mirror of
https://gitlab.com/game-loader/hugo.git
synced 2026-03-05 22:45:09 +08:00
leetcode update
This commit is contained in:
@@ -23563,3 +23563,142 @@ public:
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
## day350 2025-02-23
|
||||
### 889. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Postorder Traversal
|
||||
Given two integer arrays, preorder and postorder where preorder is the preorder traversal of a binary tree of distinct values and postorder is the postorder traversal of the same tree, reconstruct and return the binary tree.
|
||||
|
||||
If there exist multiple answers, you can return any of them.
|
||||
|
||||
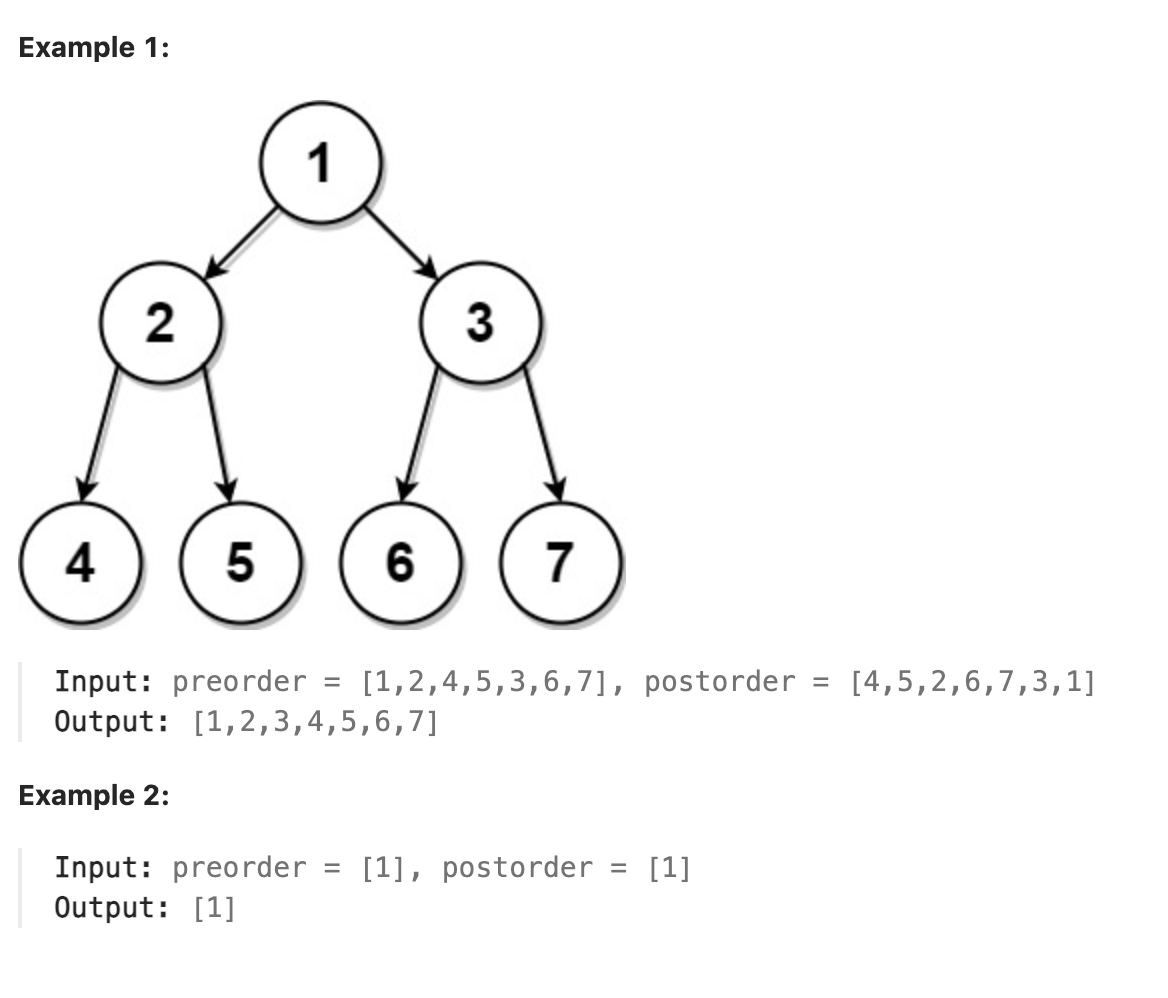
|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
本题要思考前序遍历和后序遍历的特点,可以先模拟先序遍历的过程,在模拟的过程中使用一个栈,当栈顶数字和当前 后序遍历指针指向的数字相同时将栈顶出栈并将后序遍历指针后移直到栈顶和后序指针指向数字不同,构造节点并将节点值入栈,构造节点的过程为使用当前遍历的先序数组的数字构造一个新节点,将这个节点作为当前栈顶节点的左子节点或者右子节点(当当前已经有左子节点时)。
|
||||
|
||||
这里考虑的主要是用栈来模拟前序和后序遍历两种,对于前序遍历来说,栈的增长过程是一直向下搜索的过程,当搜索到叶子节点时,就要开始缩小栈直到栈顶节点拥有未被遍历的子节点,再继续向下搜索,前序遍历对当前节点的处理(如打印数值)等是在栈的增长过程中完成的,而后序遍历对节点的处理(如打印数值)是在栈的缩小过程中完成的,即每次弹出栈顶元素时进行相应的处理(打印数值)。则用栈来保存值正好可以通过判断栈顶的弹出时机来确定二叉树的生长形状,栈顶弹出时应该向上走,而栈增长时则是在当前节点继续按照先序遍历向下生长树。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
* struct TreeNode {
|
||||
* int val;
|
||||
* TreeNode *left;
|
||||
* TreeNode *right;
|
||||
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
|
||||
* };
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
TreeNode* constructFromPrePost(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
|
||||
if(preorder.empty()) return nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
|
||||
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
|
||||
stk.push(root);
|
||||
|
||||
int postIndex = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < preorder.size(); i++) {
|
||||
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(preorder[i]);
|
||||
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top()->val == postorder[postIndex]) {
|
||||
stk.pop();
|
||||
postIndex++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (!stk.empty()) {
|
||||
if (stk.top()->left == nullptr)
|
||||
stk.top()->left = node;
|
||||
else
|
||||
stk.top()->right = node;
|
||||
}
|
||||
stk.push(node);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
## day351 2025-02-24
|
||||
### 2467. Most Profitable Path in a Tree
|
||||
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1 where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
|
||||
|
||||
At every node i, there is a gate. You are also given an array of even integers amount, where amount[i] represents:
|
||||
|
||||
the price needed to open the gate at node i, if amount[i] is negative, or,
|
||||
the cash reward obtained on opening the gate at node i, otherwise.
|
||||
The game goes on as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
Initially, Alice is at node 0 and Bob is at node bob.
|
||||
At every second, Alice and Bob each move to an adjacent node. Alice moves towards some leaf node, while Bob moves towards node 0.
|
||||
For every node along their path, Alice and Bob either spend money to open the gate at that node, or accept the reward. Note that:
|
||||
If the gate is already open, no price will be required, nor will there be any cash reward.
|
||||
If Alice and Bob reach the node simultaneously, they share the price/reward for opening the gate there. In other words, if the price to open the gate is c, then both Alice and Bob pay c / 2 each. Similarly, if the reward at the gate is c, both of them receive c / 2 each.
|
||||
If Alice reaches a leaf node, she stops moving. Similarly, if Bob reaches node 0, he stops moving. Note that these events are independent of each other.
|
||||
Return the maximum net income Alice can have if she travels towards the optimal leaf node.
|
||||
|
||||
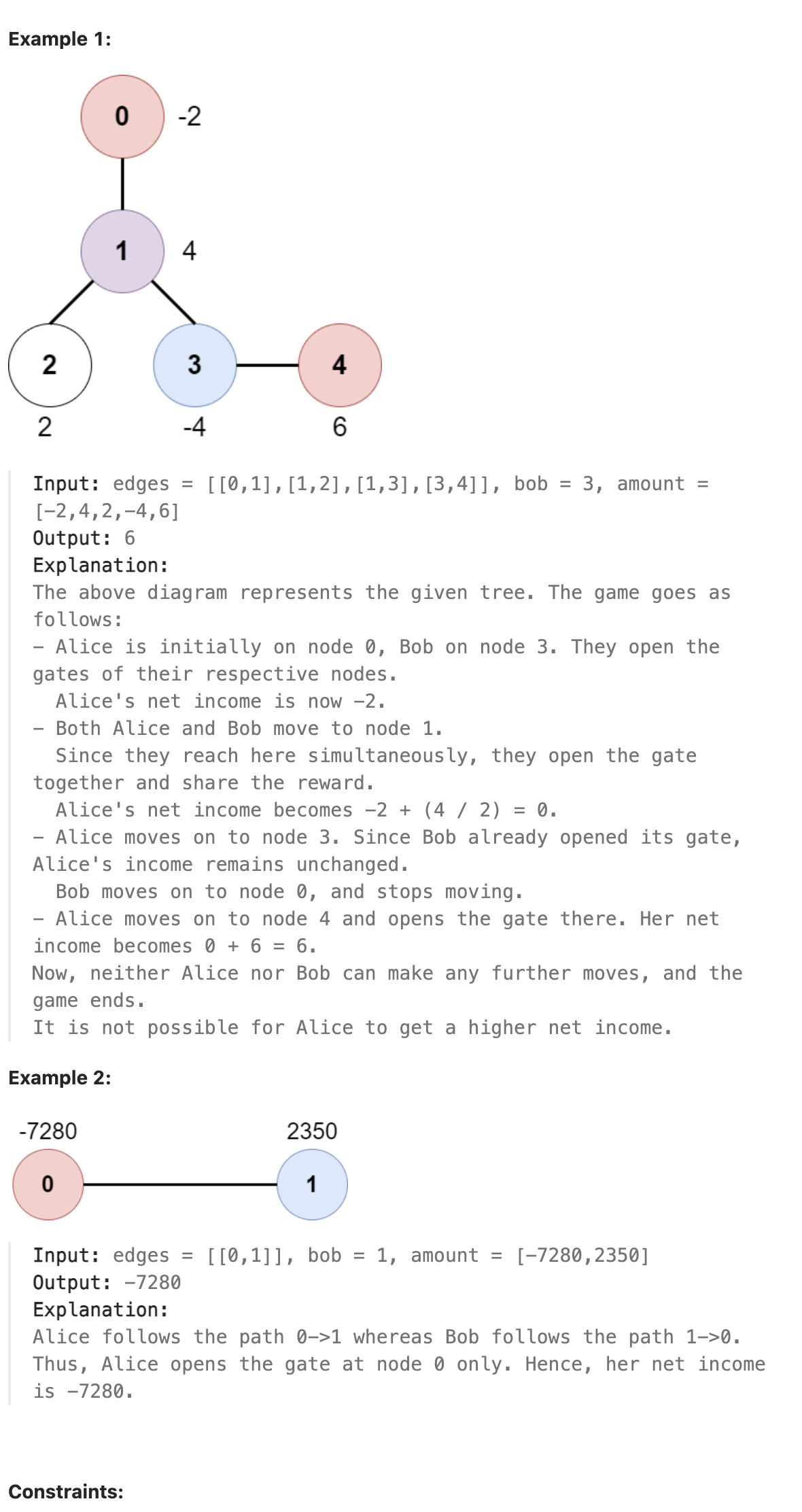
|
||||
|
||||
### 题解
|
||||
本题首先注意因为是一棵无向树,且节点0确定为树的根,则bob到根节点的路径只能有一条,而对Alice来说,找到能获得最大价值的路径,要通过dfs遍历所有可能的路径并比较,在此过程中,必定会经过Bob经过的路径,考虑Alice是从节点0出发的,因此经过Bob的起始节点时Alice经过的路径必定为Bob经过路径的逆序,根据题目所述可知二人在路径的中间位置必定相遇,因此Alice的路径的后半段Bob已经走过了,根据题目条件可知这段路径上的全部节点的开门奖励均为0(已经被Bob开过了)。则可以先找到Bob到节点0的路径并保存路径上每个节点Bob经过的时间(可以Bob的起始节点作为根节点进行dfs),对Alice来说,如果经过某个节点的时间大于Bob经过的时间,则该节点上Alice能取得的值为0,如果相等则为一半,其余情况均可取到完整的值。
|
||||
|
||||
使用dfs遍历所有可能路径并计算到达各个叶子节点的路径开门成本和,每当到达一个新的叶子节点时即将到该节点的路径成本和与保存的最大值比较,直到遍历完整棵树。
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
int mostProfitablePath(vector<vector<int>>& edges, int bob, vector<int>& amount) {
|
||||
int n = amount.size();
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> graph(n);
|
||||
for (auto &e : edges) {
|
||||
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
|
||||
graph[u].push_back(v);
|
||||
graph[v].push_back(u);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const int INF = 1e9;
|
||||
vector<int> bobTime(n, INF);
|
||||
|
||||
function<int(int, int, int)> dfsBob = [&](int node, int parent, int time) -> int {
|
||||
if (node == 0){
|
||||
bobTime[0] = time;
|
||||
return time;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int nxt : graph[node]) {
|
||||
if (nxt == parent) continue;
|
||||
int d = dfsBob(nxt, node, time+1);
|
||||
if (d != -1) {
|
||||
bobTime[node] = time;
|
||||
cout << node << " "<< time <<endl;
|
||||
return time;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
dfsBob(bob, -1, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int ans = -1e9;
|
||||
function<void(int, int, int, int)> dfsAlice = [&](int node, int parent, int t, int profit) {
|
||||
if (t < bobTime[node])
|
||||
profit += amount[node];
|
||||
else if (t == bobTime[node])
|
||||
profit += amount[node] / 2;
|
||||
|
||||
if(graph[node].size()==1 && node != 0){
|
||||
ans = max(ans, profit);
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int nxt : graph[node]) {
|
||||
if (nxt == parent) continue;
|
||||
dfsAlice(nxt, node, t + 1, profit);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
dfsAlice(0, -1, 0, 0);
|
||||
return ans;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user