mirror of
https://gitlab.com/game-loader/hugo.git
synced 2026-03-14 19:16:18 +08:00
leetcode update
This commit is contained in:
@@ -17245,3 +17245,790 @@ public:
|
|||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day246 2024-11-09
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 3133. Minimum Array End
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You are given two integers n and x. You have to construct an array of positive integers nums of size n where for every 0 <= i < n - 1, nums[i + 1] is greater than nums[i], and the result of the bitwise AND operation between all elements of nums is x.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Return the minimum possible value of nums[n - 1].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题仍然是一道位运算相关的题目,要得到题目中的目标结果,必然要以x作为起始数字,因为按位与得到的结果不大于参与运算的数字,则若将x和小于x的数字做按位与,得到的结果必然小于x,不可能满足题目要求。考虑比x大的数字若要与x进行按位与后仍等于x,则该数字必须满足所有x中为1的二进制位也为1。则我们要得到的是从小到大排列的满足该条件的数字中第n大(包含x)的数字。考虑如何构造这样的数字,可以通过固定必须为1的二进制位,再去填充其余二进制位来得到这样的数字,因为我们只要得到第n大的数,不需要产生中间的数字,则直接将n-1(第n大包含x,去掉x还剩n-1个数)的二进制从低到高按位填入x从低到高的0二进制位中即得最终结果。如图
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
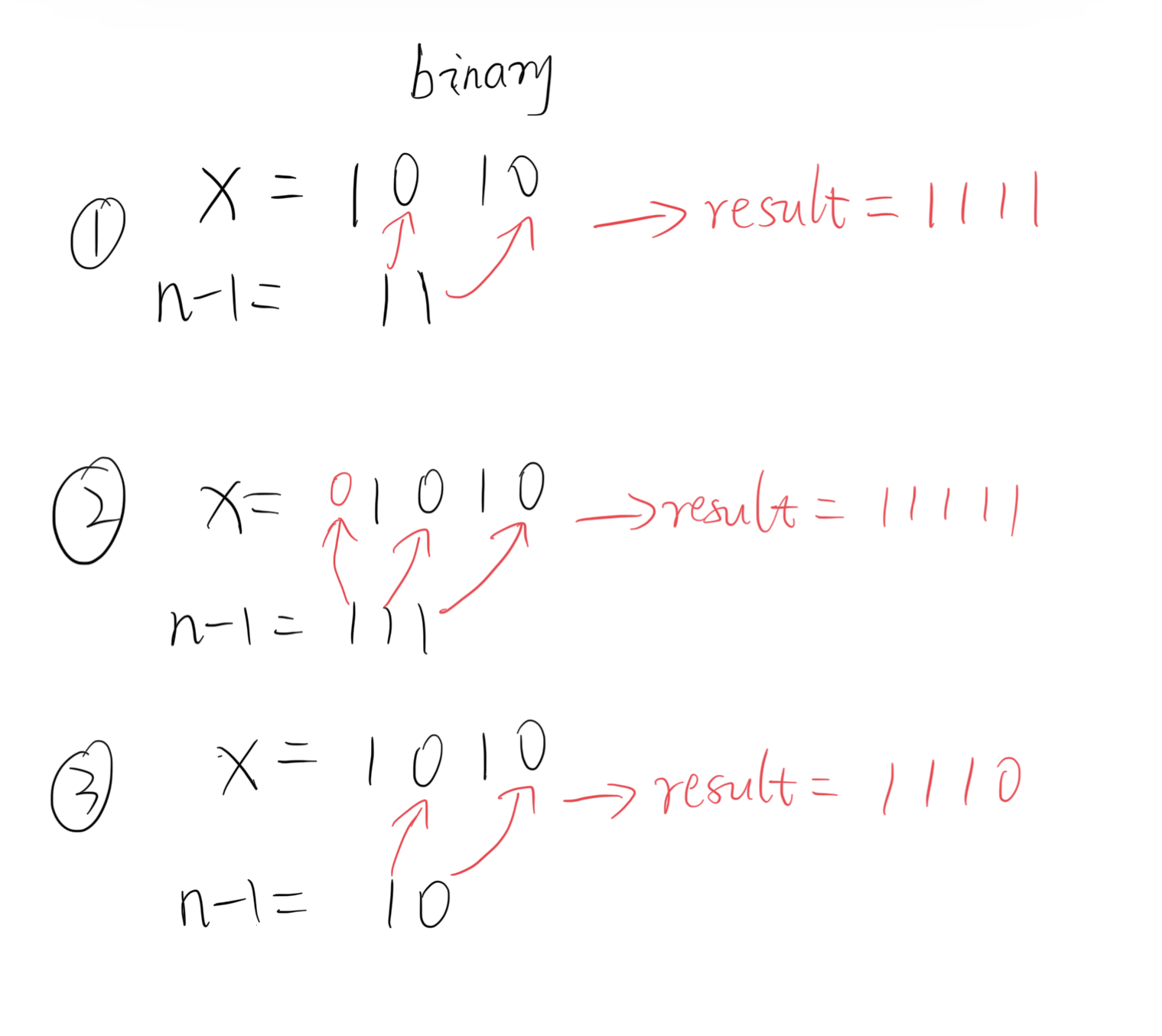
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
long long minEnd(int n, int x) {
|
||||||
|
long long int xlong = x;
|
||||||
|
long long int bitadd = n-1;
|
||||||
|
long long int copyx = xlong;
|
||||||
|
int xcurrent = 0;
|
||||||
|
int bitaddcurrent = 0;
|
||||||
|
int shift = 0;
|
||||||
|
while(bitadd > 0){
|
||||||
|
xcurrent = copyx & 1;
|
||||||
|
if (xcurrent == 0){
|
||||||
|
bitaddcurrent = bitadd & 1;
|
||||||
|
if (bitaddcurrent == 1){
|
||||||
|
xlong |= ((long long int)1 << shift);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
bitadd = bitadd >> 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
copyx = copyx >> 1;
|
||||||
|
shift++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return xlong;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day247 2024-11-10
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 3097. Shortest Subarray With OR at Least K II
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You are given an array nums of non-negative integers and an integer k.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
An array is called special if the bitwise OR of all of its elements is at least k.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Return the length of the shortest special non-empty
|
||||||
|
subarray of nums, or return -1 if no special subarray exists.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
按位或运算的结果大于等于参与运算的数字,故可以使用滑动窗口,窗口扩大的终止条件为当前窗口内所有数字的按位或大于等于k。问题在于,如何缩小窗口,缩小窗口的终止条件是什么。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
考虑对窗口左侧的数字,在我们只有整个窗口的按位或的结果和该数字的情况下,无法判断缺少该数字后新窗口的按位或的结果和原始窗口的按位或结果之间的关系,因为或运算对每个二进制位只要有一个数字为1最终结果中这个二进制位就为1,因此可以同时保存窗口内各个二进制位上出现1的次数,在缩小窗口时,对移出窗口的数字中所有为1的二进制位,从保存的次数中减1,若减1后该二进制位在该窗口中出现次数为0,则从或运算结果中减去该二进制位为1,其余位置为0对应的数(如1000即为减8),这样就成功处理了窗口左侧数字移出后的情况。缩小窗口的终止条件为窗口内的所有数字按位或的结果小于k。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
按上述方式不断移动窗口,每当窗口内数字按位或的结果大于等于k,均将其和保存的当前的最小窗口长度比较并更新最小窗口长度,此处可以进行简单的剪枝,当最小窗口长度已经为1时可以不用再继续遍历,因为1就是能得到的最小结果。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
int minimumSubarrayLength(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
|
||||||
|
int n = nums.size();
|
||||||
|
// 维护每个位上1的出现次数
|
||||||
|
int bitCount[32] = {0};
|
||||||
|
int currentOR = 0;
|
||||||
|
int minLen = n + 1;
|
||||||
|
int left = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for(int right = 0; right < n; ++right){
|
||||||
|
if(nums[right] != 0){
|
||||||
|
int num = nums[right];
|
||||||
|
while(num > 0){
|
||||||
|
int bit = num & -num; // 获取最低位的1
|
||||||
|
int bitPos = __builtin_ctz(bit); // 计算该位的位置
|
||||||
|
bitCount[bitPos]++;
|
||||||
|
currentOR |= (1 << bitPos);
|
||||||
|
num -= bit;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 当currentOR >= k时,尝试缩小窗口
|
||||||
|
while(currentOR >= k && left <= right){
|
||||||
|
// 更新最小长度
|
||||||
|
minLen = min(minLen, right - left + 1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 如果已经找到最小长度,提前终止
|
||||||
|
if(minLen == 1){
|
||||||
|
return 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if(nums[left] != 0){
|
||||||
|
int num = nums[left];
|
||||||
|
while(num > 0){
|
||||||
|
int bit = num & -num; // 获取最低位的1
|
||||||
|
int bitPos = __builtin_ctz(bit); // 计算该位的位置
|
||||||
|
bitCount[bitPos]--;
|
||||||
|
if(bitCount[bitPos] == 0){
|
||||||
|
currentOR &= ~(1 << bitPos);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
num -= bit;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
left++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return minLen <= n ? minLen : -1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day248 2024-11-11
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 2601. Prime Subtraction Operation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums of length n.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You can perform the following operation as many times as you want:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Pick an index i that you haven’t picked before, and pick a prime p strictly less than nums[i], then subtract p from nums[i].
|
||||||
|
Return true if you can make nums a strictly increasing array using the above operation and false otherwise.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A strictly increasing array is an array whose each element is strictly greater than its preceding element.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
注意题目nums\[i\]的取值范围在1~1000之间,数字范围不大,则可先用筛法求出该范围内的所有素数备用。这里使用线性筛法。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
考虑本题中要求最终得到的是严格递增的数组,则需要求出最后一部分符合严格递增的子数组的起始位置,对于末尾的这部分符合严格递增的子数组不需要做任何改动,因为本题中只能将数字减小,不能变大,而对这段严格递增子数组的起始数字,如果将其变得更小,则前面的数字可调整的范围就会变得更小,就不一定能够构造出符合题目要求的数组。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在找到起始位置后,设该位置的数字为p,对在该位置之前的子数组,可从头遍历并使用贪心算法结合二分搜索,贪心是指每次都将数字变得尽可能小,假设下标为k的数字为n,遍历到下标k+1时数字应该大于n,假设k+1处的数字当前为m,则我们要找的即为小于m-n的最大素数。二分搜索用于在求出的全部素数中快速找到满足该要求的素数,如果找不到则说明不可能构造出满足题目要求的数组。同时在每次找到这样的素数后,得到的下标k+1处对应的新数字应严格小于p,如果不小于p则由于要构造严格递增的数组,后面的数字只会大于p,由于最后一部分严格递增的子数组不能变动,因此前面若有数字大于p最终无法构造出严格递增的数组,这两种情况均返回false,正常遍历到数字p处则返回true。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
bool primeSubOperation(std::vector<int>& nums) {
|
||||||
|
// 筛法求素数
|
||||||
|
vector<int> primes = linearSieve(1000);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int n = nums.size();
|
||||||
|
int start_suffix = n - 1;
|
||||||
|
while(start_suffix > 0 && nums[start_suffix-1] < nums[start_suffix]){
|
||||||
|
start_suffix--;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 整个数组本来就递增直接返回
|
||||||
|
if(start_suffix == 0){
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int p = nums[start_suffix];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int last = 0;
|
||||||
|
for(int i = 0; i < start_suffix; ++i){
|
||||||
|
int current = nums[i];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int upper = nums[i] - last ;
|
||||||
|
int idx = lower_bound(primes.begin(), primes.end(), upper) - primes.begin();
|
||||||
|
// 满足条件m-n的最大素数下标为idx-1
|
||||||
|
int chosen_prime = 0;
|
||||||
|
if(idx != 0 ){
|
||||||
|
chosen_prime = primes[idx - 1];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
int new_num = nums[i] - chosen_prime;
|
||||||
|
if(new_num <= last || new_num >= p){
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
last = new_num;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private:
|
||||||
|
vector<int> linearSieve(int max){
|
||||||
|
vector<int> primes;
|
||||||
|
vector<bool> is_prime(max + 1, true);
|
||||||
|
is_prime[0] = is_prime[1] = false;
|
||||||
|
for(int i = 2; i <= max; ++i){
|
||||||
|
if(is_prime[i]){
|
||||||
|
primes.push_back(i);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
for(auto p : primes){
|
||||||
|
if(p * i > max){
|
||||||
|
break;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
is_prime[p * i] = false;
|
||||||
|
if(i % p == 0){
|
||||||
|
break;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return primes;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 总结
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在查看他人代码时发现,可以直接逆序构造符合题目要求的数组,即让下标k的数字小于k+1,如果本来就满足这一条件则继续逆序遍历,不满足则将下标k的数字减去一个素数使其满足条件,这里减去能满足条件的最小素数即可,可以直接从头遍历素数,直到找到能满足条件的素数即减去该素数。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
bool primeSubOperation(vector<int>& nums) {
|
||||||
|
vector<int> prime(1000,true);
|
||||||
|
for(int i=2;i *i<1000;i++)
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
if(prime[i])
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
for(int j=2;j*i<1000;j++)
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
prime[j*i]=false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
int n=nums.size();
|
||||||
|
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
if(nums[i]<nums[i+1])
|
||||||
|
continue;
|
||||||
|
else
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
bool flag=true;
|
||||||
|
for(int j=2;j<nums[i];j++)
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
if(prime[j] && (nums[i]-j)<nums[i+1])
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
nums[i]=nums[i]-j;
|
||||||
|
flag=false;
|
||||||
|
break;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if(flag)
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day249 2024-11-12
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 2070. Most Beautiful Item for Each Query
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You are given a 2D integer array items where items[i] = [pricei, beautyi] denotes the price and beauty of an item respectively.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You are also given a 0-indexed integer array queries. For each queries[j], you want to determine the maximum beauty of an item whose price is less than or equal to queries[j]. If no such item exists, then the answer to this query is 0.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Return an array answer of the same length as queries where answer[j] is the answer to the jth query.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题要求对每个query,不大于该query的price能得到的最大beauty是多少。则一定需要在items中查找满足不大于query的price最大是多少,查找无疑使用经典的二分查找,二分查找需要数组是有序的,因此需要给items排序,排序后,考虑items中存在相同price对应不同的beauty,并且有可能更小的price却能得到更大的beauty,故遍历一遍有序items在过滤掉重复的price的同时,将每个price对应的beauty设置为不大于该price的所有price中能得到的beauty的最大值。再根据query的值对price二分查找,找到不大于query的最大price,其对应的beauty即为该query对应的beauty。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
vector<int> maximumBeauty(vector<vector<int>>& items, vector<int>& queries) {
|
||||||
|
sort(items.begin(), items.end());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
vector<vector<int>> newitems;
|
||||||
|
int lastprice = 0;
|
||||||
|
int maxbeauty = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (auto &item : items) {
|
||||||
|
if (item[0] != lastprice) {
|
||||||
|
newitems.emplace_back(item);
|
||||||
|
lastprice = item[0];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (maxbeauty < item[1]) {
|
||||||
|
maxbeauty = item[1];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
newitems.back()[1] = maxbeauty;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
vector<int> sols;
|
||||||
|
sols.reserve(queries.size());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (int query : queries) {
|
||||||
|
// 手动实现二分查找,找到第一个价格大于查询值的位置
|
||||||
|
int left = 0;
|
||||||
|
int right = newitems.size();
|
||||||
|
while (left < right) {
|
||||||
|
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
|
||||||
|
if (newitems[mid][0] <= query) {
|
||||||
|
left = mid + 1;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
right = mid;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (left == 0) {
|
||||||
|
sols.push_back(0);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
sols.push_back(newitems[left - 1][1]);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return sols;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 总结
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
其实过滤重复的price对本题影响不大,即使有重复的price也不影响二分查找最终找到的最大的满足条件的price和其对应的最大beauty,因此可以直接修改有序items数组,仅修改每个item的beauty为不大于该price的最大beauty即可
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
vector<int> maximumBeauty(vector<vector<int>>& items, vector<int>& queries) {
|
||||||
|
sort(items.begin(), items.end());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int maxbeauty = 0;
|
||||||
|
for (auto &item : items) {
|
||||||
|
if (maxbeauty < item[1]) {
|
||||||
|
maxbeauty = item[1];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
item[1] = maxbeauty;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
vector<int> sols;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (int query : queries) {
|
||||||
|
// 手动实现二分查找,找到第一个价格大于查询值的位置
|
||||||
|
int left = 0;
|
||||||
|
int right = items.size();
|
||||||
|
while (left < right) {
|
||||||
|
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
|
||||||
|
if (items[mid][0] <= query) {
|
||||||
|
left = mid + 1;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
right = mid;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (left == 0) {
|
||||||
|
sols.push_back(0);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
sols.push_back(items[left - 1][1]);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return sols;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day250 2024-11-13
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 2563. Count the Number of Fair Pairs
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Given a 0-indexed integer array nums of size n and two integers lower and upper, return the number of fair pairs.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A pair (i, j) is fair if:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
0 <= i < j < n, and
|
||||||
|
lower <= nums[i] + nums[j] <= upper
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题要找满足两个数的和在某个范围内且下标满足题目要求的组合有多少对,要找到和在某个范围内的两个数字,在知道其中一个数字的情况下即可知道另外一个数字的取值范围,若要能根据数字的取值范围确定数字在数组中的范围,则必须是有序数组,因此第一步先将数组排序。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在将数组排序后,遍历有序数组,对每个数字知道了其另一个匹配数字的左右边界,通过二分法找出满足左右边界的有序数组中的下标,再求出这个边界内的数组长度并加和到最终结果中。至于题目中的原始数组的下标条件其实对本题并没有什么影响,因为只要两个数字的和满足范围条件,则二者必有一个数字在前另一个数字在后。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
long long countFairPairs(vector<int>& nums, int lower, int upper) {
|
||||||
|
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
|
||||||
|
int n = nums.size();
|
||||||
|
long long count = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i){
|
||||||
|
long long min_val = static_cast<long long>(lower) - nums[i];
|
||||||
|
long long max_val = static_cast<long long>(upper) - nums[i];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int left = lower_bound(nums.begin() + i + 1, nums.end(), (int)min_val) - nums.begin();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int right = upper_bound(nums.begin() + i + 1, nums.end(), (int)max_val) - nums.begin();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
count += (right - left);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return count;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day251 2024-11-14
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 2064. Minimized Maximum of Products Distributed to Any Store
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You are given an integer n indicating there are n specialty retail stores. There are m product types of varying amounts, which are given as a 0-indexed integer array quantities, where quantities[i] represents the number of products of the ith product type.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You need to distribute all products to the retail stores following these rules:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A store can only be given at most one product type but can be given any amount of it.
|
||||||
|
After distribution, each store will have been given some number of products (possibly 0). Let x represent the maximum number of products given to any store. You want x to be as small as possible, i.e., you want to minimize the maximum number of products that are given to any store.
|
||||||
|
Return the minimum possible x.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题初始可能会想到将产品的数量加和后按照商店个数均分,让每个商店分配到的产品个数尽可能接近平均数,这样就可以最小化单个商店可能分得的最大产品个数,但这样分配未必能保证每个商店都能分到产品,抑或在给每个商店分配完接近平均数的产品后产品仍有剩余(有的产品个数远小于平均数但每个商店只能分得一个产品)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
但这样的思路有其道理,其中可取的地方在于我们需要找到一个数字p,使得每个商店分配得到的产品数量都不大于p,同时能够将产品最终分配完,但p不一定是之前考虑的平均数,而且p肯定有多个,因为当p已经能够让商店完成产品分配时,比p大的数肯定同样可以。我们需要找到的是最小的p。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
验证当每个商店分配的产品数量不大于p时能否分配完成比较简单,对每个产品,当个数大于p时,将p个分配给一个商店,否则将剩余全部产品分配给一个商店。若到最后产品能正好分配给全部商店没有剩余则分配成功。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
则此时可以想到,要找的最小的p有如下的特性,大于p的产品个数限制可以让产品分配给商店,小于p则不行,p是二者的交界,则这其实就变成了一个查找问题,考虑一般的在有序数组中查找某个具体的数,其实也隐含了类似的性质,即该数字右侧的数都大于该数字,该数字左侧的数都小于该数字,这个数字本身是与它的相对大小的分界。因此这类有二分性质的问题都可以考虑用二分查找来解决。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
// 检查是否能在每个商店最多分配 mid 个产品的情况下完成分配
|
||||||
|
bool canDistribute(int n, vector<int>& quantities, int mid) {
|
||||||
|
int stores_needed = 0;
|
||||||
|
for (int q : quantities) {
|
||||||
|
stores_needed += (q + mid - 1) / mid;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return stores_needed <= n;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int minimizedMaximum(int n, vector<int>& quantities) {
|
||||||
|
// 二分查找的左边界是1(每个商店至少能分配1个产品)
|
||||||
|
int left = 1;
|
||||||
|
// 右边界是单个产品的最大数量(因为最差情况下,最大的那堆产品也要能分完)
|
||||||
|
int right = *max_element(quantities.begin(), quantities.end());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
while (left < right) {
|
||||||
|
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
|
||||||
|
if (canDistribute(n, quantities, mid)) {
|
||||||
|
// 如果当前的mid可以完成分配,尝试减小mid
|
||||||
|
right = mid;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
// 如果当前的mid不能完成分配,需要增大mid
|
||||||
|
left = mid + 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return left;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day252 2024-11-15
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 1574. Shortest Subarray to be Removed to Make Array Sorted
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Given an integer array arr, remove a subarray (can be empty) from arr such that the remaining elements in arr are non-decreasing.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Return the length of the shortest subarray to remove.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A subarray is a contiguous subsequence of the array.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题需要移除一个子数组使得剩余的数组是一个非减数组。由于子数组一定是连续的,则我们需要从中间删去某个长度的子数组使得数组剩余的两边拼接在一起后满足题目条件,那么前后的两个子数组自身必须要满足非减条件,因此可以先找到以数组开头作为起始和以数组末尾作为末尾的两个最长的符合条件的子数组。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
找到该符合条件的子数组后,需要让两个子数组拼接后满足题目条件,则需要找到前面子数组中以某个数字结尾的部分和后面子数组中以某个数字开头的部分拼接后可以得到完整的满足条件的数组,则这个结尾的数字需不大于后面的开头的数字。同时使得从这两个数组中被丢弃的部分的长度和最小。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在得到前后两个最长数组后,若找到符合要求的同时让被丢弃部分最小的拼接数组,可使用双指针,分别指向前后两个数组的开头,前面的指针不断向后移动,指向的数字不断变大,同时移动后面的指针直到找到符合不小于前面数字的数字位置,不断计算被丢弃的数组的长度和,如此反复,直到前面的指针指向前面数组的末尾或者后面的指针指向后面数组的末尾为止。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
int findLengthOfShortestSubarray(vector<int>& arr) {
|
||||||
|
int n = arr.size();
|
||||||
|
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
while (left < n - 1 && arr[left] <= arr[left + 1]) {
|
||||||
|
left++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (left == n - 1) return 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
while (right > left && arr[right - 1] <= arr[right]) {
|
||||||
|
right--;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int result = min(n - left - 1, right);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int i = 0, j = right;
|
||||||
|
while (i <= left && j < n) {
|
||||||
|
if (arr[i] <= arr[j]) {
|
||||||
|
result = min(result, j - i - 1);
|
||||||
|
i++;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
j++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return result;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day253 2024-11-16
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 3254. Find the Power of K-Size Subarrays I
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You are given an array of integers nums of length n and a positive integer k.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The power of an array is defined as:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Its maximum element if all of its elements are consecutive and sorted in ascending order.
|
||||||
|
-1 otherwise.
|
||||||
|
You need to find the power of all
|
||||||
|
subarrays
|
||||||
|
of nums of size k.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Return an integer array results of size n - k + 1, where results[i] is the power of nums[i..(i + k - 1)].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题子数组的长度是固定的,故可以使用滑动窗口,将窗口长度固定为k不断向后滑动,记录窗口中以最后一个数字结尾的递增子数组的长度和最后一个数字。这样将窗口向后移动时每当添加了一个新的数字进入窗口,将该数字和最后一个数字比较,如果和最后一个数字相邻且比最后一个数字大则将记录的递增子数组长度加一,比最后一个数字小或者不相邻则将子数组长度初始化为1。若以最后一个数字结尾的递增子数组长度和k相同则将最后一个数字(因为是递增数组,最后一个数字就是最大的数字)放入results数组中,否则放入-1。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
vector<int> resultsArray(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
|
||||||
|
int sortedlen = 0;
|
||||||
|
int last = 0;
|
||||||
|
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
|
||||||
|
if(nums[i] > last && nums[i] == last+1){
|
||||||
|
sortedlen++;
|
||||||
|
}else{
|
||||||
|
sortedlen = 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
last = nums[i];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
vector<int> results;
|
||||||
|
for(int i=k;i<nums.size();i++){
|
||||||
|
if(sortedlen == k){
|
||||||
|
results.push_back(last);
|
||||||
|
}else{
|
||||||
|
results.push_back(-1);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if(nums[i] > last && nums[i] == last+1){
|
||||||
|
if(sortedlen < k){
|
||||||
|
sortedlen++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}else{
|
||||||
|
sortedlen = 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
last = nums[i];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if(sortedlen == k){
|
||||||
|
results.push_back(last);
|
||||||
|
}else{
|
||||||
|
results.push_back(-1);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return results;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day254 2024-11-17
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 862. Shortest Subarray with Sum at Least K
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the length of the shortest non-empty subarray of nums with a sum of at least k. If there is no such subarray, return -1.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题求子数组的和满足大于等于K的全部子数组中长度最小的长度是多少。这种求子数组和的有关性质的题目首先可以想到使用前缀和来解决,但之前使用前缀和解题时是因为前缀和有一个很重要的性质即单调性,当所有数字均为非负数时前缀和是单调增的,因此我们可以根据题目要求来找到对应的下标,如同样是求子数组和至少为K的问题,若是单调增的前缀和,则根据下标为i对应的前缀和减去K的前缀和P来找到对应的小于等于P的前缀和对应的下标,即可知道所有子数组和至少为K的子数组。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
但本题中存在负数,因此前缀和不是单调增的,这时可以考虑能否构造一个单调增的前缀和,则可使用单调栈来构造这样的前缀和,考虑栈顶前缀和的大小和新的前缀和的大小关系,若栈顶前缀和比新的前缀和大,则可弹出栈顶,因为对于还未访问到的前缀和,若后面的前缀和和栈顶的差大于等于k,则因为新的前缀和比栈顶小同时其对应的下标位置在栈顶的后面,则后面的前缀和和新前缀和的差必定也大于等于k且二者对应下标的差比和当前栈顶下标的差更小,故栈顶可以舍弃。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
要求和不小于K的子数组就需要根据当前的前缀和计算出符合要求的前缀和大小,并在单调栈中找到不大于这个符合要求的前缀和大小的前缀和对应的下标,寻找这个符合要求的前缀和每次都要从头遍历单调栈,能否通过优化减少从头遍历的次数呢。很简单,题目要求找到满足要求的前缀和的最短长度,则我们只要找到刚好满足要求前缀和对应的下标位置,在这个下标之前的都可以直接丢弃,后续不再遍历这些位置。因为后面未遍历的前缀和要么比当前的大,要么比当前的小,比当前大则当前前缀和能取得的使子数组大于等于k的下标位置对于后面的同样是可以取得的,但后面到该下标的距离一定比当前下标大,如果比当前小,那么要取得使子数组大于等于k需要在当前前缀和对应的解的位置前面找更小的前缀和来使得子数组满足要求,这样得到的长度最多只能和当前前缀和对应的解的长度相同,不会更优。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
根据这两个优化,可以构造一个单调的队列,使得两端都能弹出元素并满足上面的优化方法。先计算出前缀和,再不断遍历前缀和并求得满足条件的子数组长度与记录的最小长度比较并不断更新即可。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
int shortestSubarray(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
|
||||||
|
int n = nums.size();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
vector<long long> preSum(n + 1);
|
||||||
|
preSum[0] = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||||
|
preSum[i + 1] = preSum[i] + nums[i];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int res = n + 1;
|
||||||
|
// 使用双端队列存储下标
|
||||||
|
deque<int> dq;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 遍历前缀和数组
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
while (!dq.empty() && preSum[i] <= preSum[dq.back()]) {
|
||||||
|
dq.pop_back();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
while (!dq.empty() && preSum[i] - preSum[dq.front()] >= k) {
|
||||||
|
res = min(res, i - dq.front());
|
||||||
|
dq.pop_front();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
dq.push_back(i);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return res == n + 1 ? -1 : res;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day255 2024-11-18
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 1652. Defuse the Bomb
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You have a bomb to defuse, and your time is running out! Your informer will provide you with a circular array code of length of n and a key k.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To decrypt the code, you must replace every number. All the numbers are replaced simultaneously.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If k > 0, replace the ith number with the sum of the next k numbers.
|
||||||
|
If k < 0, replace the ith number with the sum of the previous k numbers.
|
||||||
|
If k == 0, replace the ith number with 0.
|
||||||
|
As code is circular, the next element of code[n-1] is code[0], and the previous element of code[0] is code[n-1].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Given the circular array code and an integer key k, return the decrypted code to defuse the bomb!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题是简单题,题目场景的设置非常有意思,题目本身只需按照题面将对应的数字按条件替换,只要了解循环数组即可,因为本题要么使用ith后面的k个数字要么使用ith前面的k个数字,即窗口大小是固定的,因此可使用滑动窗口。当k大于0时,从头遍历数组向后滑动,k小于0则从尾部遍历数组向前滑动,使用滑动窗口每次去掉一个数字再加上新加入窗口的数字即得当前窗口内的数字和。可以避免重复计算已有的部分数字和。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
vector<int> decrypt(vector<int>& code, int k) {
|
||||||
|
int n = code.size();
|
||||||
|
if (k == 0) {
|
||||||
|
return vector<int>(n, 0);
|
||||||
|
} else if (k > 0) {
|
||||||
|
int sumnow = 0;
|
||||||
|
vector<int> result;
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
|
||||||
|
sumnow += code[i];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
|
||||||
|
result.push_back(sumnow);
|
||||||
|
sumnow -= code[j % n];
|
||||||
|
sumnow += code[(j + k) % n];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return result;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
k = -k;
|
||||||
|
int start = n - k;
|
||||||
|
int end = n - 1;
|
||||||
|
int sumnow = 0;
|
||||||
|
vector<int> result;
|
||||||
|
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { // Calculate initial sum
|
||||||
|
sumnow += code[i];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
|
||||||
|
result.push_back(sumnow);
|
||||||
|
sumnow -= code[(j + n -k)%n];
|
||||||
|
sumnow += code[j];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return result;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day256 2024-11-19
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 2461. Maximum Sum of Distinct Subarrays With Length K
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You are given an integer array nums and an integer k. Find the maximum subarray sum of all the subarrays of nums that meet the following conditions:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The length of the subarray is k, and
|
||||||
|
All the elements of the subarray are distinct.
|
||||||
|
Return the maximum subarray sum of all the subarrays that meet the conditions. If no subarray meets the conditions, return 0.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A subarray is a contiguous non-empty sequence of elements within an array.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
对于这样固定长度的子数组问题,首先肯定要使用滑动窗口,再思考本题中的限制条件,子数组中所有的数字都必须是不相同的,那么可以用一个数组来记录窗口中所有数字的个数,但仅记录某个数字自身的出现次数仍不方便我们了解窗口中有重复的数字有多少个。因此还可以用一个变量记录窗口中有重复的数字个数,个数为0时说明窗口中不再有重复数字。向前不断滑动窗口,根据移出数字和移入数字处理相关情况,在窗口内没有重复数字时更新窗口数字和的最大值即可。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```cpp
|
||||||
|
class Solution {
|
||||||
|
public:
|
||||||
|
long long maximumSubarraySum(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
|
||||||
|
int exist[100001] = {};
|
||||||
|
long long int maxsum = 0;
|
||||||
|
int repeat = 0;
|
||||||
|
long long int arraysum = 0;
|
||||||
|
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
|
||||||
|
if(exist[nums[i]] == 1){
|
||||||
|
repeat++;
|
||||||
|
exist[nums[i]]++;
|
||||||
|
arraysum += nums[i];
|
||||||
|
}else{
|
||||||
|
exist[nums[i]]++;
|
||||||
|
arraysum += nums[i];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if(repeat == 0){
|
||||||
|
maxsum = arraysum;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
int left = 0;
|
||||||
|
int right = k;
|
||||||
|
while(right < nums.size()){
|
||||||
|
if(exist[nums[right]] == 1){
|
||||||
|
repeat++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
exist[nums[right]]++;
|
||||||
|
arraysum += nums[right];
|
||||||
|
if(exist[nums[left]] == 2){
|
||||||
|
repeat--;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
exist[nums[left]]--;
|
||||||
|
arraysum -= nums[left];
|
||||||
|
if(repeat == 0){
|
||||||
|
maxsum = max(maxsum, arraysum);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
right++;
|
||||||
|
left++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return maxsum;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user