mirror of
https://gitlab.com/game-loader/hugo.git
synced 2026-03-14 19:16:18 +08:00
leetcode update
This commit is contained in:
@@ -13390,3 +13390,289 @@ public:
|
|||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day202 2024-09-16
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 539. Minimum Time Difference
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Given a list of 24-hour clock time points in "HH:MM" format, return the minimum minutes difference between any two time-points in the list.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题要求列表中任意两个时间之间的最短时间差, 注意仅要求求出时间差, 不要求给出是具体哪两个时间对应的时间差, 也不要求给出时间的具体位置. 则通过给时间排序, 再遍历排好序的时间数组找到相邻有序时间之间差值的最小值. 排序可以先将时间全部转换为从0点开始的分钟数再给分钟数排序, 这样排序时只需对整数排序, 也方便计算时间差值.
|
||||||
|
在排序时从0点开始排序, 24点为最大值, 则在计算时间之间的差值时最后还要计算一下最后一个时间和第一个时间反向的差值(排序是顺时针的, 这里相当于计算下逆时针的时间差, 因为时间相当于一个圆形)与最小差值比较并更新. 注意以上针对的均为所有时间都不相同的情况, 若存在两个时间相同, 直接返回0.
|
||||||
|
c++中的set 标准库表示的有序集合是内部自动有序且不含重复元素的容器, 因此可以利用这个数据结构来保存给出的时间转换后的分钟数.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
int findMinDifference(vector<string>& timePoints) {
|
||||||
|
set<int> minutesSet;
|
||||||
|
for (const auto& timePoint : timePoints){
|
||||||
|
int hours = stoi(timePoint.substr(0, 2));
|
||||||
|
int minute = stoi(timePoint.substr(3, 2));
|
||||||
|
int minutes = hours*60 + minute;
|
||||||
|
if (minutesSet.contains(minutes)){
|
||||||
|
return 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
minutesSet.insert(minutes);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
int last = 0;
|
||||||
|
int mintime = 1441;
|
||||||
|
set<int>::iterator first = minutesSet.begin();
|
||||||
|
set<int>::iterator it = minutesSet.begin();
|
||||||
|
last = *it;
|
||||||
|
it++;
|
||||||
|
while (it != minutesSet.end()){
|
||||||
|
mintime = min(mintime, *it-last);
|
||||||
|
last = *it;
|
||||||
|
it++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
mintime = min(mintime, *first+1440-last);
|
||||||
|
return mintime;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day203 2024-09-17
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 884. Uncommon Words from Two Sentences
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A sentence is a string of single-space separated words where each word consists only of lowercase letters.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A word is uncommon if it appears exactly once in one of the sentences, and does not appear in the other sentence.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Given two sentences s1 and s2, return a list of all the uncommon words. You may return the answer in any order.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题读懂题目可以发现, 实际上只是要求记下所有在所有字符串中均只出现了一次的单词, 最终返回这些单词. 则先将字符串按空格分割, 再使用map记录所有单词出现的次数, 将单词作为key, 出现次数作为value. 最终遍历map并将只出现一次的单词放入数组中返回.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
vector<string> uncommonFromSentences(string s1, string s2) {
|
||||||
|
map<string, int> word;
|
||||||
|
cutSentence(s1, word);
|
||||||
|
cutSentence(s2, word);
|
||||||
|
vector<string> res;
|
||||||
|
for (map<string, int>::iterator it = word.begin();it != word.end();it++){
|
||||||
|
if (it->second == 1){
|
||||||
|
res.push_back(it->first);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return res;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void cutSentence(string input, map<string, int>& words){
|
||||||
|
istringstream ss(input);
|
||||||
|
string word;
|
||||||
|
while(ss>>word) {
|
||||||
|
if (words.find(word) == words.end()) {
|
||||||
|
words[word] = 1;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
words[word]++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day204 2024-09-18
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 179. Largest Number
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Given a list of non-negative integers nums, arrange them such that they form the largest number and return it.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Since the result may be very large, so you need to return a string instead of an integer.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
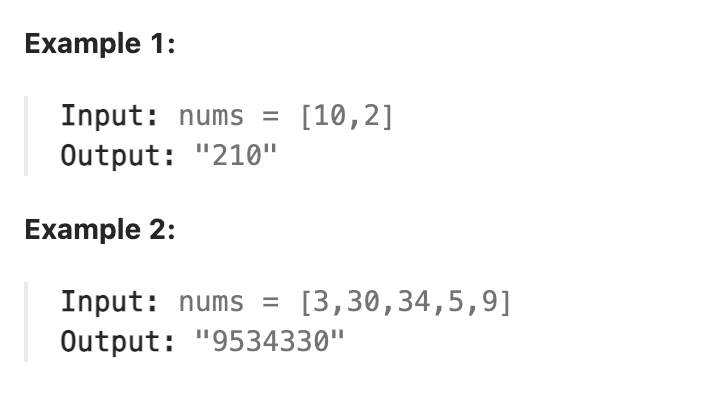
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题将数字当作字符串, 按照字符序从大到小排序再将排好序后的字符串连接起来即得到答案. 在这里定义的数字字符串的大小顺序要满足以下条件:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 逐字符比较, 字符大的字符串序大.
|
||||||
|
2. 两个不同长度的字符串, 短字符串与长字符串逐字符比较后全部相同, 而长字符串还有剩余字符, 则比较将两个字符串按两种方式(短前长后和长前短后)连接后得到的新字符串的字符串序.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
注意处理全为0的特殊情况, 若最终得到的字符串起始为0, 直接返回单个0组成的字符串即可.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
bool customCompare(const string& a, const string& b) {
|
||||||
|
size_t i = 0;
|
||||||
|
while (i < a.length() && i < b.length()) {
|
||||||
|
if (a[i] != b[i]) {
|
||||||
|
return a[i] > b[i]; // 逐字符比较,字符大的字符串序大
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
i++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (a.length() == b.length()){
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// 如果短字符串是长字符串的前缀,则比较将两个字符串两种方式连接后的字符串大小
|
||||||
|
return customCompare(a+b, b+a);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
string largestNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
|
||||||
|
vector<string> numstr;
|
||||||
|
for (auto num : nums){
|
||||||
|
numstr.push_back(to_string(num));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
sort(numstr.begin(), numstr.end(), customCompare);
|
||||||
|
string result;
|
||||||
|
for (auto str : numstr){
|
||||||
|
result += str;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (result[0] == '0'){
|
||||||
|
return "0";
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return result;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day205 2024-09-19
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 241. Different Ways to Add Parentheses
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Given a string expression of numbers and operators, return all possible results from computing all the different possible ways to group numbers and operators. You may return the answer in any order.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The test cases are generated such that the output values fit in a 32-bit integer and the number of different results does not exceed 10^4.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题算是一道比较典型的递归加记忆化问题, 首先确定终止条件, 当某个子表达式中仅包含数字时, 则直接返回这个数字. 当是一个表达式时, 则分别递归计算运算符两侧的表达式可能得到的结果并根据运算符对两侧结果进行运算得到当前表达式所有可能得到的运算结果. 感觉和学习编译原理时经典的递归下降解析表达式的值有些相似.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
举例来说, 对"2\*3-4\*5" 这样的式子, 我们只需将其看作不同表达式和运算符的组合, 分别计算这些表达式的值就能得出最终结果, 而计算表达式值的过程都是结构相似的问题, 因此可以不断分解成子问题. 这里就可以分解成2,\*, 3-4\*5. 即表达式2, 乘号以及后面的表达式. 也可以分解成2\*3, -, 4\*5. 这个分解可以用简单的字符串遍历来完成, 遍历整个表达式串, 遇到运算符则对运算符两侧的表达式进行递归求值, 继续遍历下一个运算符, 直到结尾.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
显然这个过程中会有一些子表达式被重复计算, 因此可以想办法保存递归过程中算得的中间结果, 可以用一个二维数组表示从下标i开始到下标j的表达式的可能值. 即matrix\[i\]\[j\]记录了i-j的表达式的所有可能运算结果. 二维数组可以使用一维数组表示, 即用i\*length(表达式长度)+j来表示matrix\[i\]\[j\]的值. 这样就可以用一个vector<vector<int>>来表示记忆化的数组.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
对于递归的问题, 思路一定要清楚, 只需找到递归的终止条件, 并写出解决最小的子问题的过程, 剩下的就是将问题分解, 分别使用递归求解分解后的问题再将结果整合起来进行处理, 至于中间递归的过程不要试图去想的太详细, 只要在宏观上能实现 分解问题->解决子问题->合并解决子问题的结果. 就能得到正确答案.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
const int Big = 100000;
|
||||||
|
vector<int> diffWaysToCompute(string expression) {
|
||||||
|
int leng = expression.length();
|
||||||
|
vector<vector<int>> memo(leng*leng);
|
||||||
|
vector<int> result = subCompute(expression, 0, leng-1, memo, leng);
|
||||||
|
return result;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private:
|
||||||
|
vector<int> subCompute(const string& expression, int begin, int end, vector<vector<int>>& memo, int leng) {
|
||||||
|
if (memo[begin*leng+end].size() > 0) {
|
||||||
|
return memo[begin*leng+end];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
vector<int> result;
|
||||||
|
bool hasOperator = false;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
|
||||||
|
if (expression[i] == '+' || expression[i] == '-' || expression[i] == '*') {
|
||||||
|
hasOperator = true;
|
||||||
|
vector<int> left = subCompute(expression, begin, i-1, memo, leng);
|
||||||
|
vector<int> right = subCompute(expression, i+1, end, memo, leng);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (int l : left) {
|
||||||
|
for (int r : right) {
|
||||||
|
if (expression[i] == '+') {
|
||||||
|
result.push_back(l + r);
|
||||||
|
} else if (expression[i] == '-') {
|
||||||
|
result.push_back(l - r);
|
||||||
|
} else if (expression[i] == '*') {
|
||||||
|
result.push_back(l * r);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (!hasOperator) {
|
||||||
|
result.push_back(stoi(expression.substr(begin, end-begin+1)));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
memo[begin*leng+end] = result;
|
||||||
|
return result;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day206 2024-09-20
|
||||||
|
### 214. Shortest Palindrome
|
||||||
|
You are given a string s. You can convert s to a
|
||||||
|
palindrome
|
||||||
|
by adding characters in front of it.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Return the shortest palindrome you can find by performing this transformation.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
本题是一道难题,但整体思路是比较简洁的,我们只能在字符串的前面添加字符来构造回文串,则以字符串开头作为起始的回文子字符串是不需要构造的,需要添加的只是回文子字符串后面的部分。(如aabaac,则aabaa是不需要做任何变动的,只需添加c),如果在字符串中间位置有一个回文串对于构造整个回文串影响不大(如acbcd,显然要构造回文串必须将cbcd反转一遍)。则解题思路为先找到以字符串开头为起始的原始字符串中的最长回文子串,再将该子串后面的字符串反转添加到字符串前面即得到目标字符串。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
接下来要解决的问题是,如何得到以开头作为起始的最长回文子串有多长。如果我们将字符串逆序, 问题就变成了能找到的包含原始字符串开头和包含逆转后的字符串末尾的两个字符串中相同的子字符串最长有多长(如aabaac逆转后为caabaa则前一个字符串开头的aa和后一个字符串结尾的aa完全相同,则最长为2)。这是一个模式匹配的问题,如果熟悉kmp算法的话,就会发现这和kmp算法中next数组的含义非常相似,如果把原始字符串和逆转后的字符串连接在一起,就变成了求这个连接后的字符串的最长公共前后缀的长度问题,若字符串长度为n,则此问题即为求next\[n-1\]。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
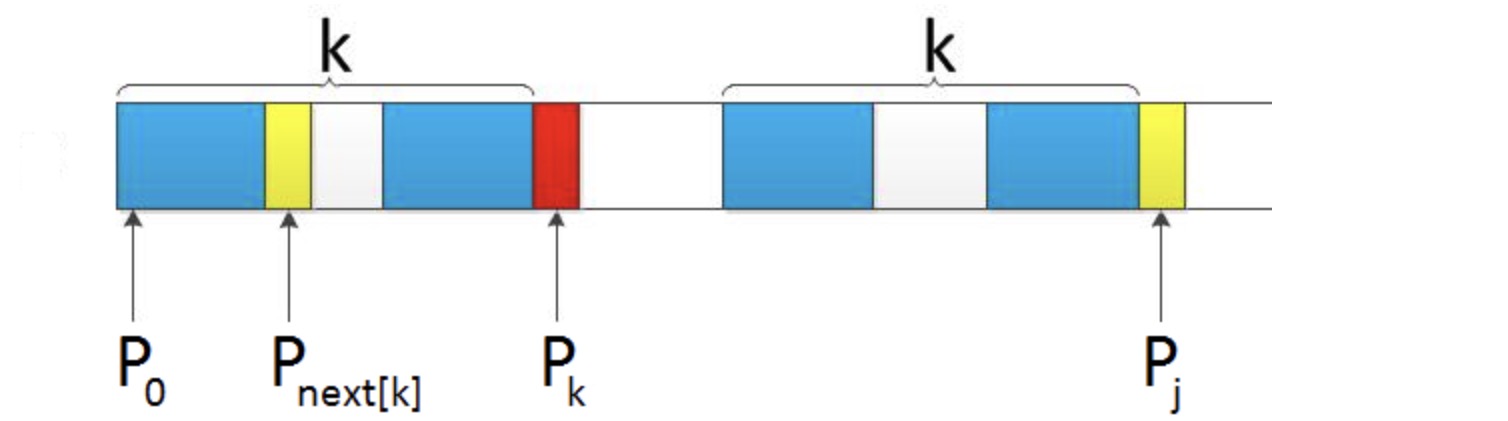
kmp算法的next的求法网上已经有很多讲解,以下面的情况为例,
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如果pk和pj相同,则将长度加1,但当pk和pj不同时,为什么要去找pnext\[k\]。实际上这里pk和pj不同时,我们的目标是找到pk之前的某个公共前后缀,这个更小的公共前后缀中前缀的下一位恰为pj,则由于这是一个公共前后缀,这个公共前后缀是之前的pk对应的公共前后缀的一部分,则这个更小的公共前缀也会和pj前面的一个更小的公共后缀对应起来。这时之前的公共前缀后面恰好有一个pj就和后面pj前面的公共后缀再加上pj对应起来构成了一个新的公共前后缀。我们就知道了新的公共前后缀的长度。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题还可以使用滚动哈希来解决。即Rabin-Karp算法,这里不再讲解该算法,可参考下面的资料
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[Rabin-Karp算法](https://algo.itcharge.cn/06.String/02.String-Single-Pattern-Matching/02.String-Rabin-Karp/#_2-2-%E6%BB%9A%E5%8A%A8%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
string shortestPalindrome(string s) {
|
||||||
|
string rev_s = s;
|
||||||
|
reverse(rev_s.begin(), rev_s.end());
|
||||||
|
string temp = s + "#" + rev_s;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int n = temp.length();
|
||||||
|
vector<int> lps(n, 0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 1, len = 0; i < n;) {
|
||||||
|
if (temp[i] == temp[len]) {
|
||||||
|
lps[i++] = ++len;
|
||||||
|
} else if (len) {
|
||||||
|
len = lps[len - 1];
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
lps[i++] = 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// 最长回文前缀的长度
|
||||||
|
int longest_palindrome_prefix = lps[n - 1];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 需要反转并添加到前面的子串
|
||||||
|
string to_reverse = s.substr(longest_palindrome_prefix);
|
||||||
|
reverse(to_reverse.begin(), to_reverse.end());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 拼接并返回结果
|
||||||
|
return to_reverse + s;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user