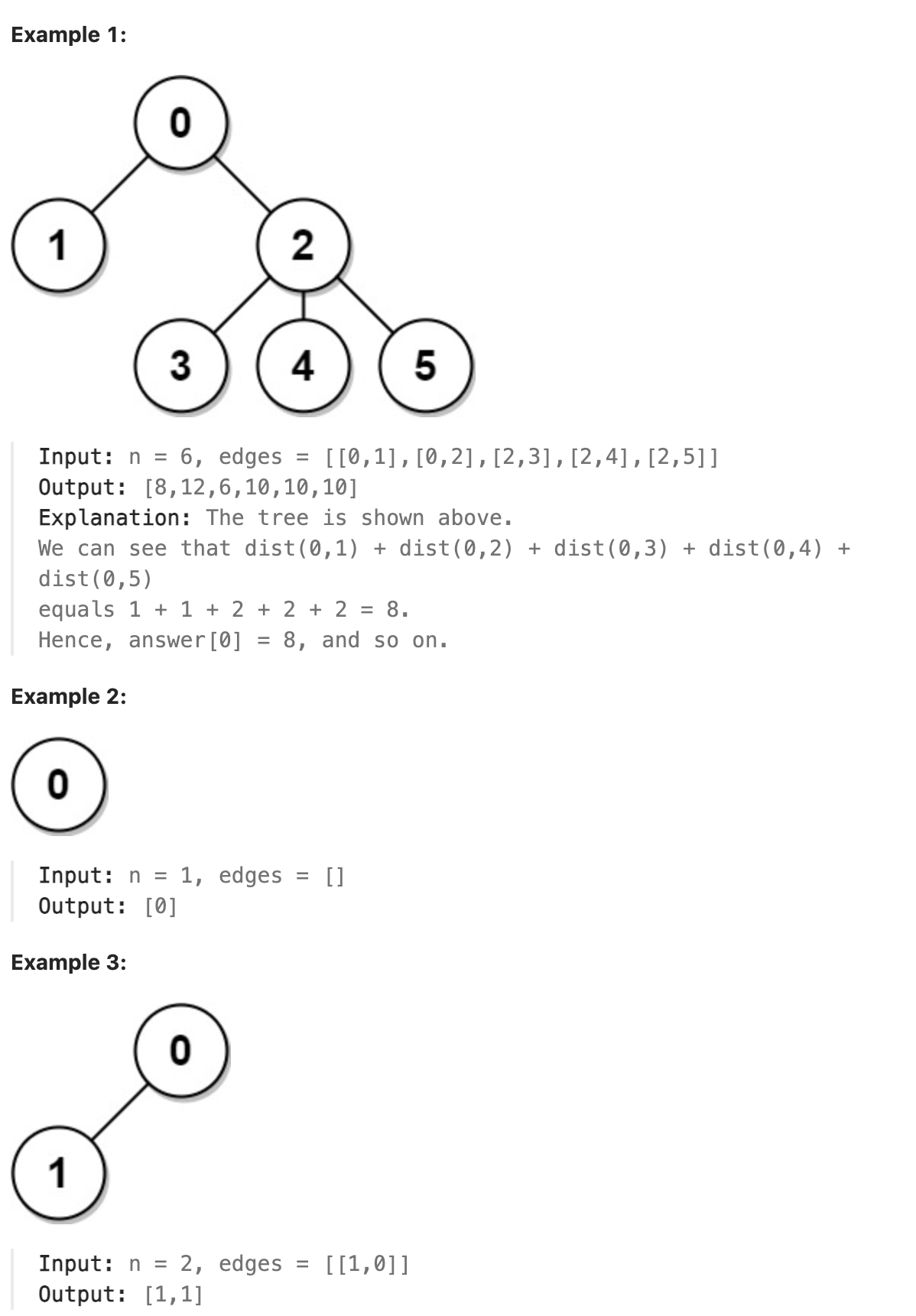
There is an undirected connected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1 and n - 1 edges.
|
||||
|
||||
You are given the integer n and the array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
|
||||
|
||||
Return an array answer of length n where answer[i] is the sum of the distances between the ith node in the tree and all other nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
|
||||
考虑这棵树,其实将任意一个节点作为树的根节点都不影响结果, 这也意味着这个树中各个元素地位相同, 更像是一张无向图. 对于树中任意一个节点而言, 若将其看作根节点, 只要知道了其所有连通节点到连通节点的的"子树"的距离和和这个"子树"中包含的节点数量, 就能算出根节点到其他所有节点的距离和. 而求其连通节点到连通节点的子树的距离和可以继续采用这种思路, 显然可以通过递归的方式求解, 思想是动态规划的思想. 最直接的解法就是将这个递归式写出来, 同时保存在求解过程中解出的某节点对应的一个连通节点的"子树"的距离和. 但这种方法会超时, 因此需要思考哪里还有重复计算的部分, 考虑一个极端例子, 一共有30000个节点, 其中29999个节点都和节点0相连. 这种情况下, 如果依次遍历各个节点并计算其相邻节点的"子树"距离和, 会发现尽管已经保存了节点0到其余节点的距离和, 但还是要将0到剩余29998个节点都遍历一遍(不用计算,只直接拿结果), 这样显然是$n^2$的复杂度, 显然这里可以简化, 对于节点0, 已经计算得到了它到其余所有节点的距离和, 只需要使用这个距离和减掉从0到当前节点的"子树"包含的距离和再加上0剩余的连通节点的"子树"包含的节点数目(原本的距离是到节点0, 从节点0到当前节点要将每个节点距离加1)就得到了当前节点到其余各节点的距离和.
|
||||
|
||||
想到这会发现, 其实只要任选一个节点计算其到其他节点的距离和, 若将这个节点作为根节点, 那么在计算过程中就已经将全部节点的"子树"距离和计算出来, 与真正的节点距离和相比, 只缺少了一个分支的距离和. 则在算出当前节点的距离和后, 可直接继续计算相邻节点的距离和, 计算方式为当前节点距离和减掉当前节点到相邻节点这一分支的距离和加上剩余的节点数, 再加上这个相邻节点到它的其余相邻节点的距离和, 这在之前的递归计算过程中已经保存了. 本题想高效求解, 不但要保存求解过程中的的中间结果, 还要充分利用已经求解出来的结果.
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
|
||||
初始版本:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func sumOfDistancesInTree(n int, edges [][]int) []int {
|
||||
connected := [][]int{}
|
||||
dis := make([]map[int][]int,n)
|
||||
results := []int{}
|
||||
for i:=0;i<n;i++{
|
||||
connected = append(connected, []int{})
|
||||
dis[i] = map[int][]int{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _,edge := range edges{
|
||||
connected[edge[0]] = append(connected[edge[0]],edge[1])
|
||||
connected[edge[1]] = append(connected[edge[1]],edge[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var recusive func(int, int)(int,int)
|
||||
recusive = func(parent int, now int)(int,int){
|
||||
value, exist := dis[parent][now]
|
||||
if exist{
|
||||
return value[0], value[1]
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
if len(connected[now]) == 1{
|
||||
return 0,1
|
||||
}
|
||||
distance := 0
|
||||
numbers := 0
|
||||
for _, neibor := range connected[now]{
|
||||
if neibor != parent{
|
||||
subdistance, number := recusive(now, neibor)
|
||||
distance += subdistance + number
|
||||
numbers += number
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
numbers++
|
||||
newslice := []int{distance, numbers}
|
||||
dis[parent][now] = newslice
|
||||
return distance, numbers
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for index,neibors := range connected{
|
||||
result := 0
|
||||
for _, neibor := range neibors{
|
||||
if neibor < index {
|
||||
resultverse, numb := recusive(neibor,index)
|
||||
result += results[neibor] - resultverse - numb + n - numb
|
||||
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
oneway, numbers := recusive(index, neibor)
|
||||
result += oneway + numbers
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
results = append(results, result)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return results
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
优化版本:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func dfs0(node int, parent int, t [][]int, dp []int, c []int) {
|
||||
n := len(t[node])
|
||||
c[node] = 1
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
child := t[node][i]
|
||||
if child != parent {
|
||||
dfs0(child, node, t, dp, c)
|
||||
dp[node] += dp[child] + c[child]
|
||||
c[node] += c[child]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func dfs1(node int, parent int, sum int, t [][]int, dp []int, c []int, res []int) {
|
||||
res[node] = sum
|
||||
n := len(t[node])
|
||||
s := 0
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
child := t[node][i]
|
||||
if child != parent {
|
||||
res[node] += dp[child] + c[child]
|
||||
s += dp[child] + c[child]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
child := t[node][i]
|
||||
if child != parent {
|
||||
dfs1(child, node, sum+(s-dp[child]-c[child])+(len(t)-c[child]), t, dp, c, res)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func sumOfDistancesInTree(n int, e [][]int) []int {
|
||||
t := make([][]int, n)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(e); i++ {
|
||||
u, v := e[i][0], e[i][1]
|
||||
t[u] = append(t[u], v)
|
||||
t[v] = append(t[v], u)
|
||||
}
|
||||
dp := make([]int, n)
|
||||
c := make([]int, n)
|
||||
dfs0(0, -1, t, dp, c)
|
||||
res := make([]int, n)
|
||||
dfs1(0, -1, 0, t, dp, c, res)
|
||||
return res
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
看讨论区时发现, 这类题目叫作`Tree rerooting DP`, 的确在本题中计算距离和的过程相当于不断更换树的根节点. 下面这个视频中对这一问题有比较系统的讲解
|
||||
|
||||
<https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7_huTWwl5jM>
|
||||
|
||||
了解下系统性的思路是好的, 但我向来不支持"套用", 要理解其内在的本质并根据实际问题灵活运用才是真正掌握. 就好像动态规划的"状态转移公式", 核心思想在于将大问题分解成小的子问题以及保存解决子问题过程中的信息(中间结果)用于后续处理, 正如我不断强调的核心观点, 利用的有效信息越多, 算法效率就越高.
|
||||
|
||||
## day62 2024-04-29
|
||||
|
||||
### 2997. Minimum Number of Operations to Make Array XOR Equal to K
|
||||
|
||||
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums and a positive integer k.
|
||||
|
||||
You can apply the following operation on the array any number of times:
|
||||
|
||||
Choose any element of the array and flip a bit in its binary representation. Flipping a bit means changing a 0 to 1 or vice versa.
|
||||
Return the minimum number of operations required to make the bitwise XOR of all elements of the final array equal to k.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you can flip leading zero bits in the binary representation of elements. For example, for the number (101)2 you can flip the fourth bit and obtain (1101)2.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
|
||||
本题最终对数组中所有的数进行异或运算, 得到目标k. 考虑到对k中的每一位而言, 数组中的数只需要在该位上做异或运算最终与k的该位相等. 对数组中的数, 对除最后一个数以外的所有数异或, 得到的结果再与最后一个数异或, 只需调整最后一个数的各个位使得最终结果与k相同. 因为调整任意一个数的某个位都是等价的, 而先将前面的数异或相当于保存了前面所有数中各个位异或后的信息. 将结果和最后一个数按位与k比较并调整即可. 只需注意如果一个数的后面的位比较完成前面全是0, 对对应的也要做相应调整.
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func minOperations(nums []int, k int) int {
|
||||
numlen := len(nums)
|
||||
before := nums[0]
|
||||
last := 0
|
||||
if numlen == 1{
|
||||
last = 0
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
for _, value := range nums[1:numlen-1]{
|
||||
before ^= value
|
||||
}
|
||||
last = nums[numlen-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
result := 0
|
||||
|
||||
first := 0
|
||||
second := 0
|
||||
target := 0
|
||||
for before != 0 || last != 0 || k != 0{
|
||||
first = before % 2
|
||||
second = last % 2
|
||||
target = k % 2
|
||||
if first ^ second != target{
|
||||
result++
|
||||
}
|
||||
before /= 2
|
||||
last /= 2
|
||||
k /= 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
其实将所有数异或后直接和k进行异或, 得到的结果中如果某位为1则说明和k的这一位不同, 为0则相同, 将结果不断右移并判断最后一位是否为1即可得到需要翻转的次数.
|
||||
|
||||
## day63 2024-04-30
|
||||
|
||||
### 1915. Number of Wonderful Substrings
|
||||
|
||||
A wonderful string is a string where at most one letter appears an odd number of times.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, "ccjjc" and "abab" are wonderful, but "ab" is not.
|
||||
Given a string word that consists of the first ten lowercase English letters ('a' through 'j'), return the number of wonderful non-empty substrings in word. If the same substring appears multiple times in word, then count each occurrence separately.
|
||||
|
||||
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
|
||||
这种子字符串的问题大概要保存一些状态以供后续的判断, 关键在于保存什么状态是有用的, 这里可以保存到某个下标为止的前缀字符串中各个字符的数量, 但是注意本题只要求判断字符串中出现了奇数次的字符的数量, 因此关键在于字符串中的某个字符的数量是否为奇数. 考虑这样的情况, 如果以下标3为结尾的字符串中字符'a'出现了奇数次, 以下标5为结尾的字符串中字符'a'也出现了奇数次, 那么这两个下标之间的字符串中'a'必定出现了偶数次(两奇数做差, 必定为偶数). 同样两偶数做差也必定为偶数, 只有偶数和奇数做差时才会出现奇数. 因此只需要保存到某个下标结尾处字符串中各个字符出现次数的奇偶性再与其他下标做比较, 字符奇偶性不同的字符小于2则二者之间的字符串是可行的, 否则不可行.
|
||||
|
||||
保存各个字符的奇偶性可以使用位标记, 从a到z每个字母用一个二进制位表示, 用一个十维数组也可行, 但在只需要保存一个二值状态时用位更节省空间. 求出到各个下标的各个字符的奇偶串后, 依次遍历每个位置, 分别与后面的所有位置做异或, 再判断异或后的数字的二进制表示中1的个数是否大于1个, 大于则这两个下标之间的字符串奇数个字符大于1, 判断是否大于一个可以使用n&(n-1)来消掉最低的1, 再判断剩余的数字是否为0, 不为0说明大于1个.
|
||||
|
||||
但使用这种方法, 每次都要将当前下标与后面的所有下标都比较一遍, 显然是$n^2$的复杂度. 这里可以发现, 使用这种方法遍历没有考虑到这种字符串差出现的先后位置与结果无关, 即差值的具体数量与结果无关. 例如, 在下标为1处的位串为0101, 在3和5处的位串都为0111, 实际上这两个位置与下标1做异或后的结果相同, 即1-3和1-5之间都只有1个位置是奇数个, 至于这个位置是3个或是5个, 或者3-5之间这个位置没发生变化其他位置多了两个, 都不影响区间字符串的奇偶性质. 这里的思想和用位来表示字符的奇偶性有异曲同工之妙, 即无需考虑具体数量, 只需考虑其拥有的性质即可.
|
||||
|
||||
有了这种想法, 那么只需要保存所有的位串, 并统计所有位串的数量, 如0101的位串有五个, 说明这五个位串代表的下标之间的四个间隙的所有字符都是偶数个那么这四个显然是符合要求的结果. 再计算有一个奇数位的情况, 只需要将每个串中的各个位依次翻转并查询翻转后的位串的数量即可. 每个串最多翻转10次(a-j 10个字符), 10位二进制串最多有1024种组合, 意味着最多翻转1024\*10=10240次. 降为常数复杂度.
|
||||
|
||||
在翻转的过程中, 两种字符串之间翻转后的组合会被计数两次(0101翻转得到0111,0111翻转得到0101), 将最终结果除以2即可.
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func wonderfulSubstrings(word string) int64 {
|
||||
|
||||
masks := map[int]int{}
|
||||
|
||||
bytes := []byte(word)
|
||||
|
||||
mask := 0
|
||||
|
||||
masks[0] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
for _, char := range bytes{
|
||||
|
||||
mask ^= (1<<(char-'a'))
|
||||
|
||||
masks[mask] = masks[mask] + 1
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
result := 0
|
||||
|
||||
flip := 0
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Println(masks[0])
|
||||
|
||||
for value, number := range masks{
|
||||
|
||||
result += number * (number - 1) / 2
|
||||
|
||||
for i:=0;i<10;i++{
|
||||
|
||||
flip += masks[value ^ (1<<i)] * number
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return int64(result+flip/2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
本题是一道比较综合的题目, 找到关键状态是解决问题的核心.
|
||||
|
||||
## day64 2024-05-01
|
||||
|
||||
### 2000. Reverse Prefix of word
|
||||
|
||||
Given a 0-indexed string word and a character ch, reverse the segment of word that starts at index 0 and ends at the index of the first occurrence of ch (inclusive). If the character ch does not exist in word, do nothing.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if word = "abcdefd" and ch = "d", then you should reverse the segment that starts at 0 and ends at 3 (inclusive). The resulting string will be "dcbaefd".
|
||||
Return the resulting string.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
|
||||
本题是一道简单题, 显然找到第一个ch的位置翻转字符串即可, 若想在找到后快速翻转字符串, 可以在找到对应字符的下标后除以2找到中间位置字符, 分别从子字符串开头和结尾开始向中间遍历并不断交换首尾字符即可实现翻转,
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func reversePrefix(word string, ch byte) string {
|
||||
bytes := []byte(word)
|
||||
first := 0
|
||||
for index, char := range bytes{
|
||||
if char == ch{
|
||||
first = index
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
mid := first/2
|
||||
copybytes := []byte(word)
|
||||
for index,_ := range copybytes[0:mid]{
|
||||
bytes[index] = copybytes[first-index]
|
||||
bytes[first-index] = copybytes[index]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if first % 2 == 1{
|
||||
bytes[mid] = copybytes[mid+1]
|
||||
bytes[mid+1] = copybytes[mid]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return string(bytes)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## day65 2024-05-02
|
||||
|
||||
### 2441. Largest Positive Integer That Exists With Its Negative
|
||||
|
||||
Given an integer array nums that does not contain any zeros, find the largest positive integer k such that -k also exists in the array.
|
||||
|
||||
Return the positive integer k. If there is no such integer, return -1.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
|
||||
本题是一道简单题, 题目中给出数字的范围为-1000到1000, 因此可以使用一个1001长度的数组来保存每个数字的状态, 状态分为未出现, 出现了一个负数, 出现了一个正数和出现过了这个数的正负两个数四种情况. 因此使用四个数字来表示这四种情况即可, 0表示未出现, -1表示只出现过负数, 1表示只出现过正数, 2表示一正一负, 遍历数组并改变相应状态, 当状态变为2时与当前的最大结果比较并更新最大值即可.
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func findMaxK(nums []int) int {
|
||||
result := -1
|
||||
numbers := make([]int,1001)
|
||||
|
||||
for _,value := range nums{
|
||||
if value > 0{
|
||||
if numbers[value] == -1{
|
||||
numbers[value] = 2
|
||||
result = max(result, value)
|
||||
}else if numbers[value] == 0{
|
||||
numbers[value] = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
if numbers[-value] == 1{
|
||||
numbers[-value] = 2
|
||||
result = max(result, -value)
|
||||
}else if numbers[-value] == 0{
|
||||
numbers[-value] = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user