mirror of
https://gitlab.com/game-loader/hugo.git
synced 2026-03-13 02:15:08 +08:00
leetcode update
This commit is contained in:
@@ -3621,3 +3621,164 @@ func dfs(root *TreeNode, parent []int) ([]int) {
|
|||||||
感兴趣的可以自行尝试只考虑子树的字典序, 对于这个例子会产生问题.
|
感兴趣的可以自行尝试只考虑子树的字典序, 对于这个例子会产生问题.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
另外一方面, 看0ms的解答代码, 其不在dfs过程中比较, 而是直接通过dfs将这棵树能产生的全部字符串保存起来, 最后再对所有的字符串进行排序, 使用了go内置的sort排序, 返回排好序后的第一个字符串即最小的字符串. 这种方法减少了递归过程中的处理逻辑, 运行起来开销小得多, 所以速度比较快.
|
另外一方面, 看0ms的解答代码, 其不在dfs过程中比较, 而是直接通过dfs将这棵树能产生的全部字符串保存起来, 最后再对所有的字符串进行排序, 使用了go内置的sort排序, 返回排好序后的第一个字符串即最小的字符串. 这种方法减少了递归过程中的处理逻辑, 运行起来开销小得多, 所以速度比较快.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day51 2024-04-18
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 463. Island Perimeter
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You are given row x col grid representing a map where grid[i][j] = 1 represents land and grid[i][j] = 0 represents water.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Grid cells are connected horizontally/vertically (not diagonally). The grid is completely surrounded by water, and there is exactly one island (i.e., one or more connected land cells).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The island doesn't have "lakes", meaning the water inside isn't connected to the water around the island. One cell is a square with side length 1. The grid is rectangular, width and height don't exceed 100. Determine the perimeter of the island.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
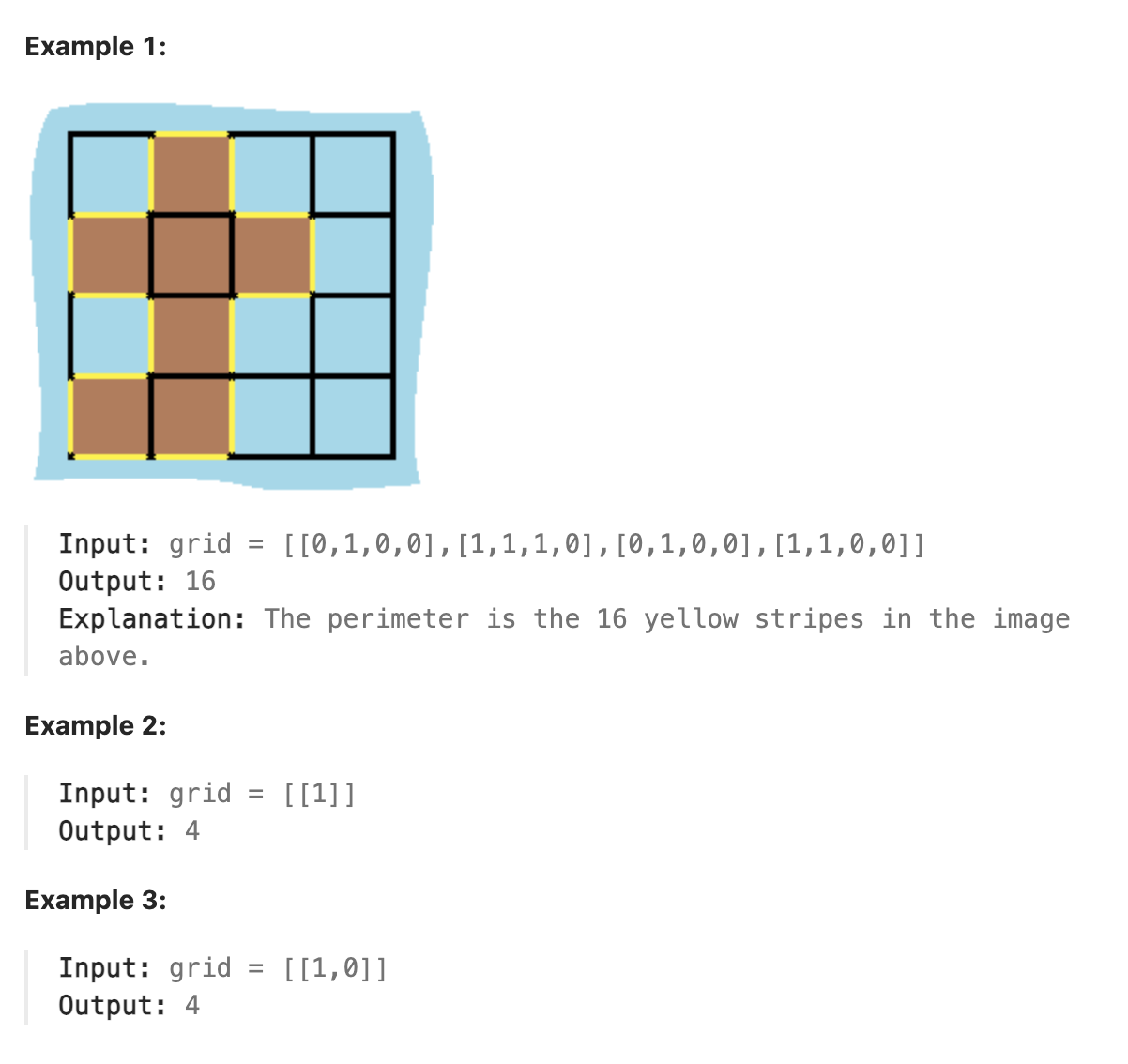
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题直接遍历二维数组, 当遇到值为1即陆地时对四个方向进行判断并对与水面相邻的陆地的边界进行累加即可.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```go
|
||||||
|
func islandPerimeter(grid [][]int) int {
|
||||||
|
result := 0
|
||||||
|
for rowindex, row := range grid{
|
||||||
|
for columnindex, value := range row{
|
||||||
|
if value == 1{
|
||||||
|
if rowindex == 0 || grid[rowindex-1][columnindex] == 0{
|
||||||
|
result++
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if rowindex == len(grid)-1 || grid[rowindex+1][columnindex] == 0{
|
||||||
|
result++
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if columnindex == 0 || grid[rowindex][columnindex-1] == 0{
|
||||||
|
result++
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if columnindex == len(grid[0]) - 1 || grid[rowindex][columnindex+1] == 0{
|
||||||
|
result++
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return result
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 总结
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在查看题解的过程中, 发现尽管算法思路相同, 但实现起来有一种比较巧妙的方法, 如下
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```go
|
||||||
|
func islandPerimeter(grid [][]int) int {
|
||||||
|
DIRS := [][]int{{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}}
|
||||||
|
sides := 0
|
||||||
|
for row, ROWS := 0, len(grid); row < ROWS; row++ {
|
||||||
|
for col, COLS := 0, len(grid[0]); col < COLS; col++ {
|
||||||
|
if grid[row][col] == 1 {
|
||||||
|
for _, dir := range DIRS {
|
||||||
|
r, c := row+dir[0], col+dir[1]
|
||||||
|
// Check to see if the neighbour is an edge tile or water.
|
||||||
|
if r < 0 || r >= ROWS || c < 0 || c >= COLS || grid[r][c] == 0 {
|
||||||
|
sides++
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return sides
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## day52 2024-04-19
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 200. Number of Islands
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Given an m x n 2D binary grid grid which represents a map of '1's (land) and '0's (water), return the number of islands.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 题解
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题遍历矩阵, 遇到1时对该元素执行bfs, 并将搜索过程中遇到的所有1置为0. 继续遍历, 重复此过程即可.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 代码
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```go
|
||||||
|
func numIslands(grid [][]byte) int {
|
||||||
|
rowlength := len(grid)
|
||||||
|
columnlength := len(grid[0])
|
||||||
|
result := 0
|
||||||
|
for rowindex, row := range grid{
|
||||||
|
for columnindex, _ := range row{
|
||||||
|
if grid[rowindex][columnindex] == '1'{
|
||||||
|
queue := [][]int{{rowindex, columnindex}}
|
||||||
|
grid[rowindex][columnindex] = '0'
|
||||||
|
for len(queue) != 0{
|
||||||
|
for _, index := range queue{
|
||||||
|
queue = queue[1:]
|
||||||
|
if index[0] != 0 && grid[index[0]-1][index[1]] == '1'{
|
||||||
|
grid[index[0]-1][index[1]] = '0'
|
||||||
|
queue = append(queue,[]int{index[0]-1,index[1]})
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if index[0] != rowlength-1 && grid[index[0]+1][index[1]] == '1'{
|
||||||
|
grid[index[0]+1][index[1]] = '0'
|
||||||
|
queue = append(queue,[]int{index[0]+1, index[1]})
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if index[1] != 0 && grid[index[0]][index[1]-1] == '1'{
|
||||||
|
grid[index[0]][index[1]-1] = '0'
|
||||||
|
queue = append(queue, []int{index[0],index[1]-1})
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if index[1] != columnlength-1 && grid[index[0]][index[1]+1] == '1'{
|
||||||
|
grid[index[0]][index[1]+1] = '0'
|
||||||
|
queue = append(queue, []int{index[0],index[1]+1})
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
result++
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 总结
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本题我的解法中使用队列来执行bfs, 使用数组来模拟队列的过程中出队入队都会消耗资源, 增加执行时间. 实际上本题无需额外空间, 因为数组是可以修改的, 只需要找到1并将与该1连接的岛屿的所有1置为0即可, 这个过程可以使用dfs来实现,在dfs的过程中目标仅为将所有相连岛屿的1置为0, 因此返回值并不重要. 这种方法省去了队列操作的开销, 下面这种总体比较简洁, 值得学习.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```go
|
||||||
|
func numIslands(grid [][]byte) int {
|
||||||
|
if grid == nil {
|
||||||
|
return 0
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
var res int
|
||||||
|
for i:=0; i<len(grid); i++ {
|
||||||
|
for j:=0; j < len(grid[0]);j++ {
|
||||||
|
res += findIsl(i, j, grid)
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return res
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
func findIsl(i, j int, m [][]byte) int {
|
||||||
|
if (i == -1 || j == -1 || i == len(m) || j == len(m[0])) {
|
||||||
|
return 0
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if m[i][j] == '1' {
|
||||||
|
m[i][j] = '0'
|
||||||
|
findIsl(i-1, j, m)
|
||||||
|
findIsl(i+1, j, m)
|
||||||
|
findIsl(i, j+1, m)
|
||||||
|
findIsl(i, j-1, m)
|
||||||
|
return 1
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return 0
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user